2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
Technology stack summary:
①Java basics (encapsulation, reflection, generics, jdbc)
②Configuration file parsing (properties)
③httpclient (send http request)
④fastjson and jsonpath process data
⑤Key points of testng automated testing framework
⑥Allure test report
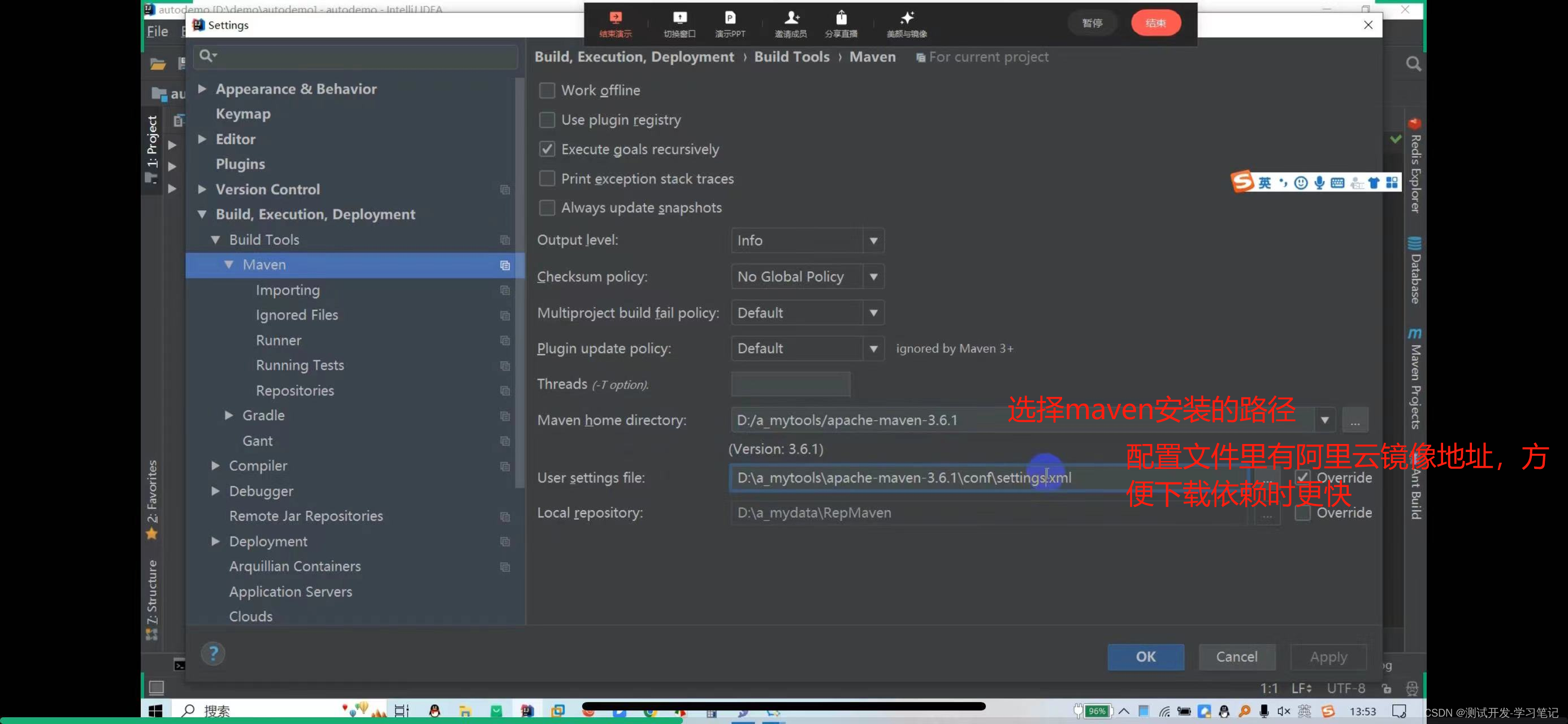
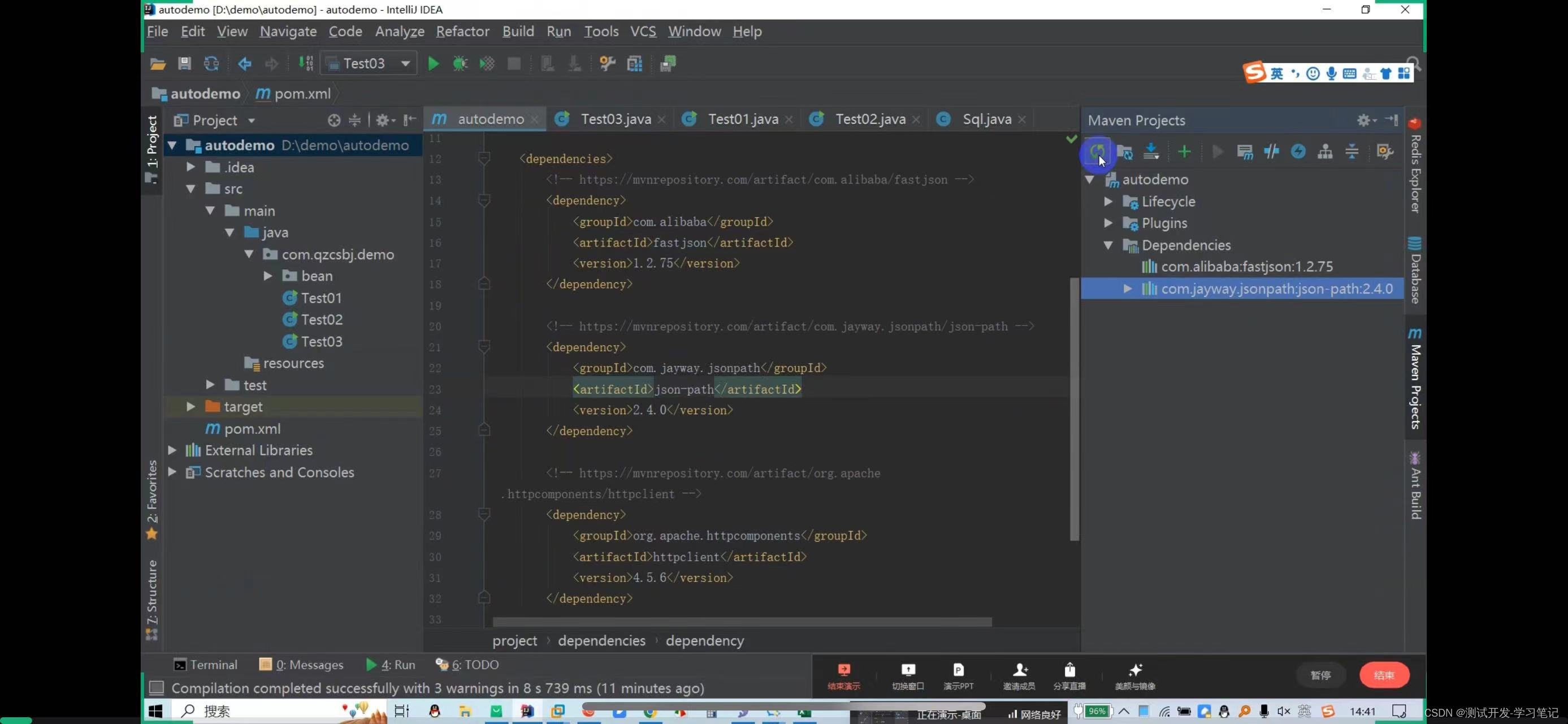
File—settings—maven
Both fastjson and jsonpath are used to process data
The key points in the test automation framework.
Allure test report
Fastjson can process json strings and json arrays
Parse the json string input and prepare for subsequent requests
<!-https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/fastjson -->
com.alibaba
fastison
1.2.75
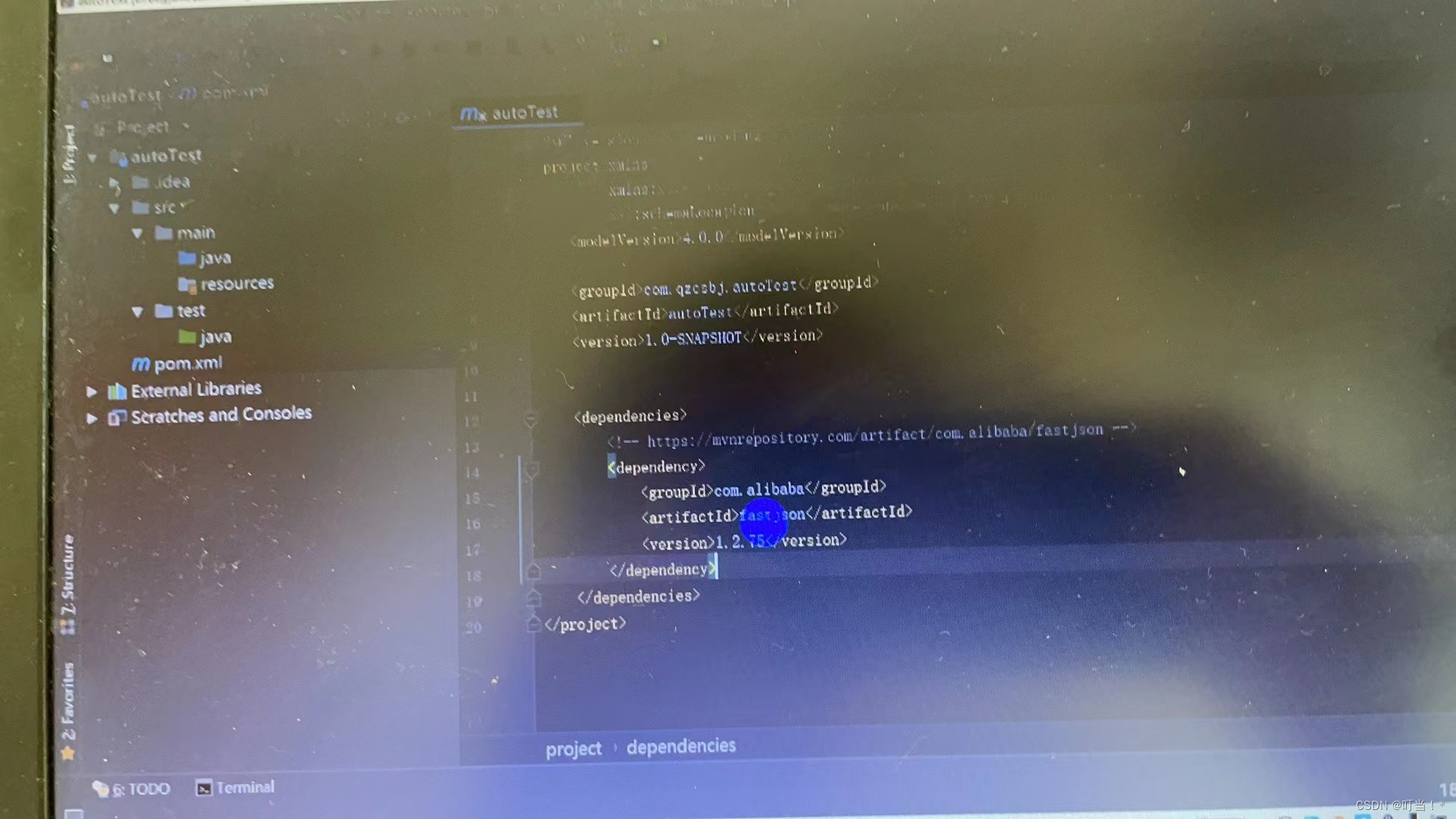
After downloading, you can see the automatically generated dependency package
For example, you need a username and password to log in.
{“username”:“qzcsbj”, “password”:“123456”}
Automation framework data source, the input parameters are all json strings, fastjson is needed
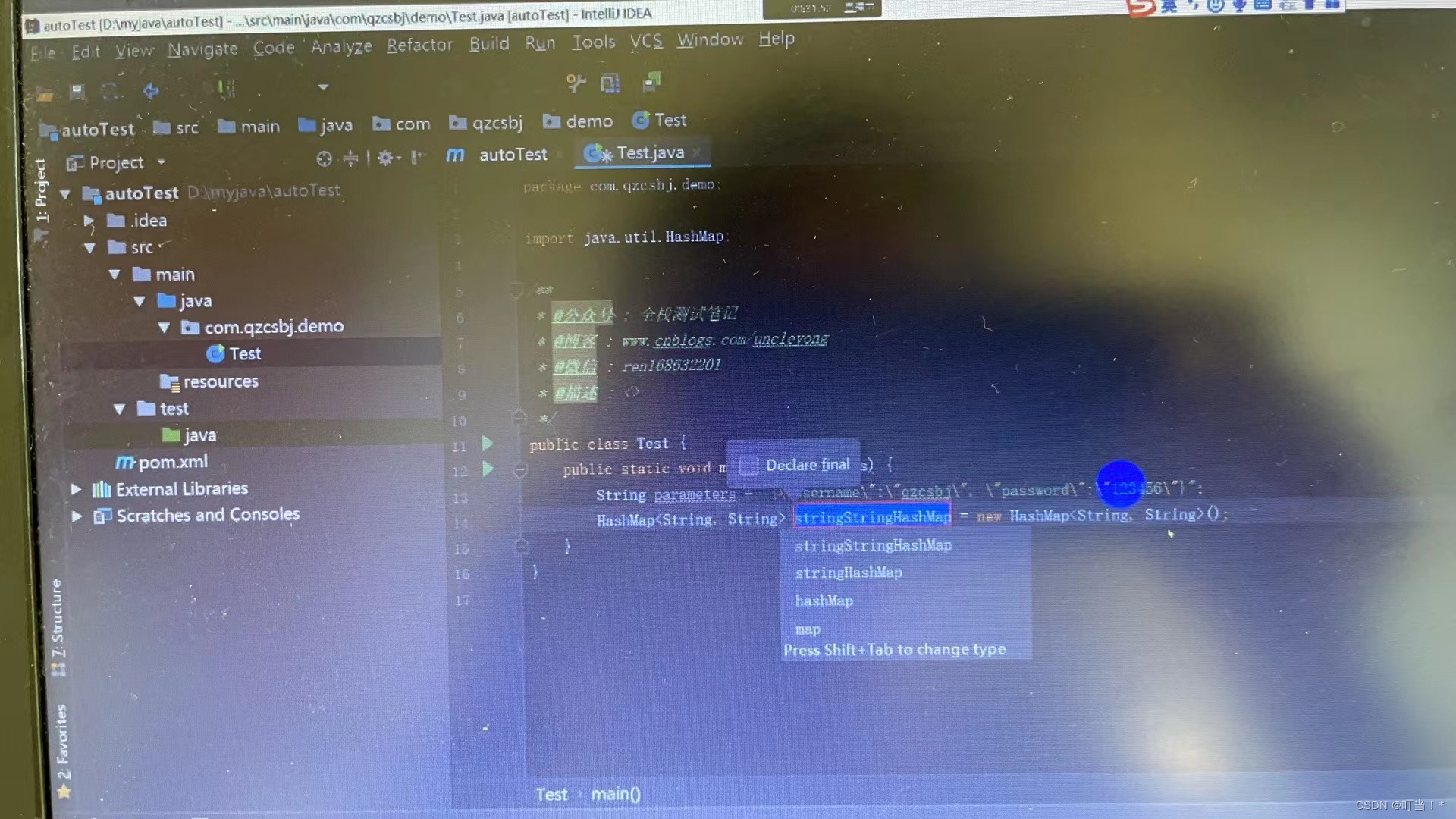
Class.Method, this method is static
Each key in the collection is a String
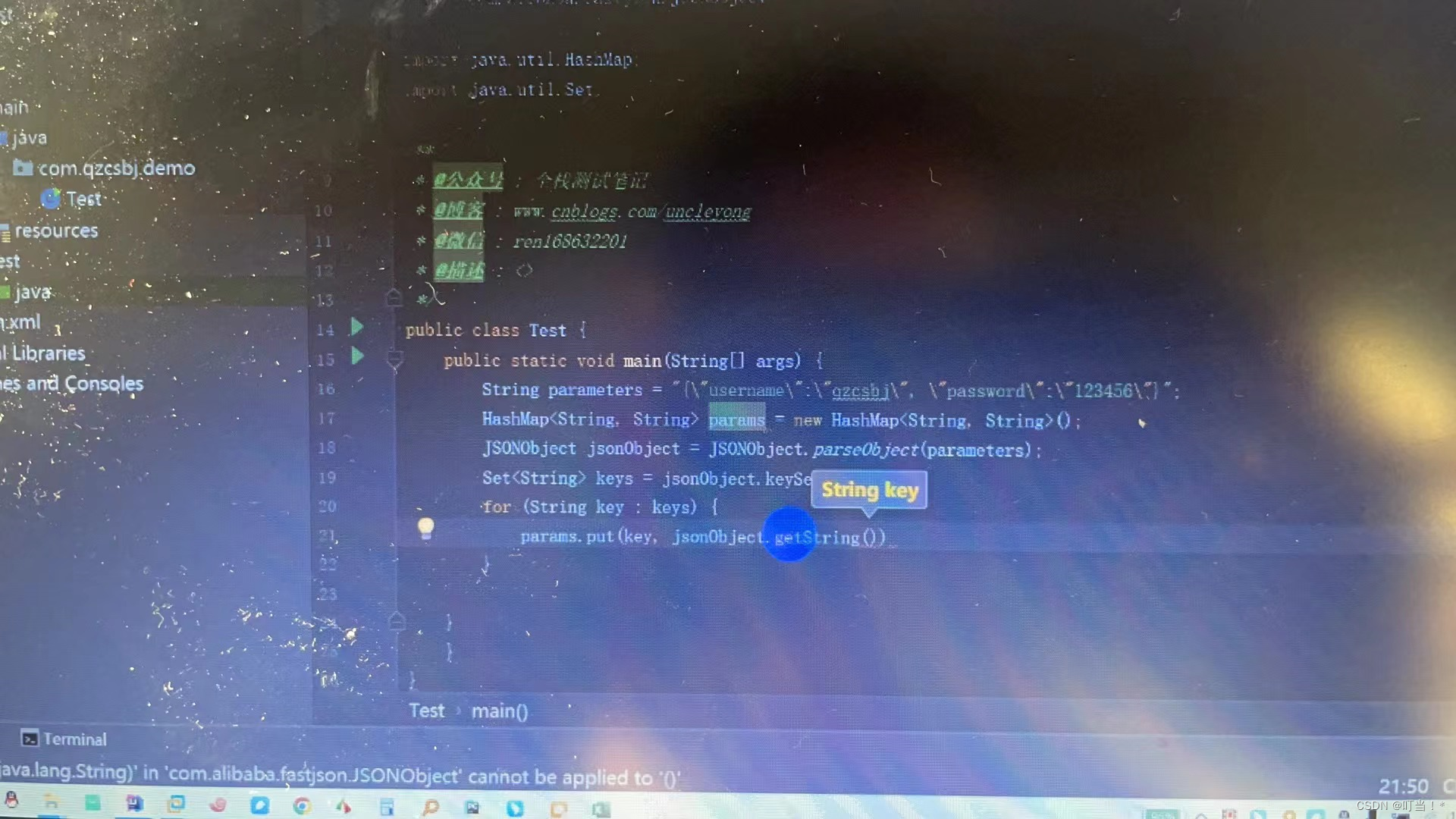
The json string defined now has been parsed and put into the Map
Description: Put the contents of the json string into the map
blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ae6feeba2eae442f961df977a6c8eac1.jpeg)
The automation framework involves initialization framework, and some need to operate the data inside. To operate the database, you need to write SQL
Here is a json array. In the array, each element is a json string, which contains key-value data. The first one is the sql number, the actual executed sql.
[{“sqlNo”:“1”,“sq!”:“select * from users where username=‘qzcsbj’;”},.“sqlNo”:“2”,“sql”:“select * from users where username=‘test00501’;”}]
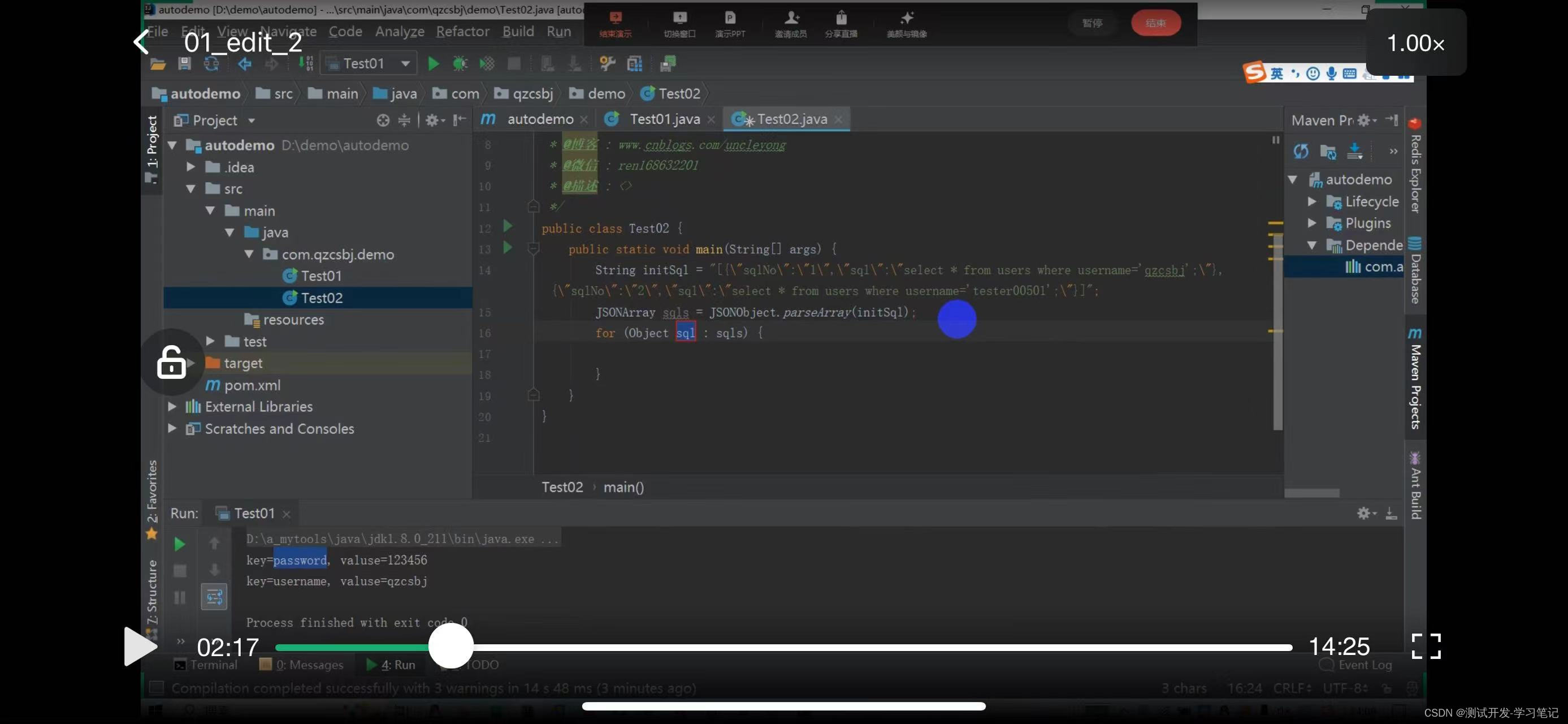
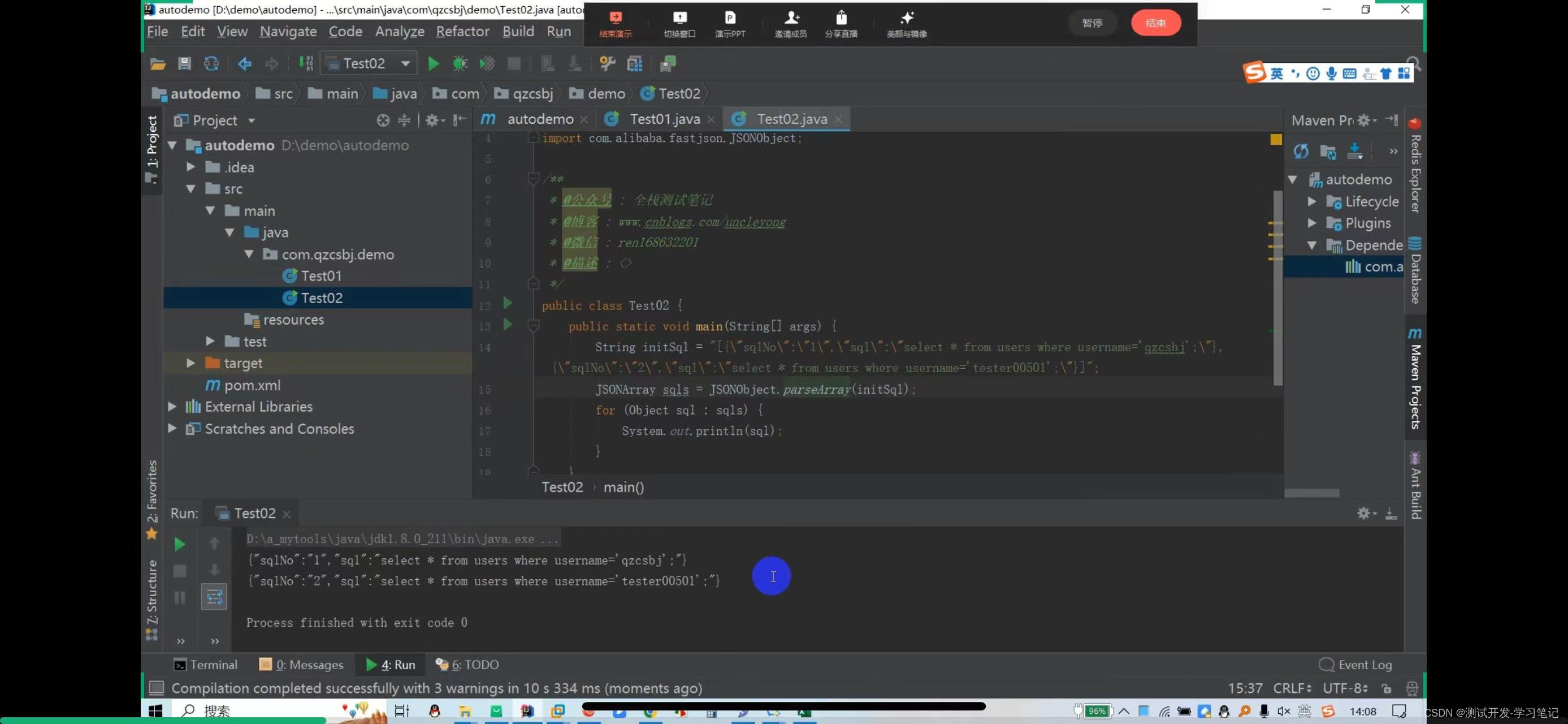
This method is not advisable
Pass two parameters, the first parameter is the String to be parsed, and the second is the bytecode file
The solution is: parse the first parameter String into a Map
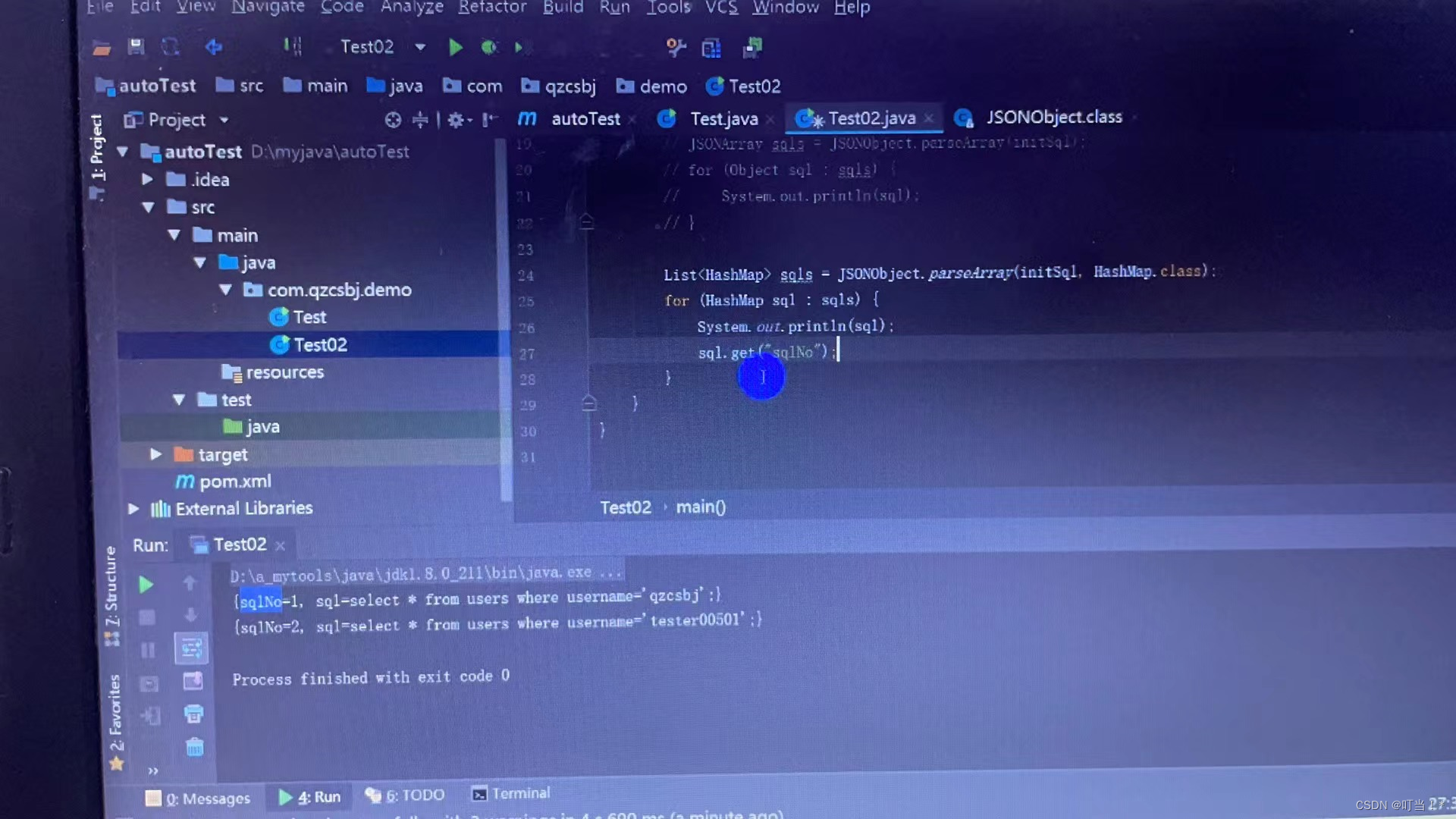
String sqlNo = (String)sql.get("sqlNo");
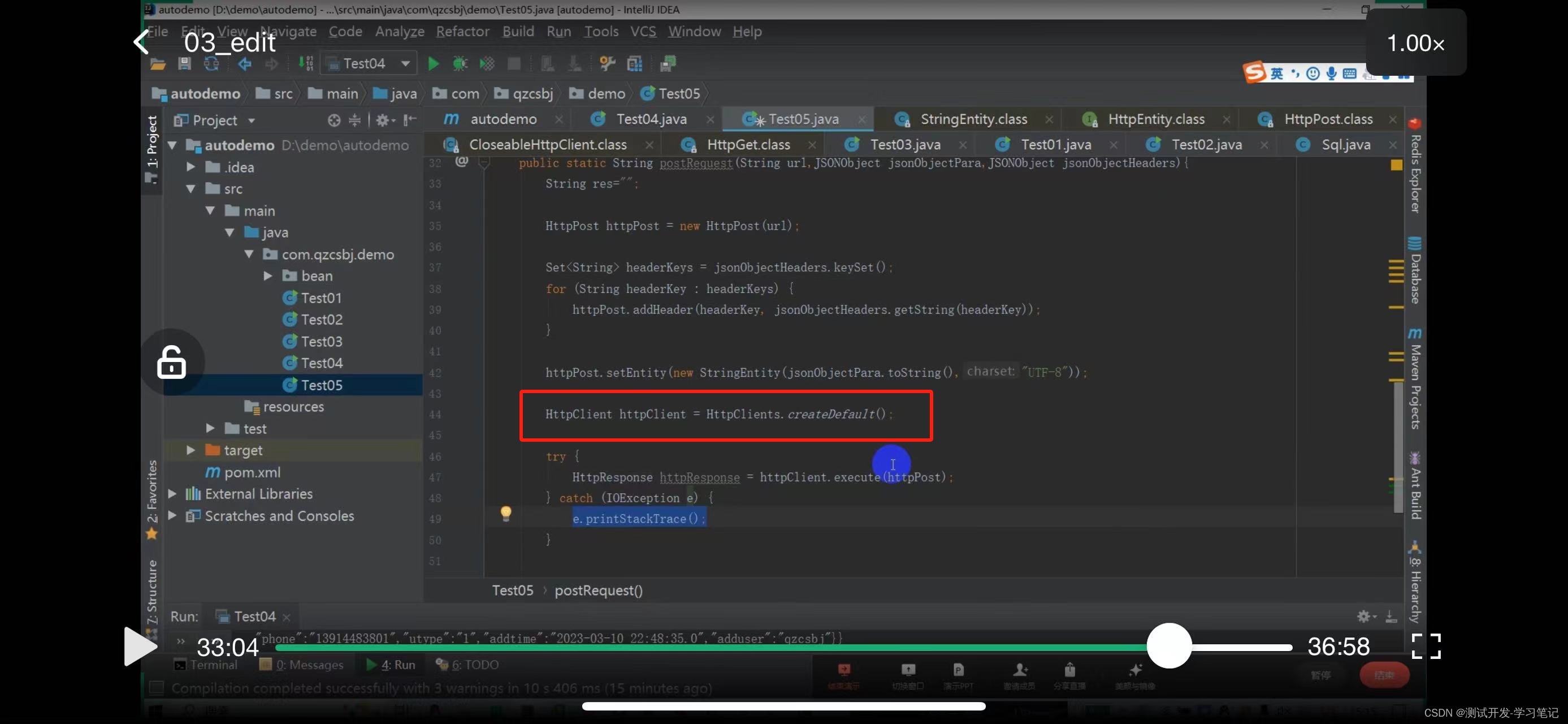
Encapsulate the contents of each json string into an object l, add get and set methods in the entity class, directly use the object.get to get the sql content. This code prompt is also convenient to write. Automation also refers to this encapsulation. That is, encapsulate sql into an object,
Encapsulate the attributes into private (sqlNo, sql), provide get and set methods, and add the parameterized constructor and the non-parameterized constructor. Reflection will call the non-parameterized constructor. If you only write the parameterized constructor and do not write the non-parameterized constructor, you will definitely get an error. To print the string result, you need to add the toString() method, otherwise the address of the object will be printed. The above entity class is written.
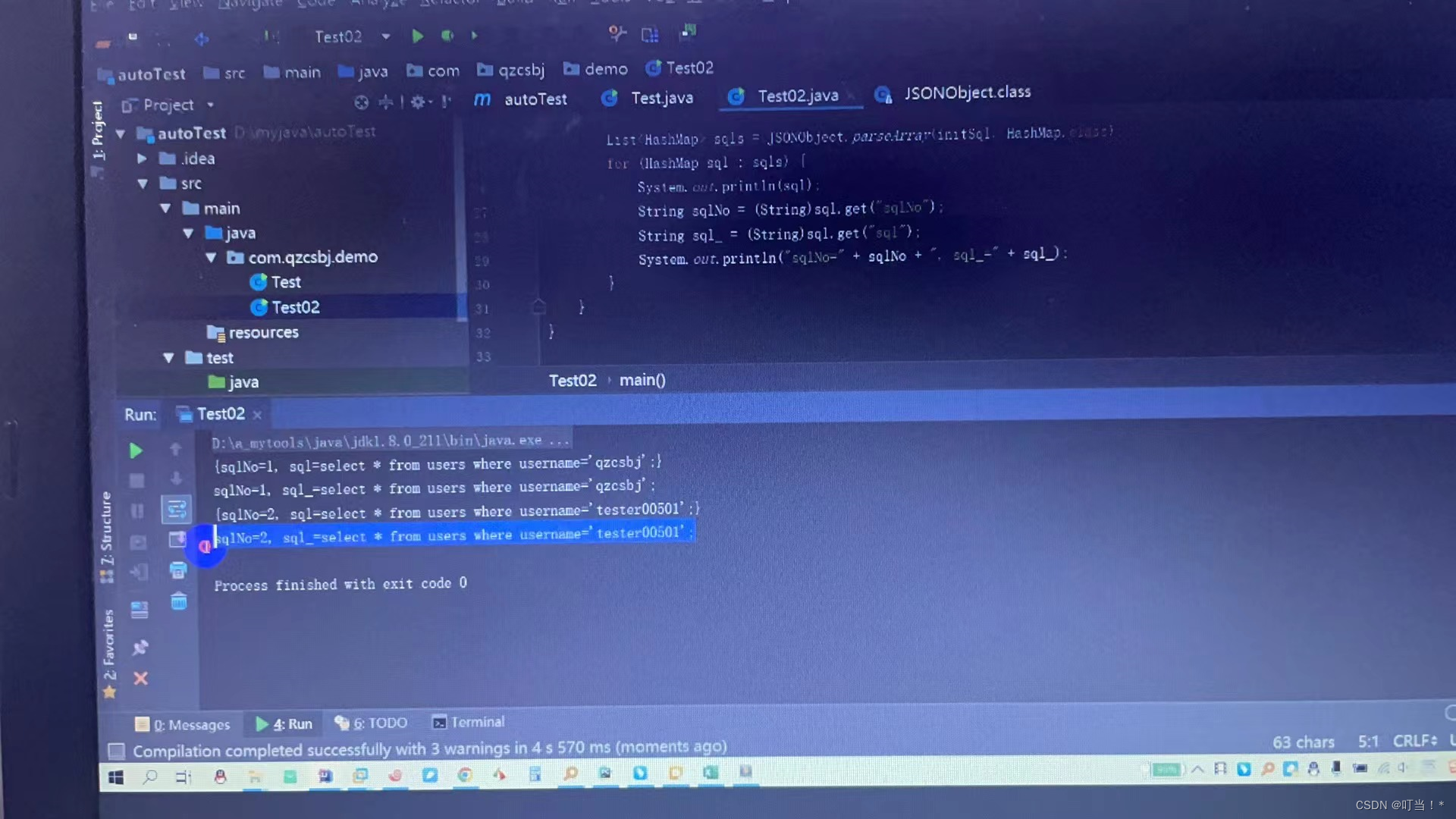
Optimize it again
To encapsulate an element into an object, change it to a class you wrote.class
That is, sql.class
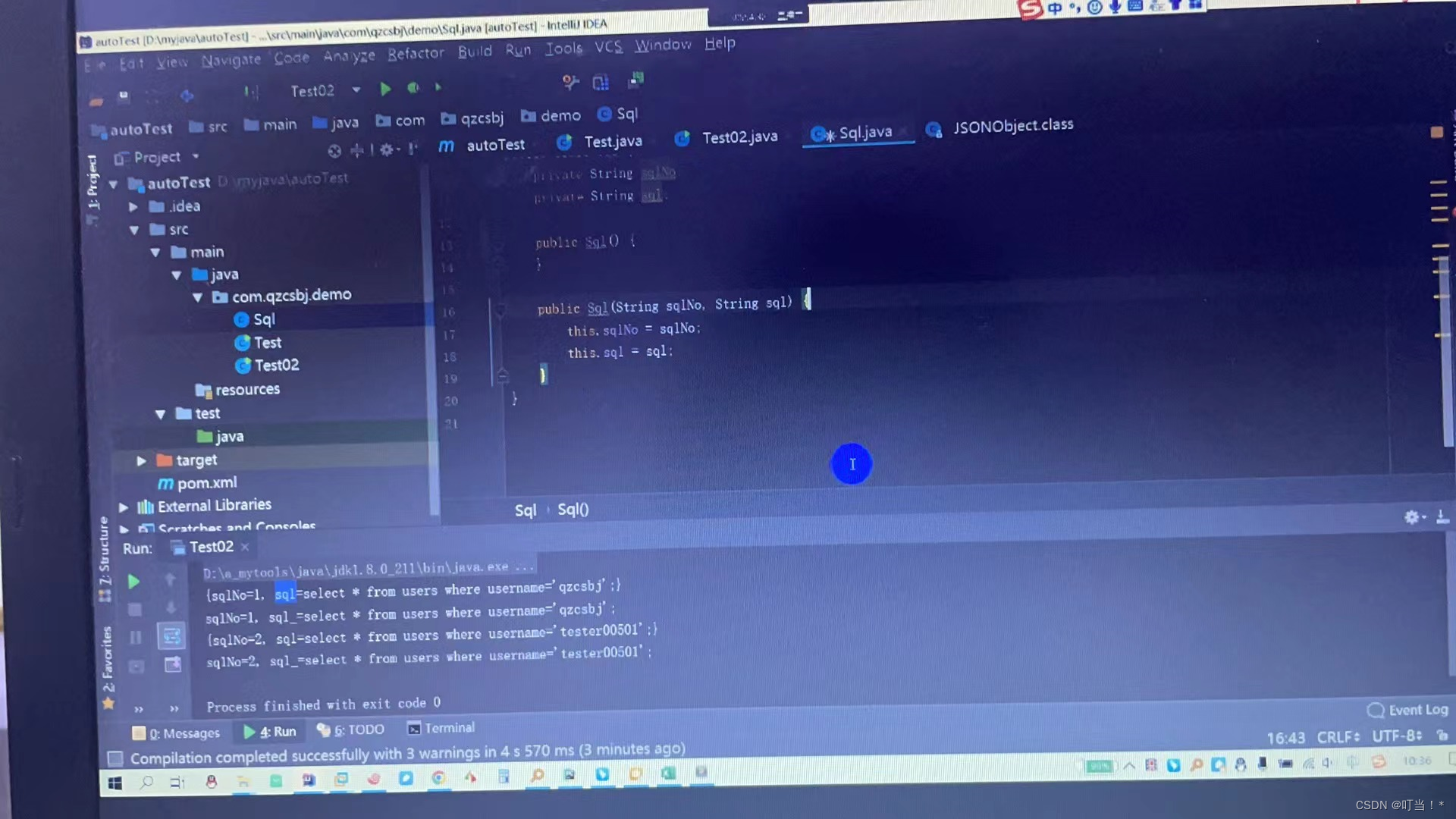
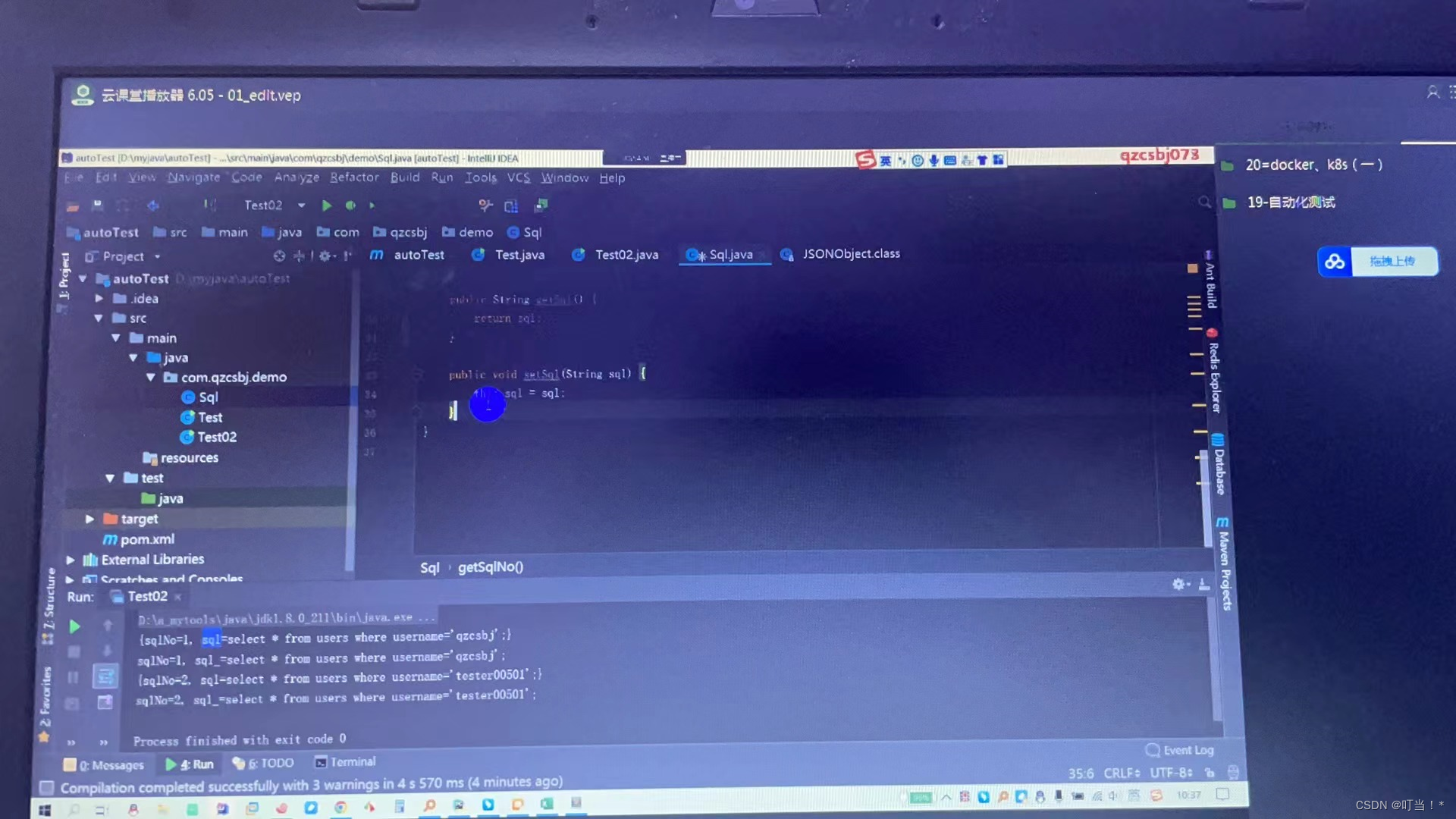
The second method above encapsulates each element into a hashMap object, while here each element is encapsulated into a sql object.
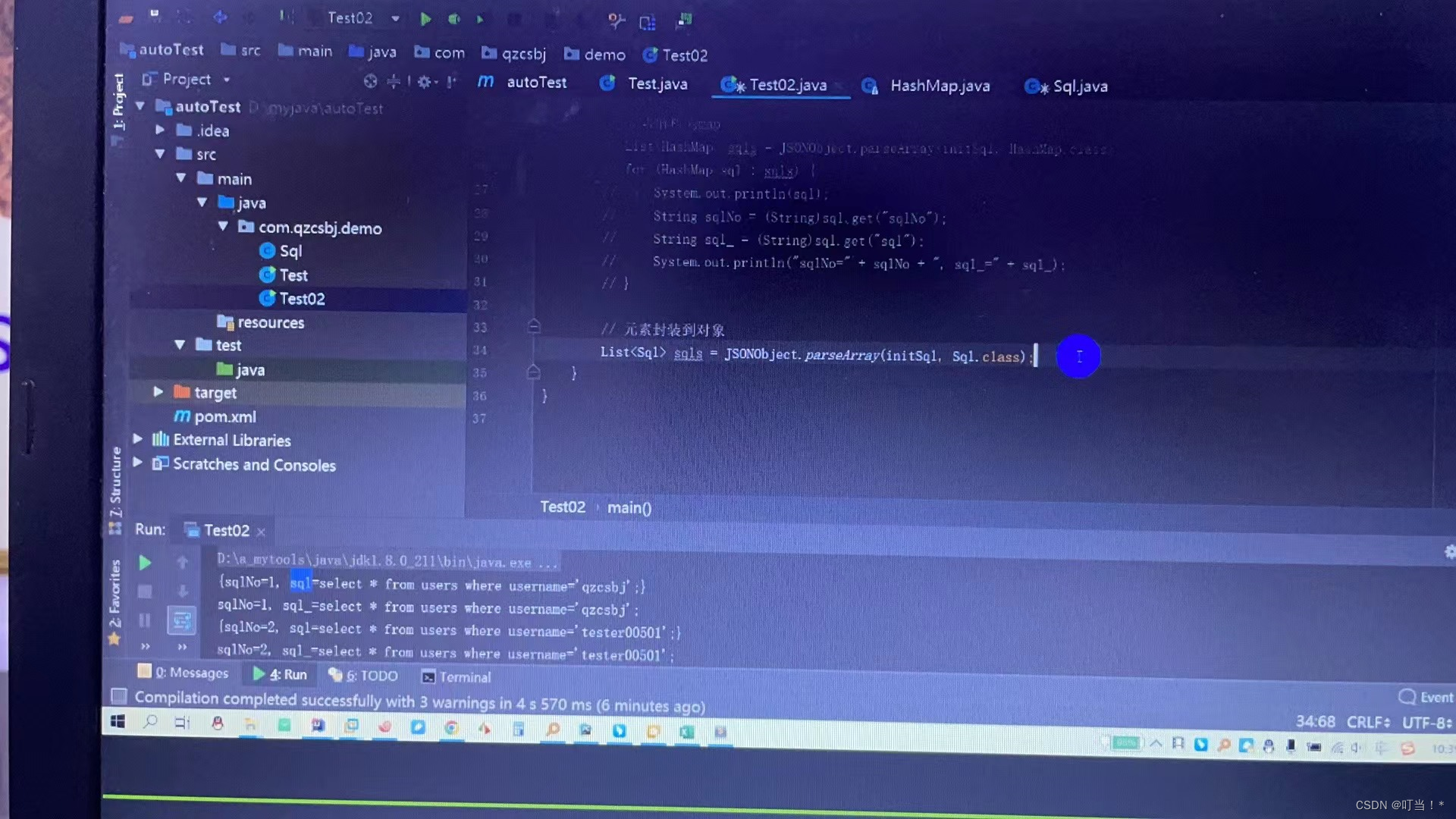
To get properties from an object, just use the get method
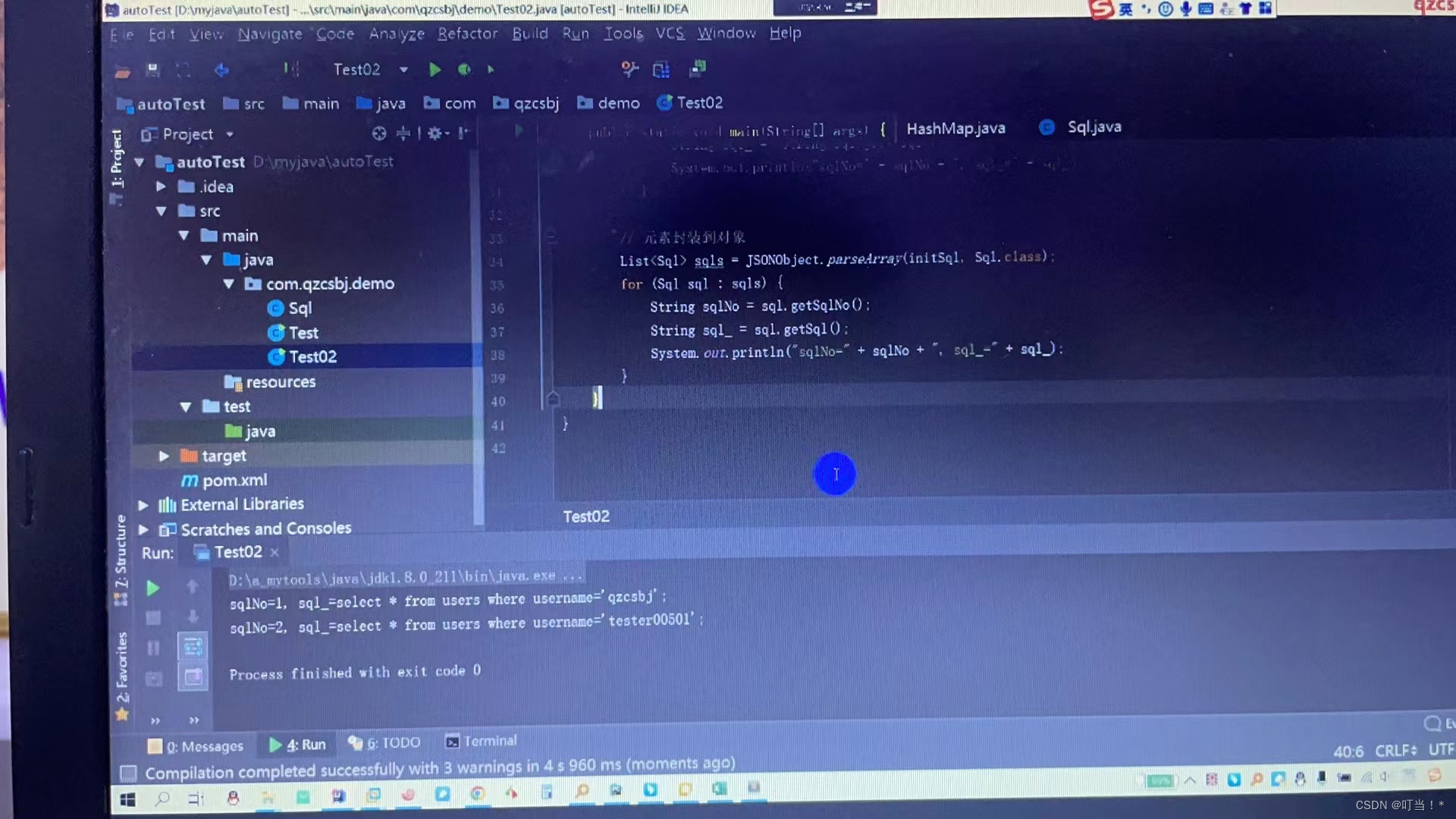
This method is more convenient and does not require obtaining many keys.
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>mavenProject</groupId>
<artifactId>mavenProject</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.75</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
SQL Class
package com.zhou.demo;
public class Sql {
private String sql;
private String sqlNo;
public Sql() {
}
public Sql(String sql) {
this.sql = sql;
}
public Sql(String sql, String sqlNo) {
this.sql = sql;
this.sqlNo = sqlNo;
}
public void setSql(String sql) {
this.sql = sql;
}
public void setSqlNo(String sqlNo) {
this.sqlNo = sqlNo;
}
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
public String getSqlNo() {
return sqlNo;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "sql{" +
"sql='" + sql + ''' +
", sqlNo='" + sqlNo + ''' +
'}';
}
}
package com.zhou.demo;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Set;
//需求:将json字符串转化成map,字符串:{"username":"qzcsbj", "password":"123456"}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String parameters="{"username":"qzcsbj", "password":"123456"}";
//先解析为JSONObject,然后转换为map
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
// 解析json格式字符串为JSONObject(JSONObject是Map接口的一个实现类,和HashMap平级)
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(parameters);
// 将JSO\\\ NObject转换为map,先获取keys,先将keyset获取,集合里的每一个key都是String,通过遍历的key获取value,再放到map中
Set<String> keys= jsonObject.keySet();
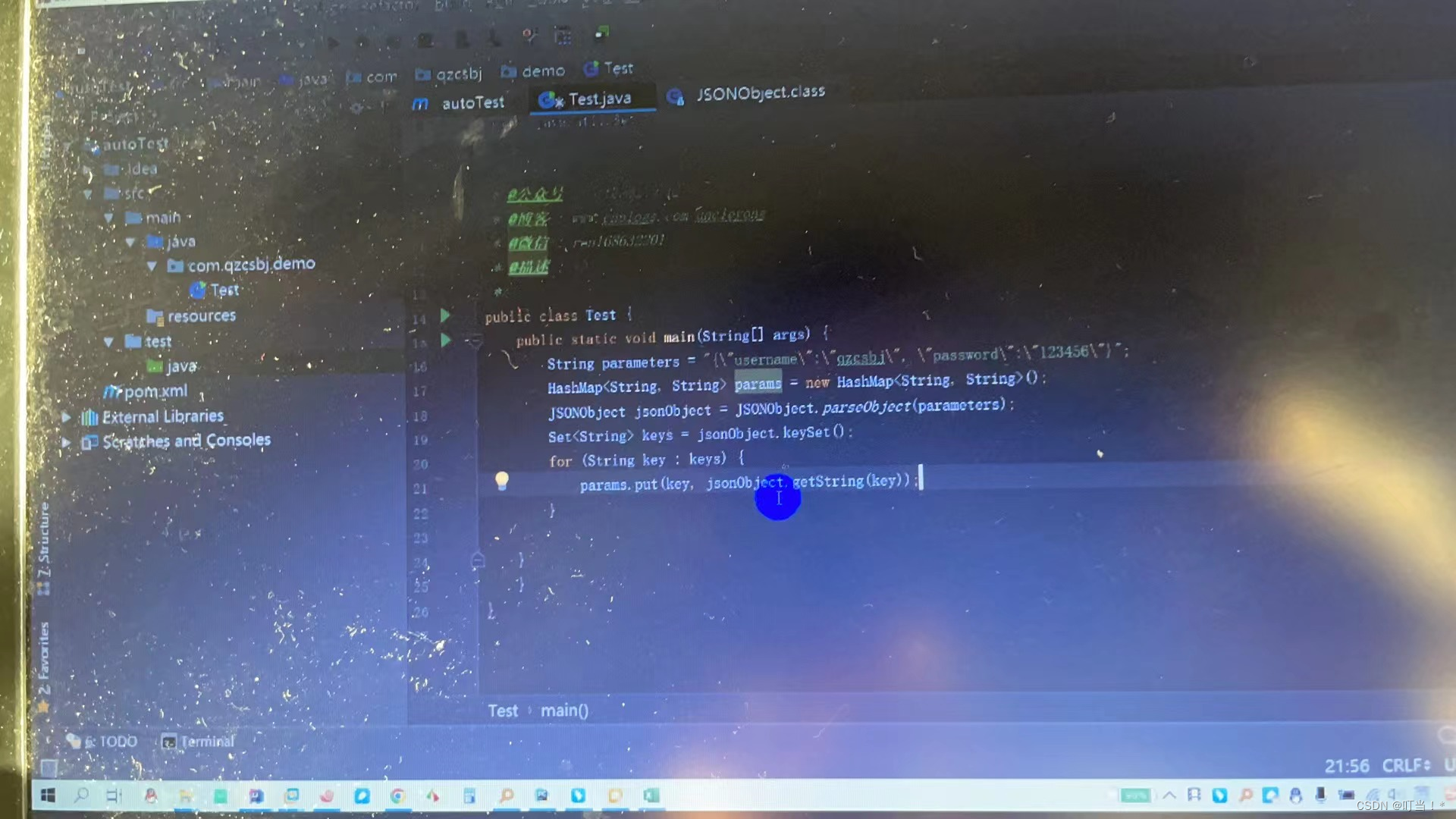
for (String key:keys) {
map.put(key,jsonObject.getString(key));
}
//验证,获取Map中的key
Set<String> keys2 = map.keySet();
for (String key :keys2) {
System.out.println(key+"="+map.get(key));
}
}
}
package com.zhou.demo;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
//JSON数组,每个元素是json字符串
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String initsql="[n" + "{"sqlNo":"1","sql":"select * from users where username='qzcsbj';"},n" +
"{"sqlNo":"2","sql":"select * from users where username='tester00501';"}n" + "n" + "]";
/* //元素解析为Map
List<HashMap> sqls = JSONObject.parseArray(initsql,HashMap.class);
for (HashMap sql:sqls) {
System.out.println(sql);
String sqlNo = (String)sql.get("sqlNo");
String sql_ = (String)sql.get("sql");
System.out.println("sqlNo-"+sqlNo+",sql_-"+sql_);
}*/
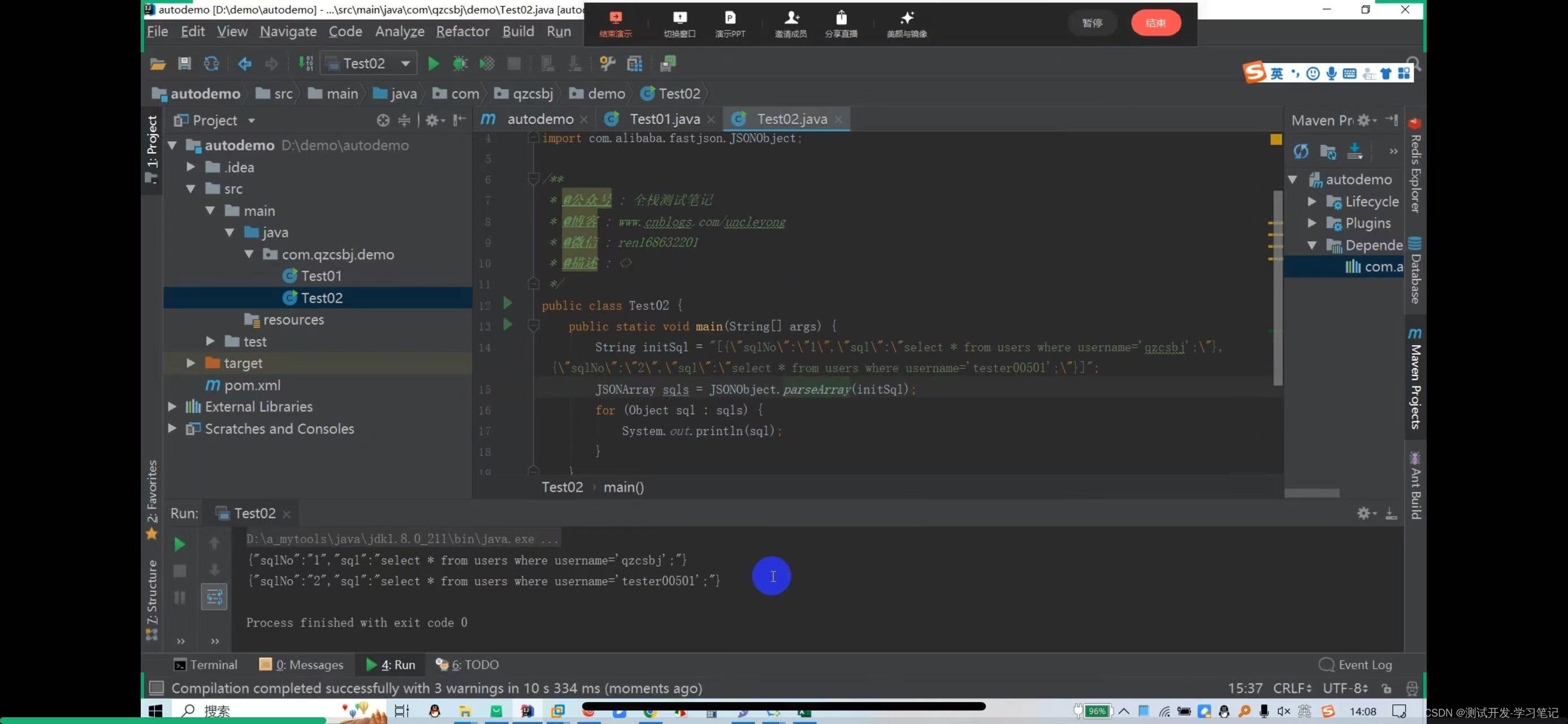
//元素封装到对象
List<Sql> sqls = JSONObject.parseArray(initsql, Sql.class);
for (Sql sql:sqls) {
String sqlNo = sql.getSqlNo();
String sql_ = sql.getSql();
System.out.println("sqlNo-"+",sql_"+sql_);
}
}
}
Because currently the projects are separated in front and back ends
The backend generally returns a json string
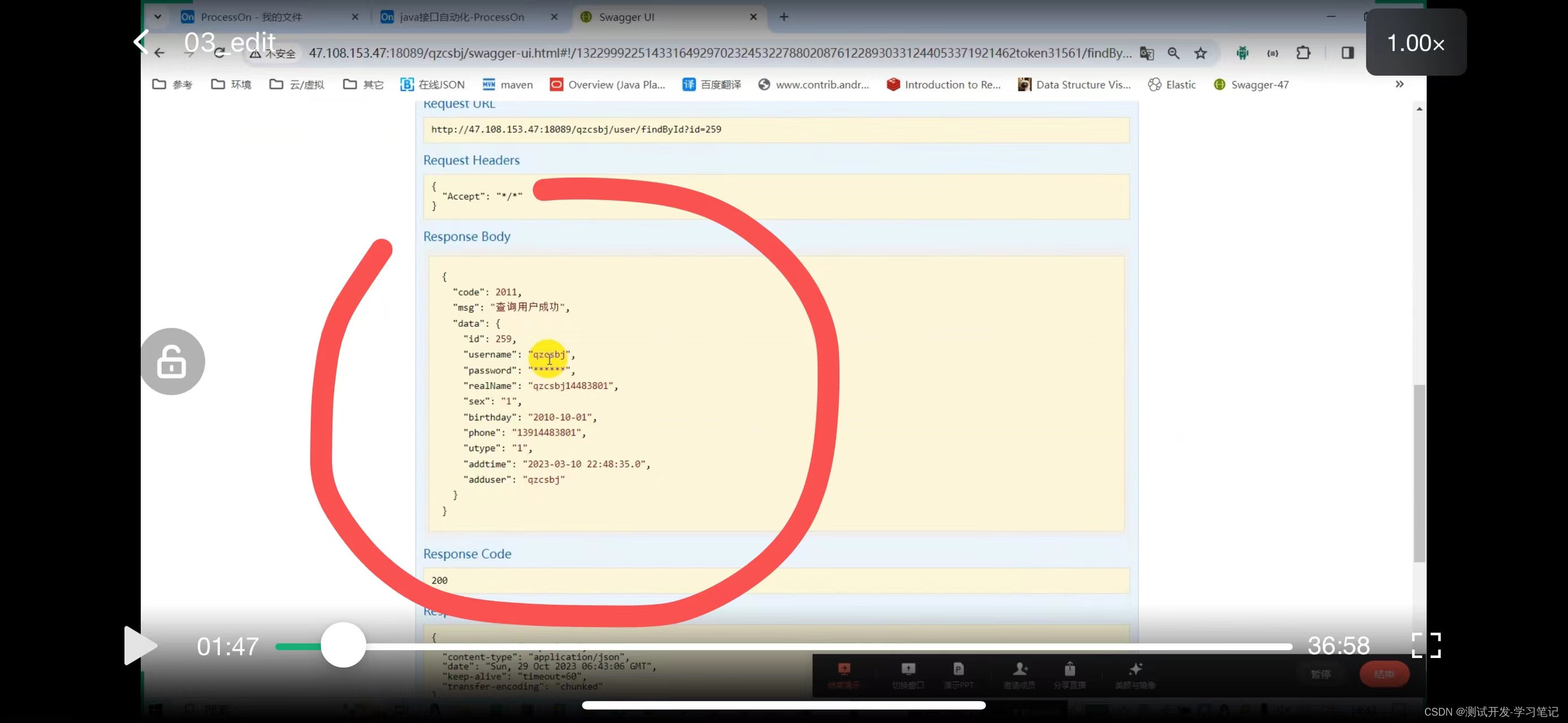
If you want to make an assertion, you usually parse the JSON, and after parsing, you usually only make assertions on key fields.
Assertions are generally code + key business fields
It is a json string, so you need to use jsonpath
blog.csdnimg.cn/5bdd9defd7db47b7a5934f79f9fd0ceb.png)
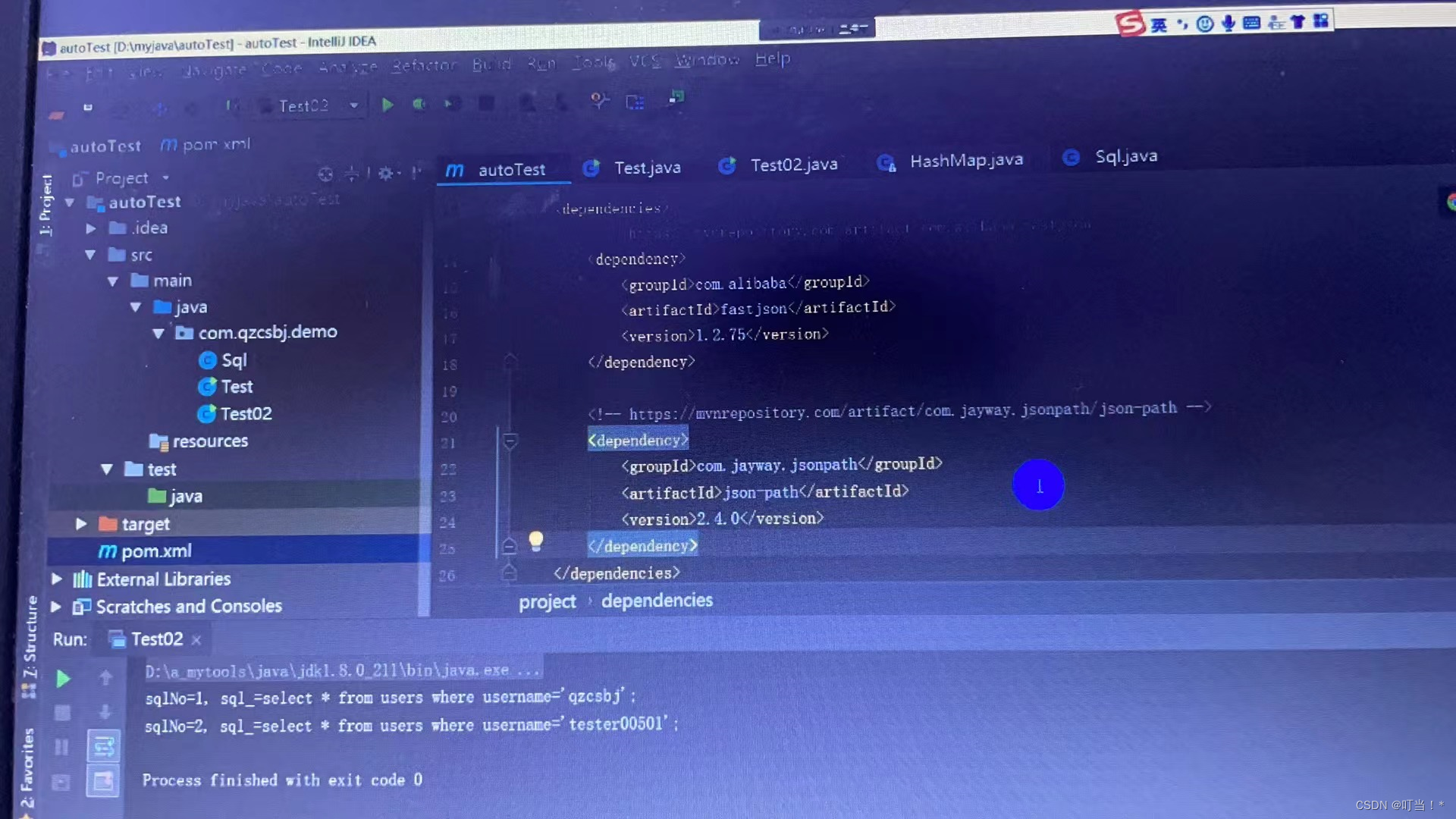
Need to confirm whether the dependencies are downloaded
This variable here is the response field returned after successful login
blog.csdnimg.cn/a20e89ee243c43f69a1b4e1c3a97b89b.png)
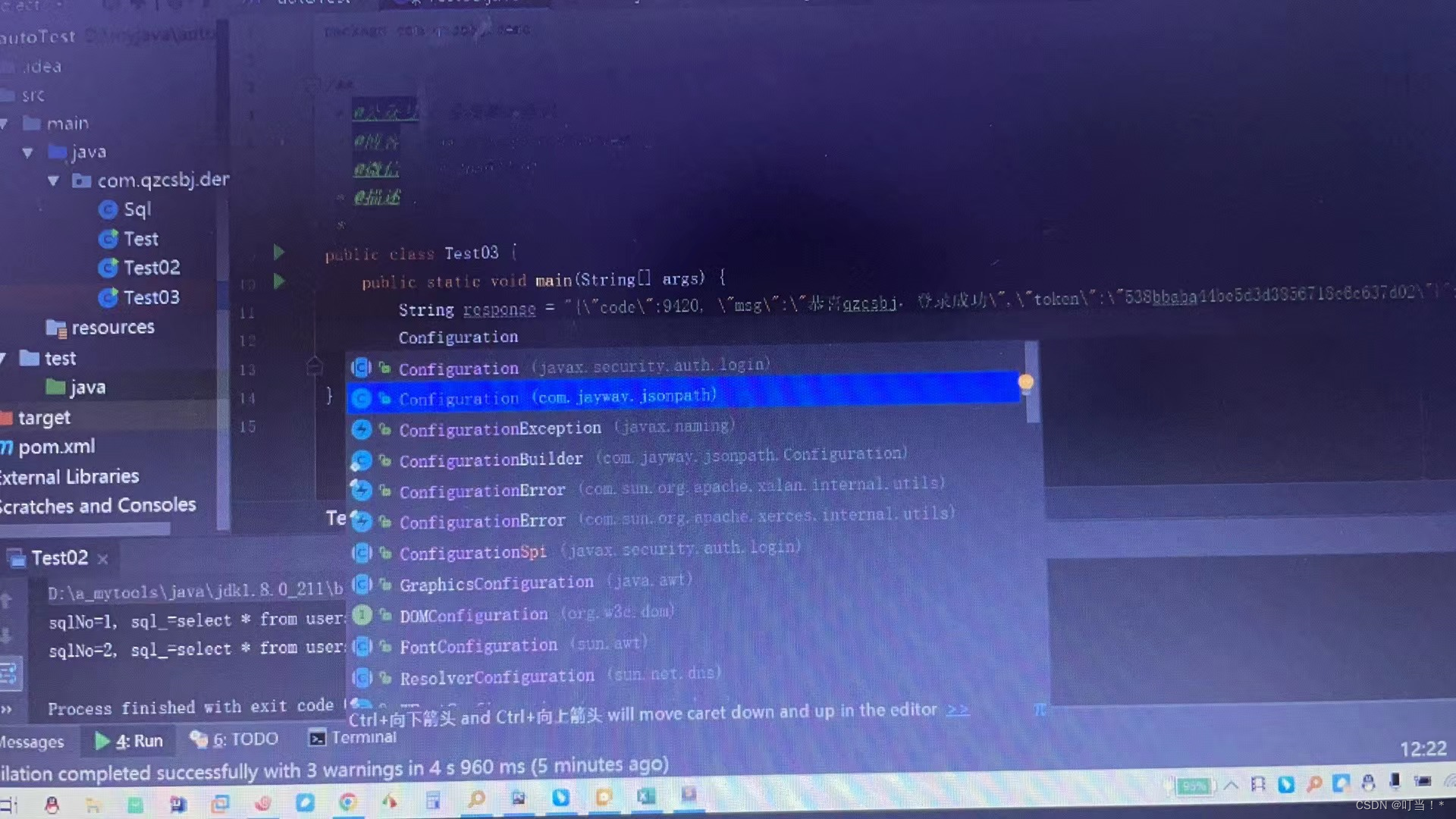
Pass the defined field response into
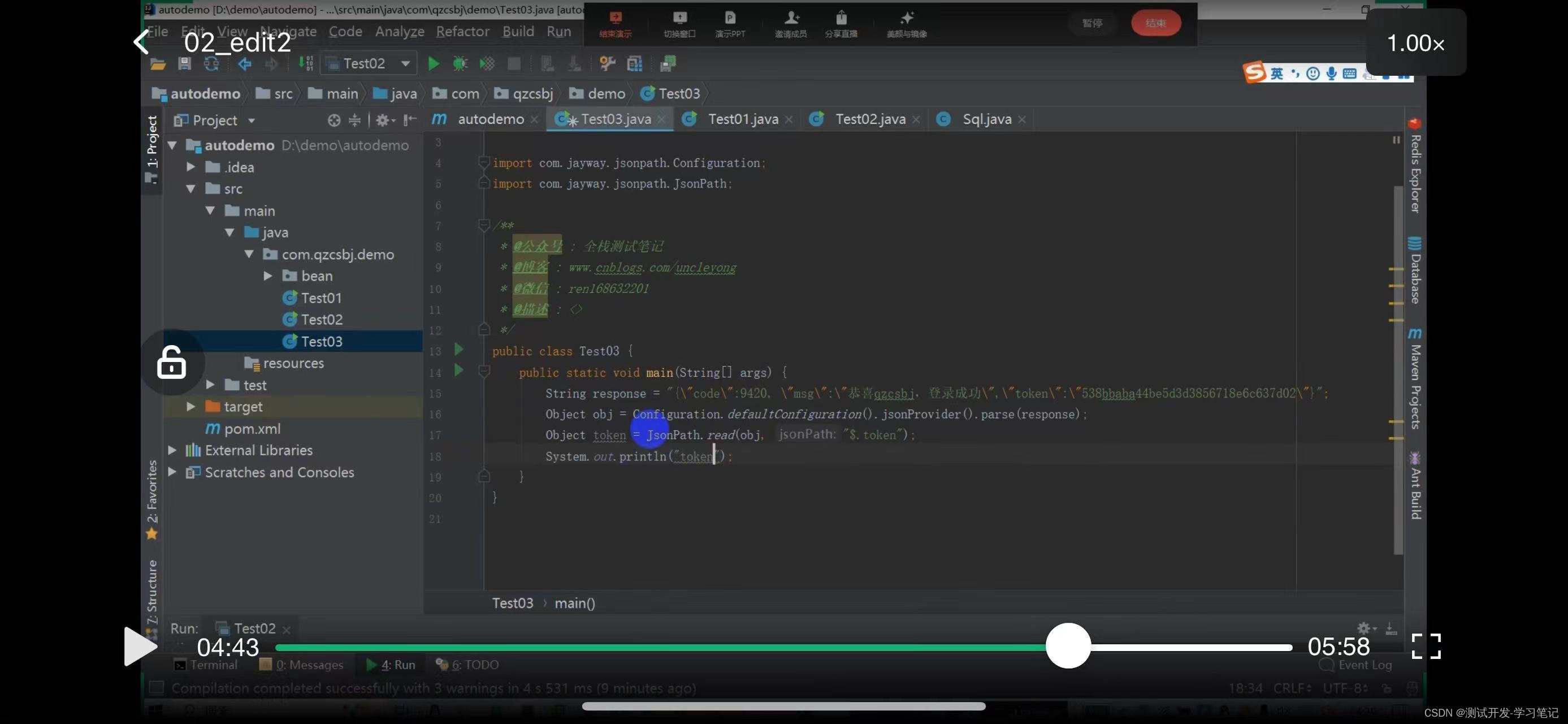
Interface automation for processing dependent data
Get the token from the front of this line, which is also $.
After obtaining it, if it is a global variable, it can be saved in the global variable
If you want to get the assertion and then get
Make another assertion
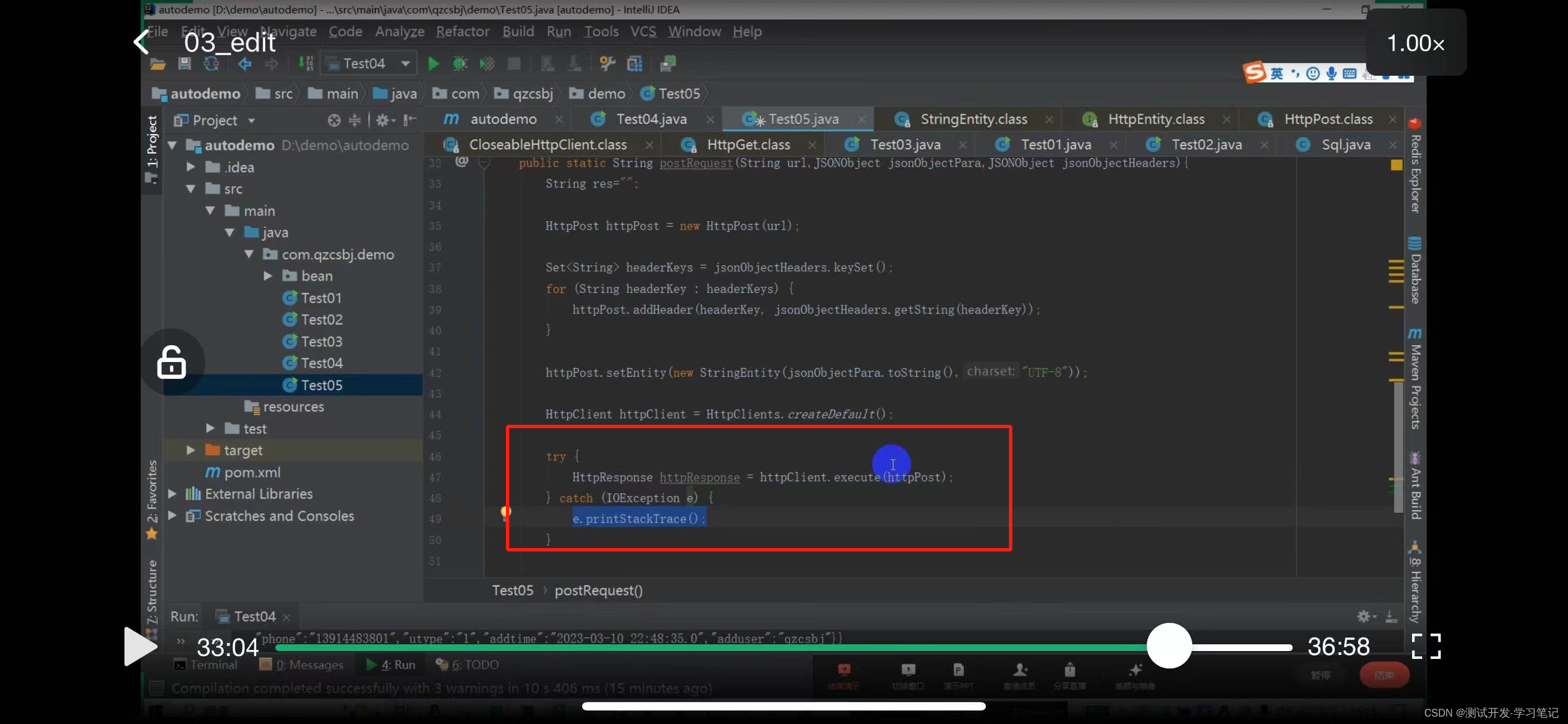
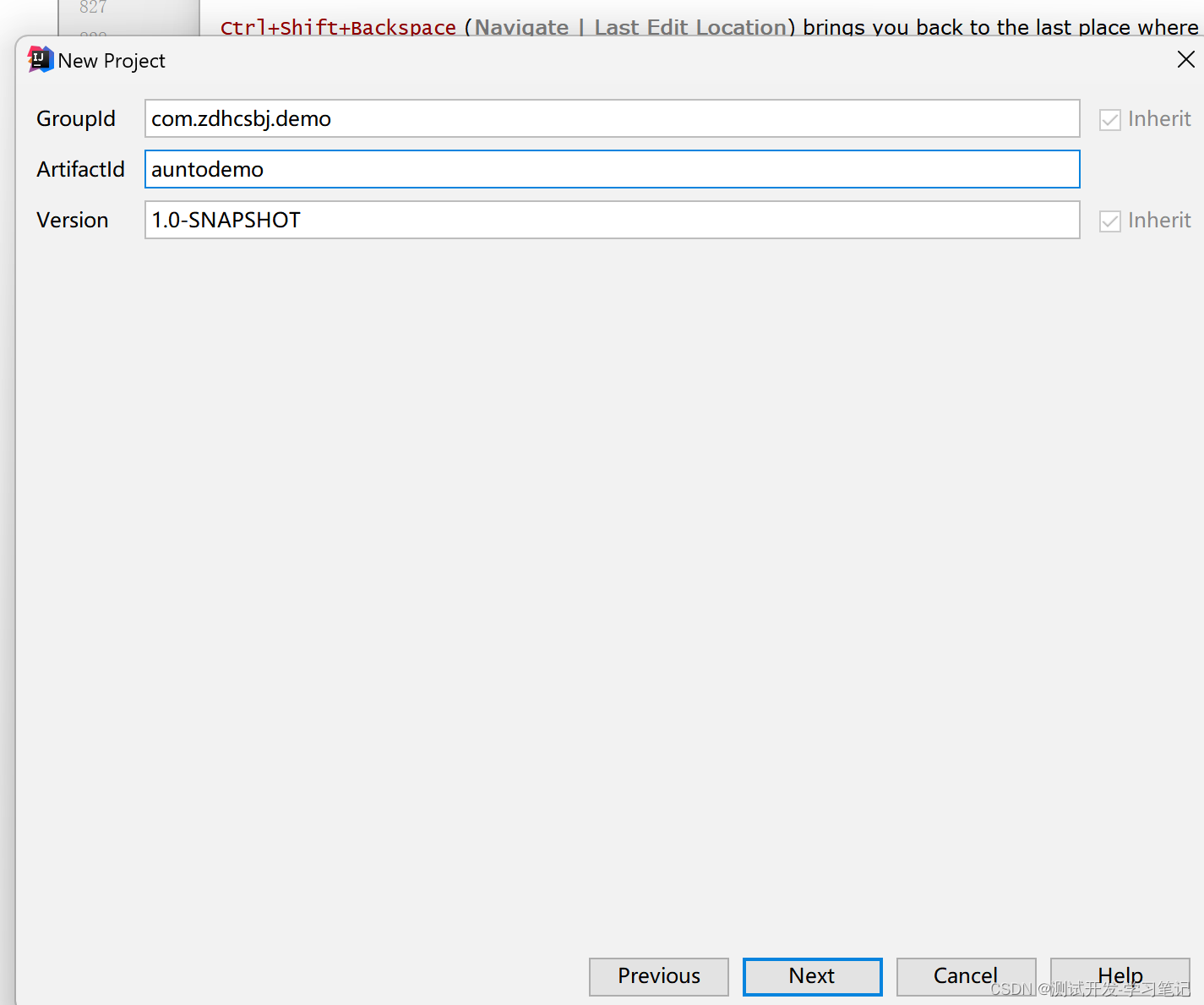
In the automation framework, requests are sent by writing code, which requires the use of httpclient, a library provided by java to interact with the server.
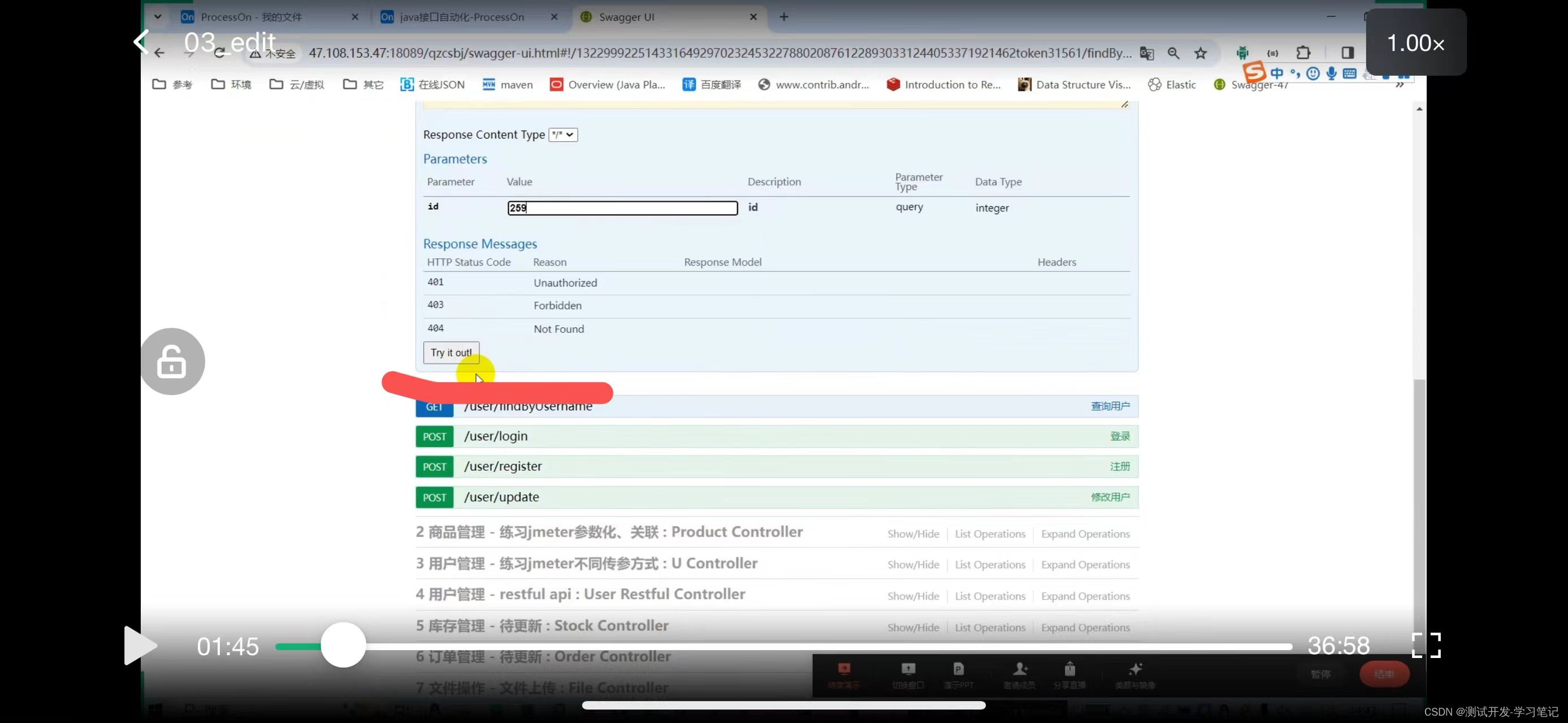
Need to pass id
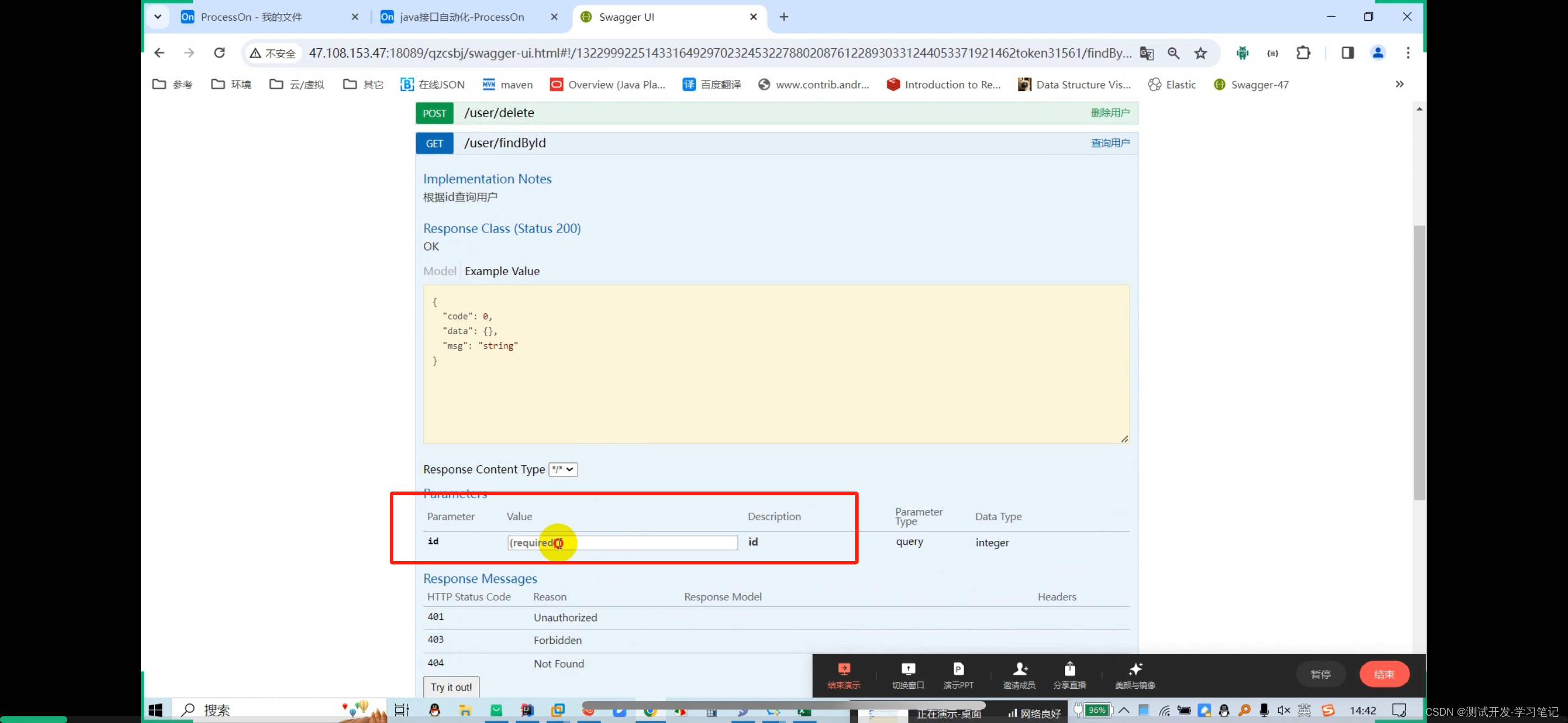
From the library, I see that the ID is 259
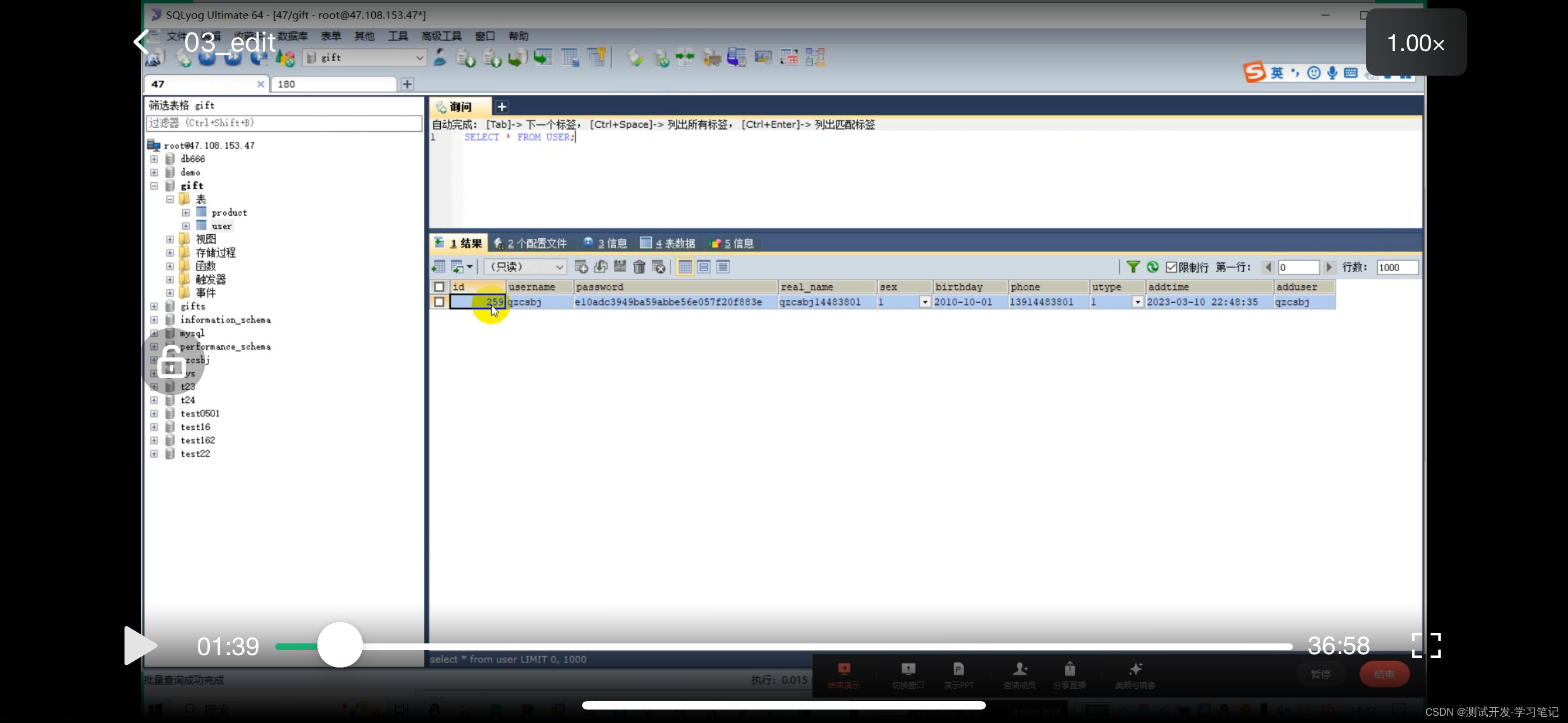
In the data file, parameters are concatenated into json strings, so id=259 is also concatenated into json strings.
Here, put 259 in double quotes to automatically escape it.
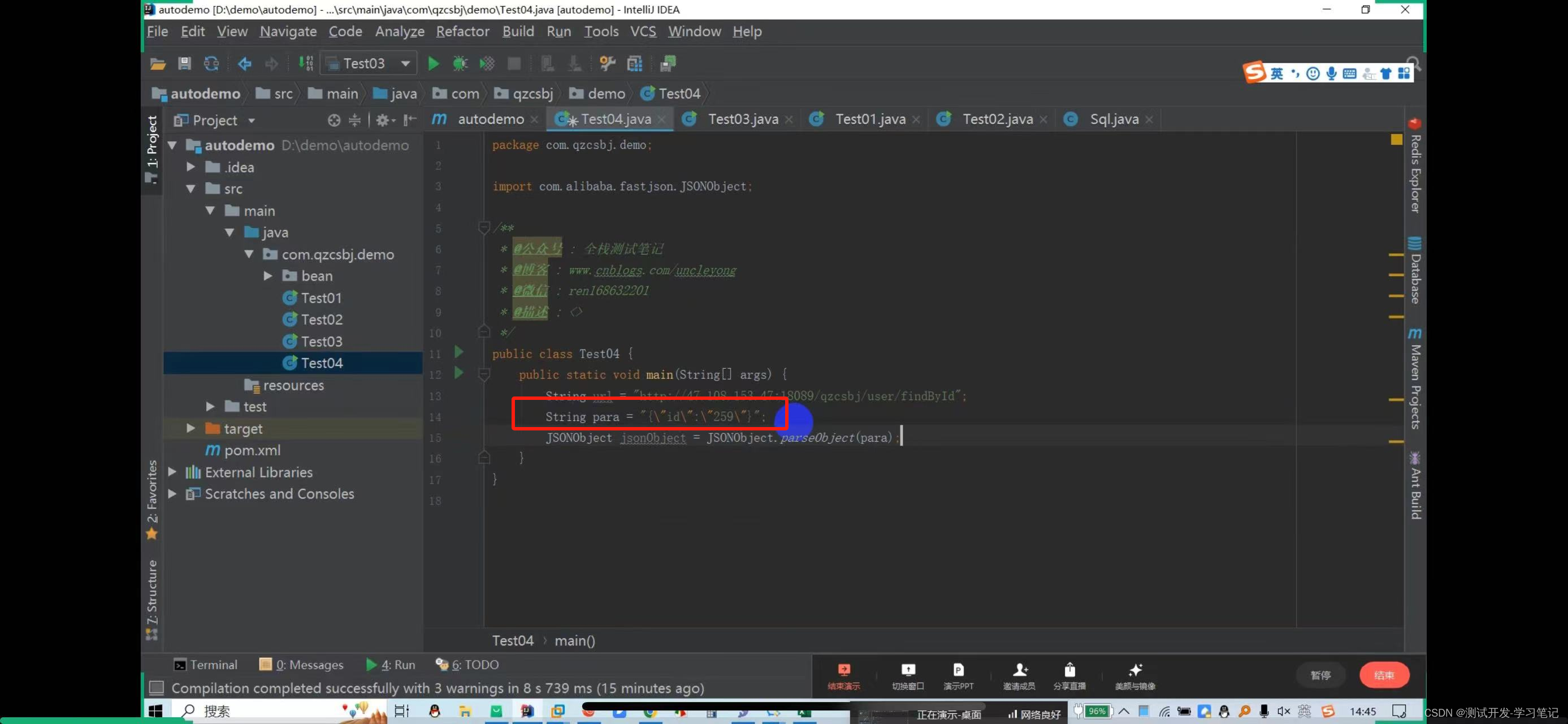
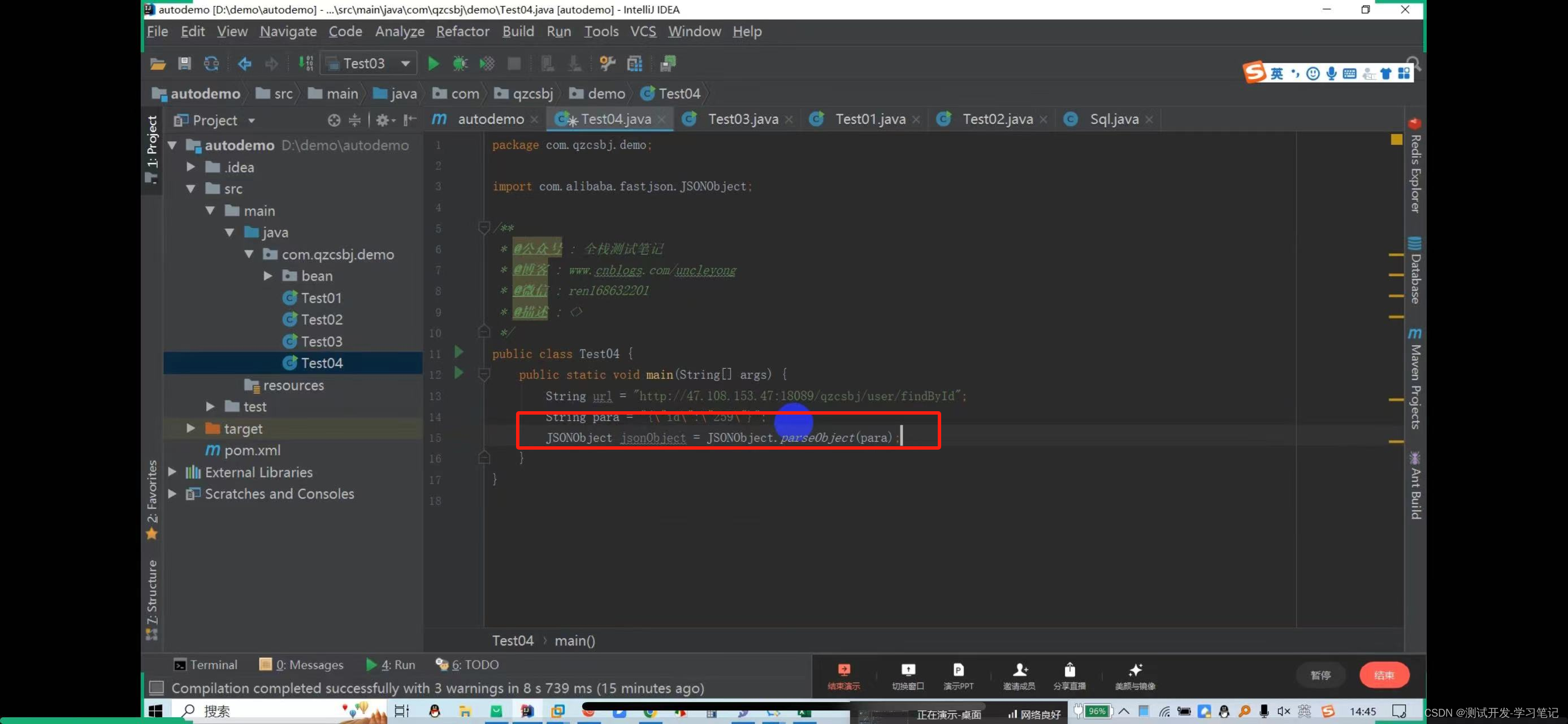
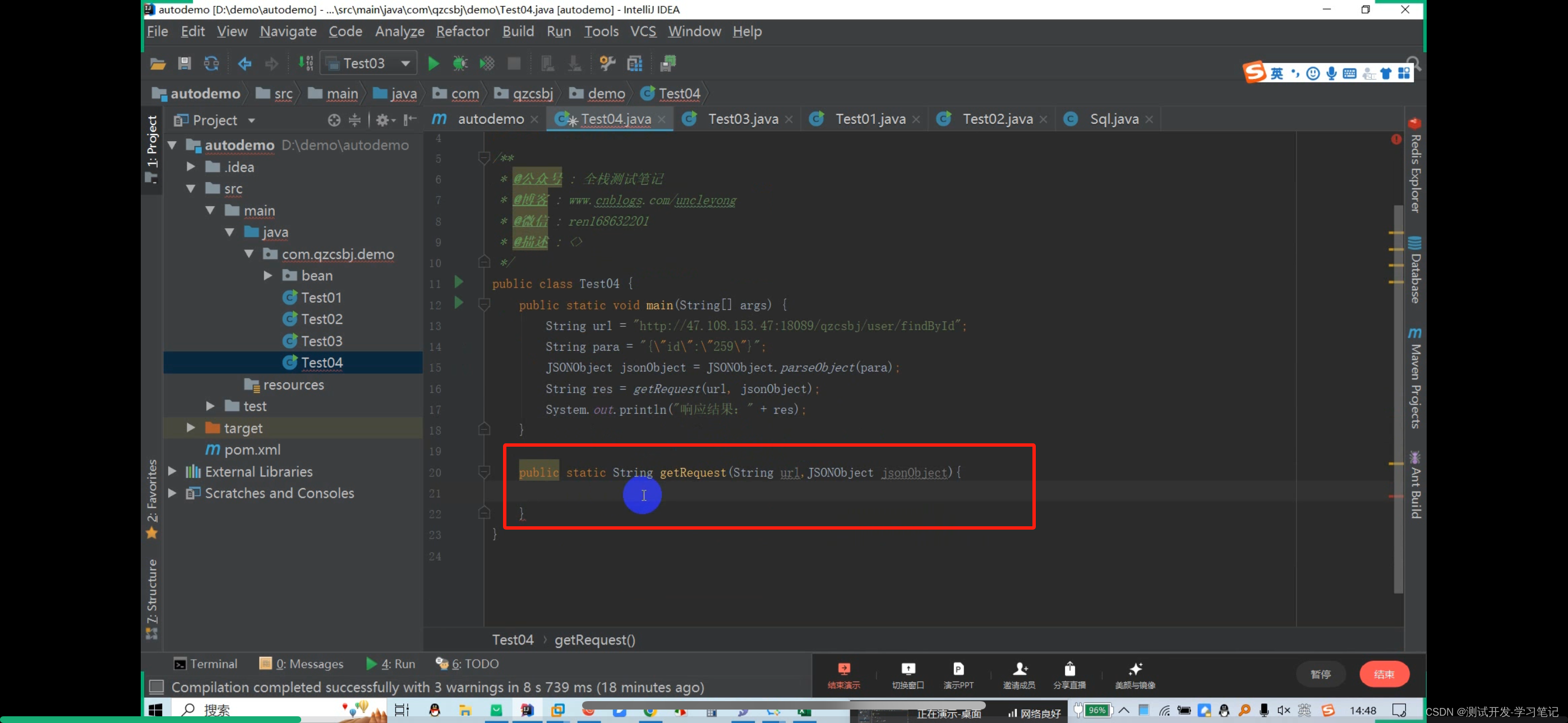
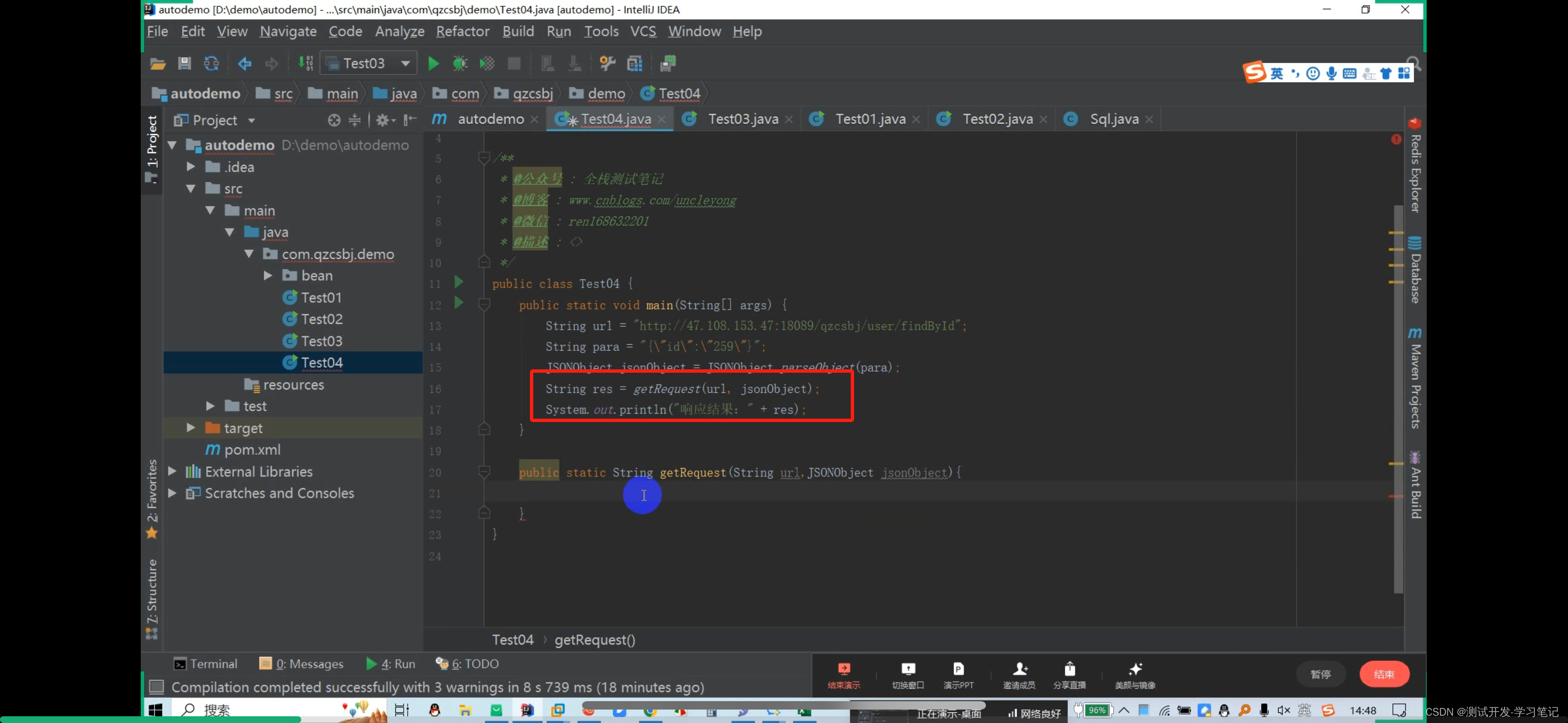
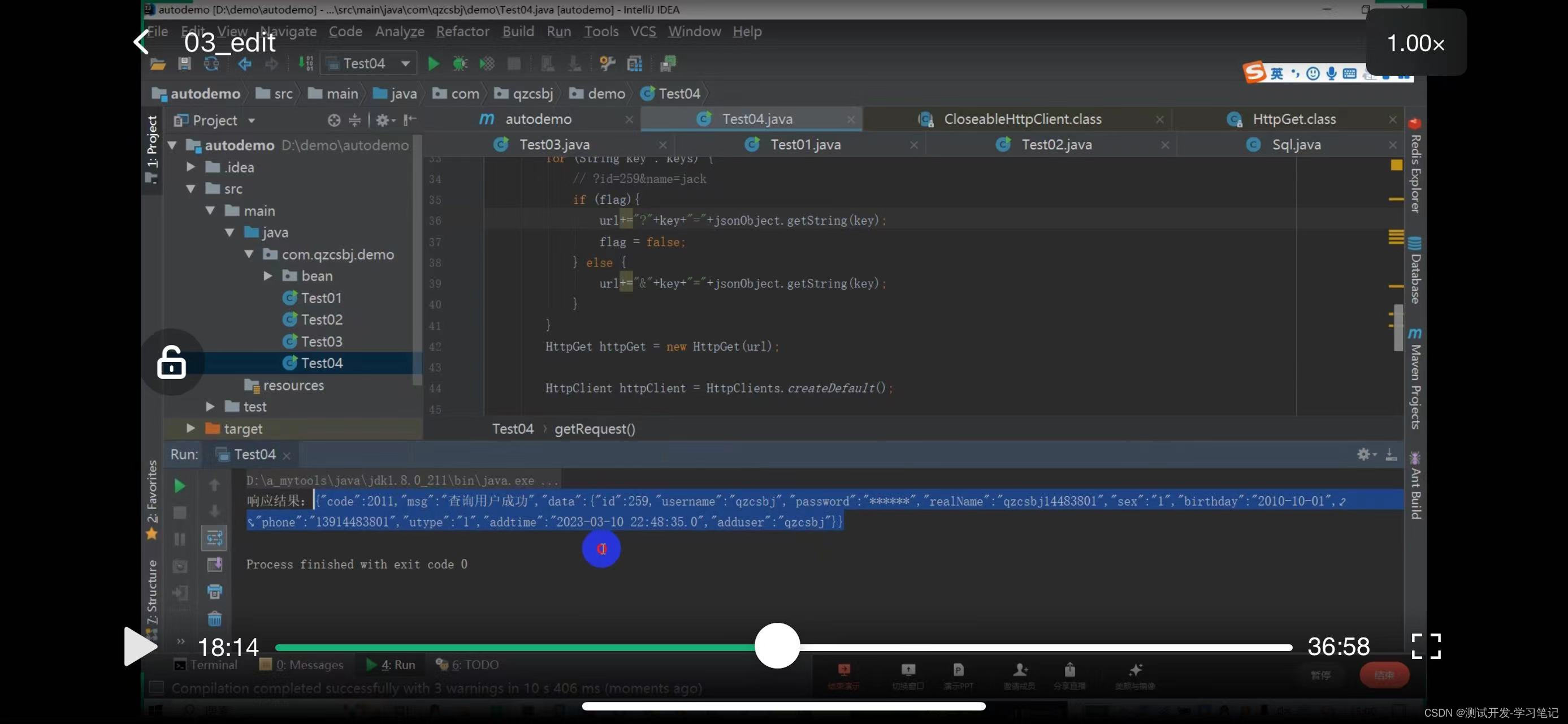
Get request: http://47.108.153.47:18089/qzcsbj/user/findById?id=259
? Then directly concatenate the parameters
There are also multiple values to consider: http://47.108.153.47:18089/qzcsbj/user/findById?id=259&name=jack
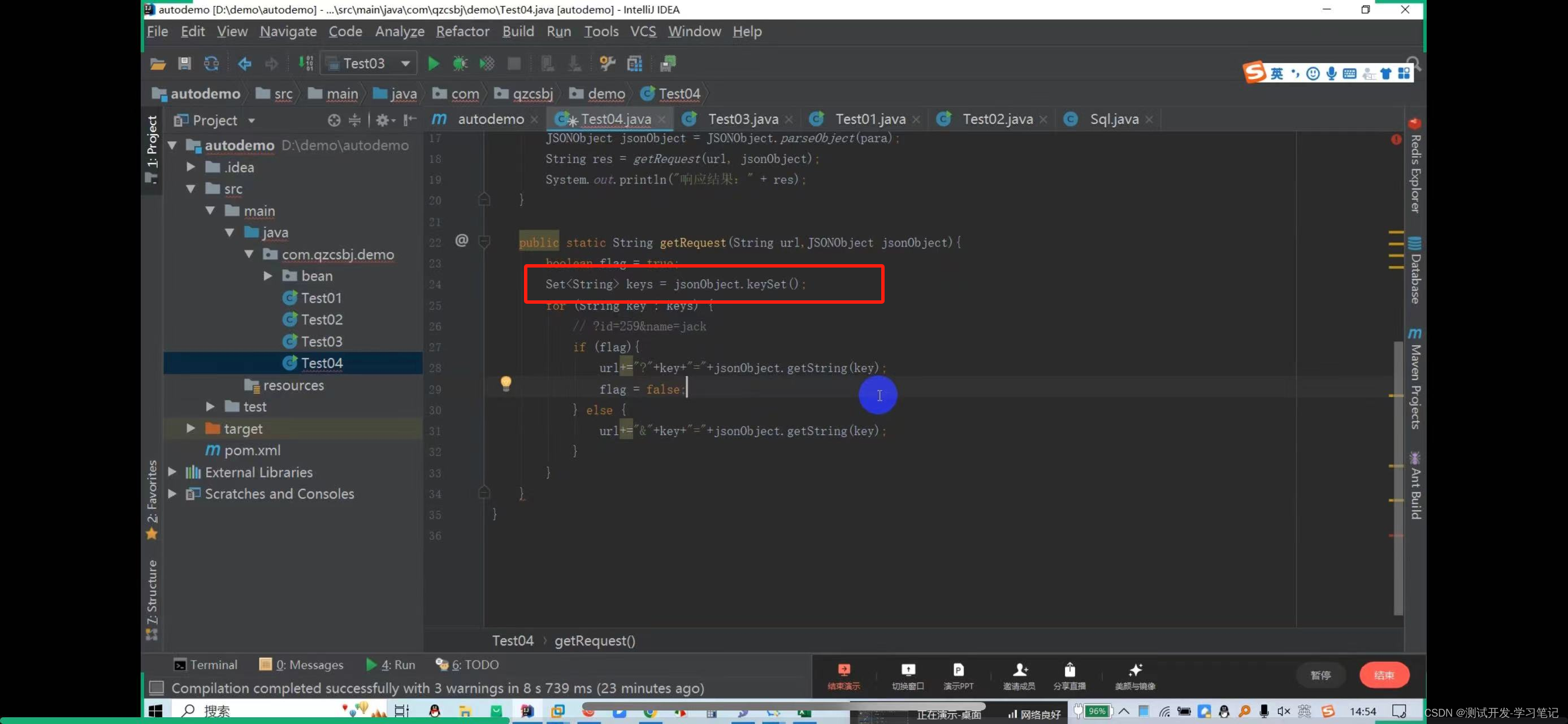
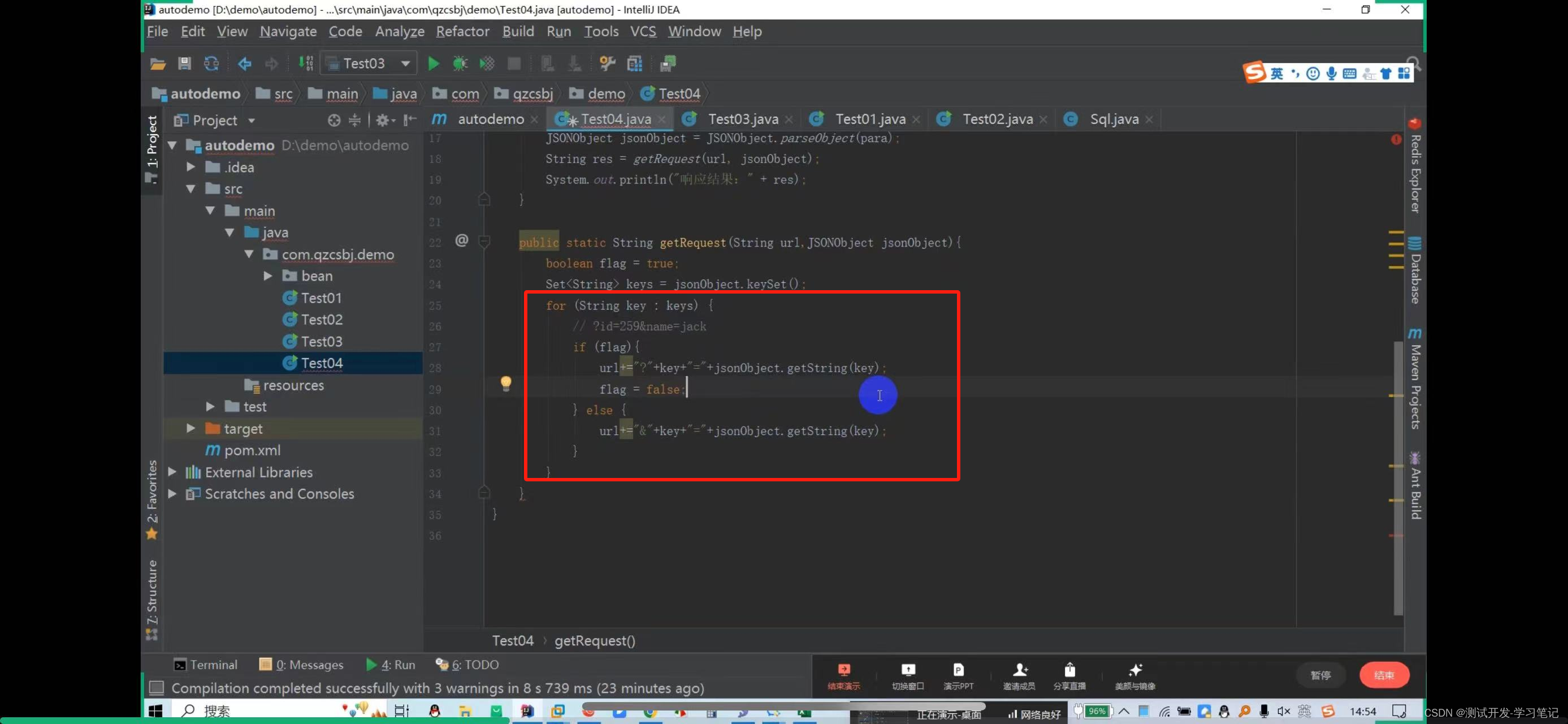
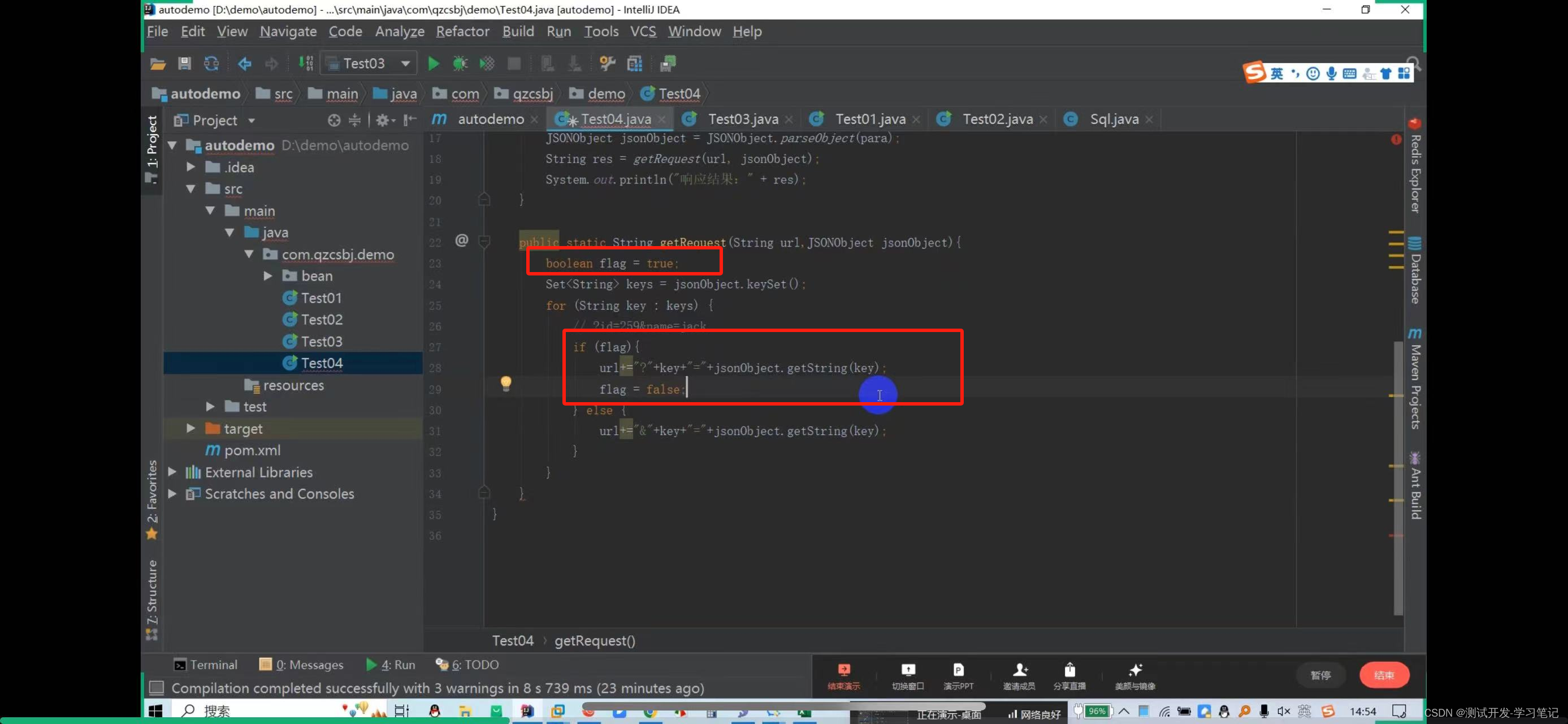
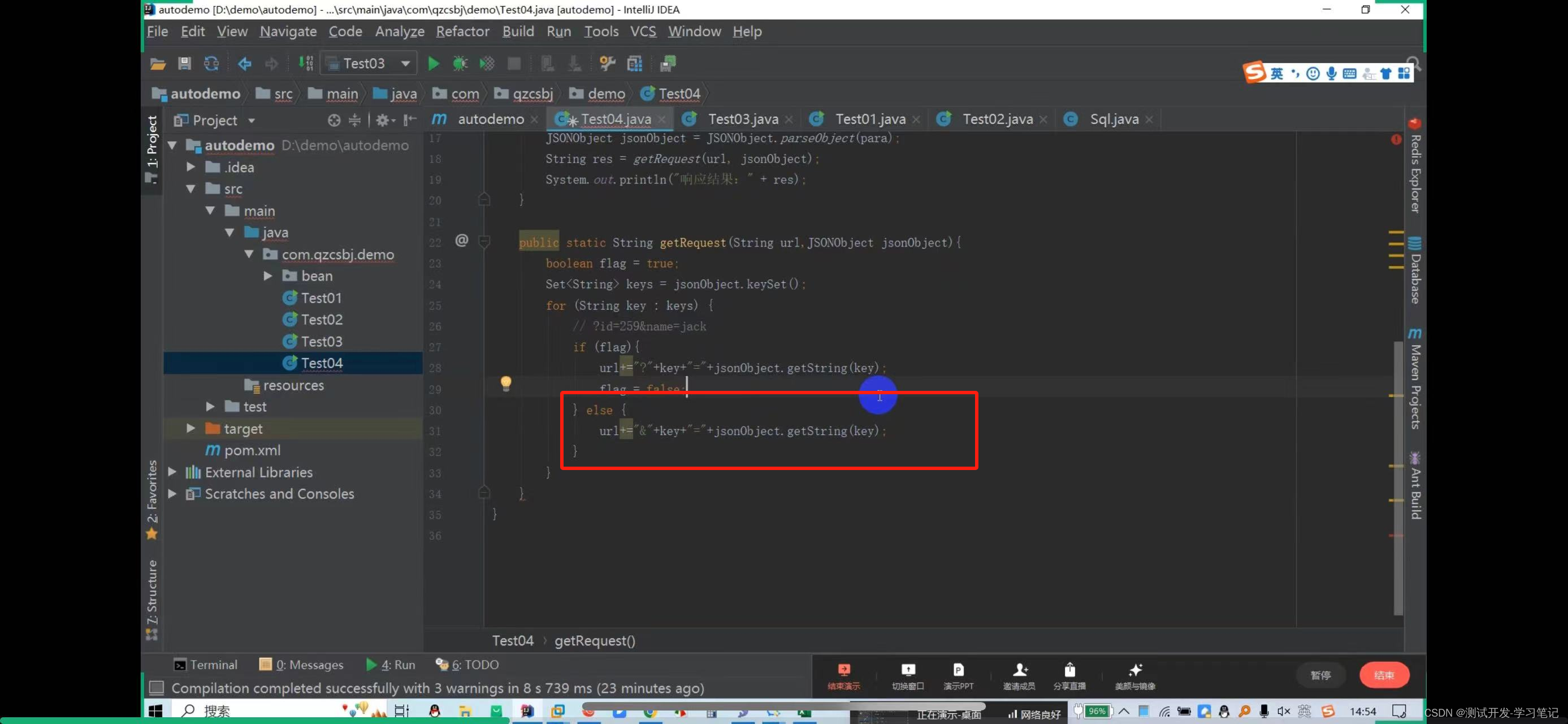
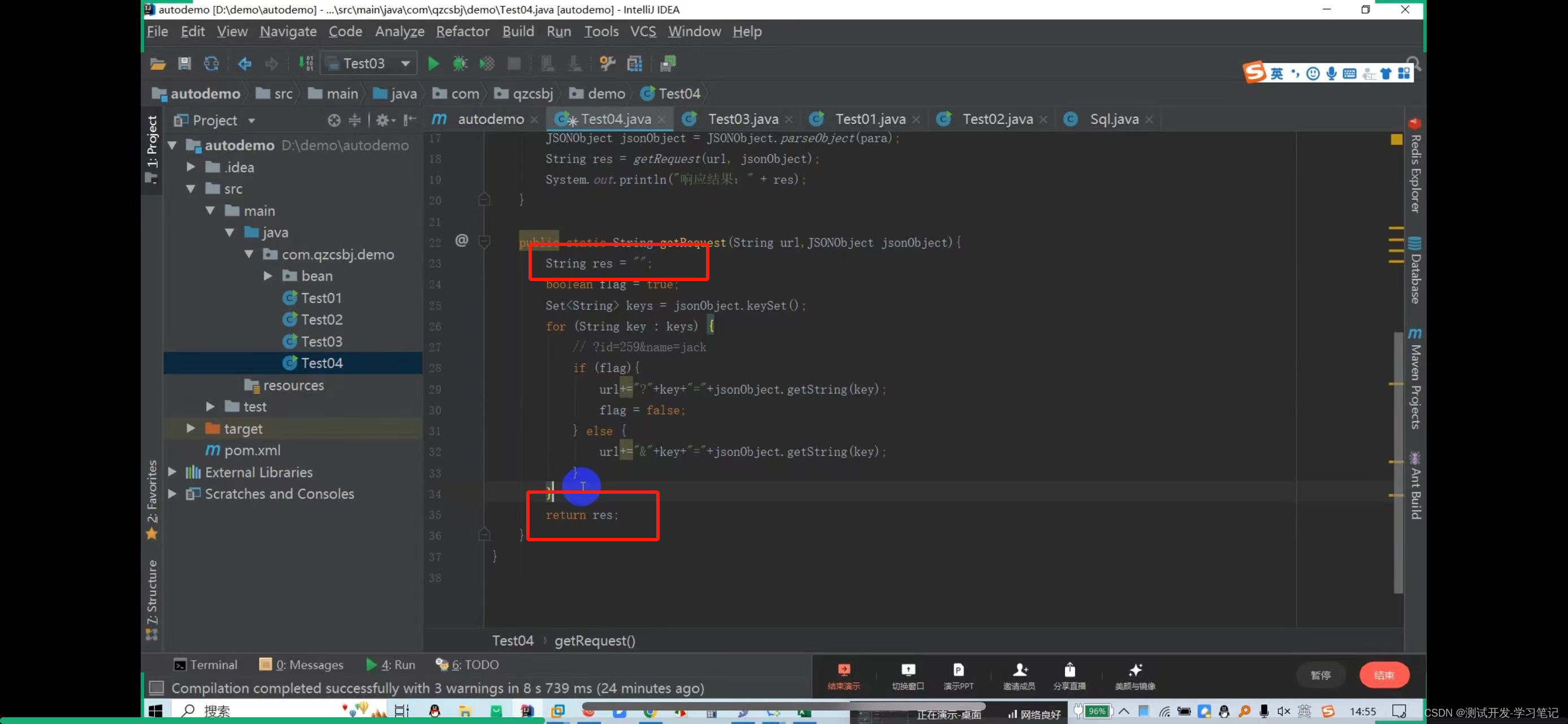
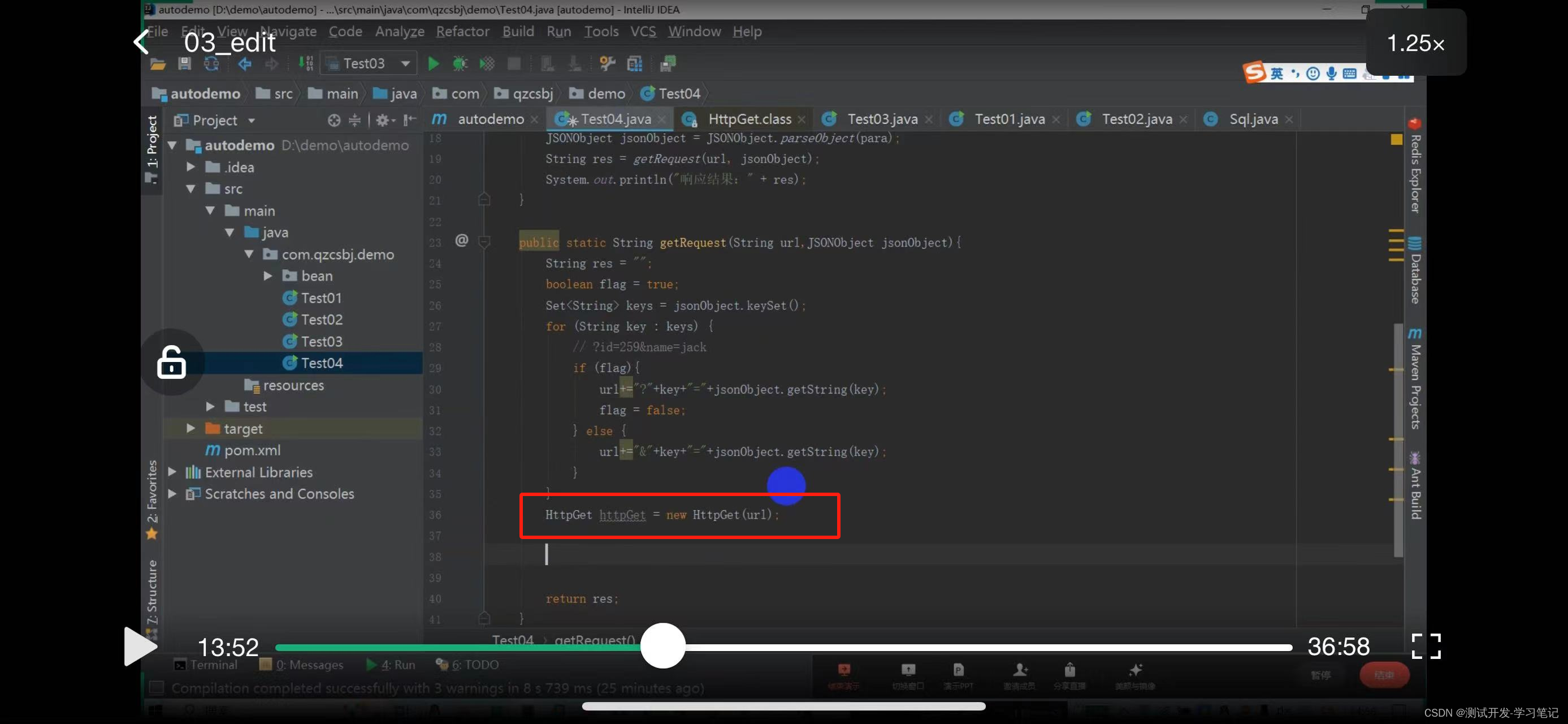
The above will concatenate the parameters of the url and parameters of the get request. After creating it, you need to create a get request object
Pass the url in
The httpget request object is obtained here
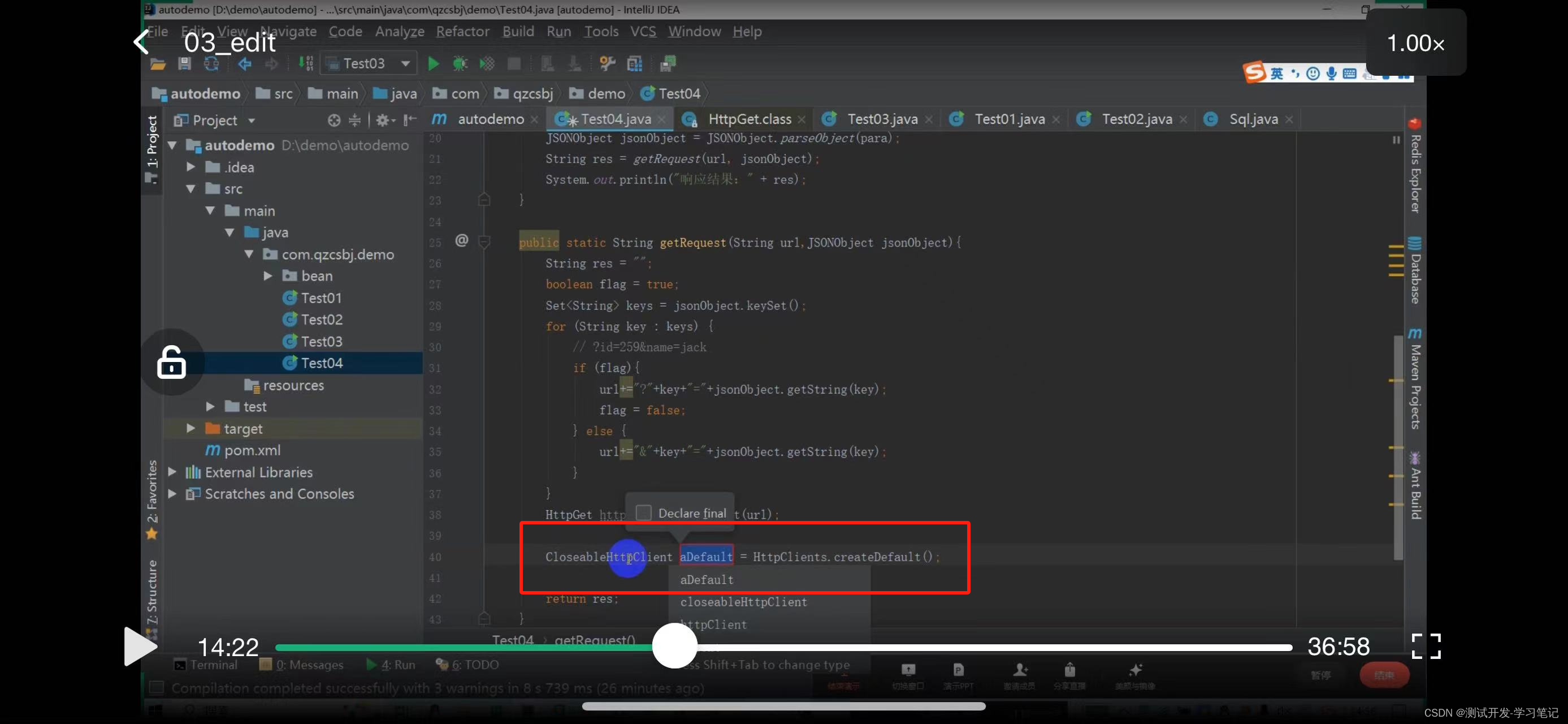
The CloseableHttpClient abstract class implements the HttpClient and Closeable interfaces.
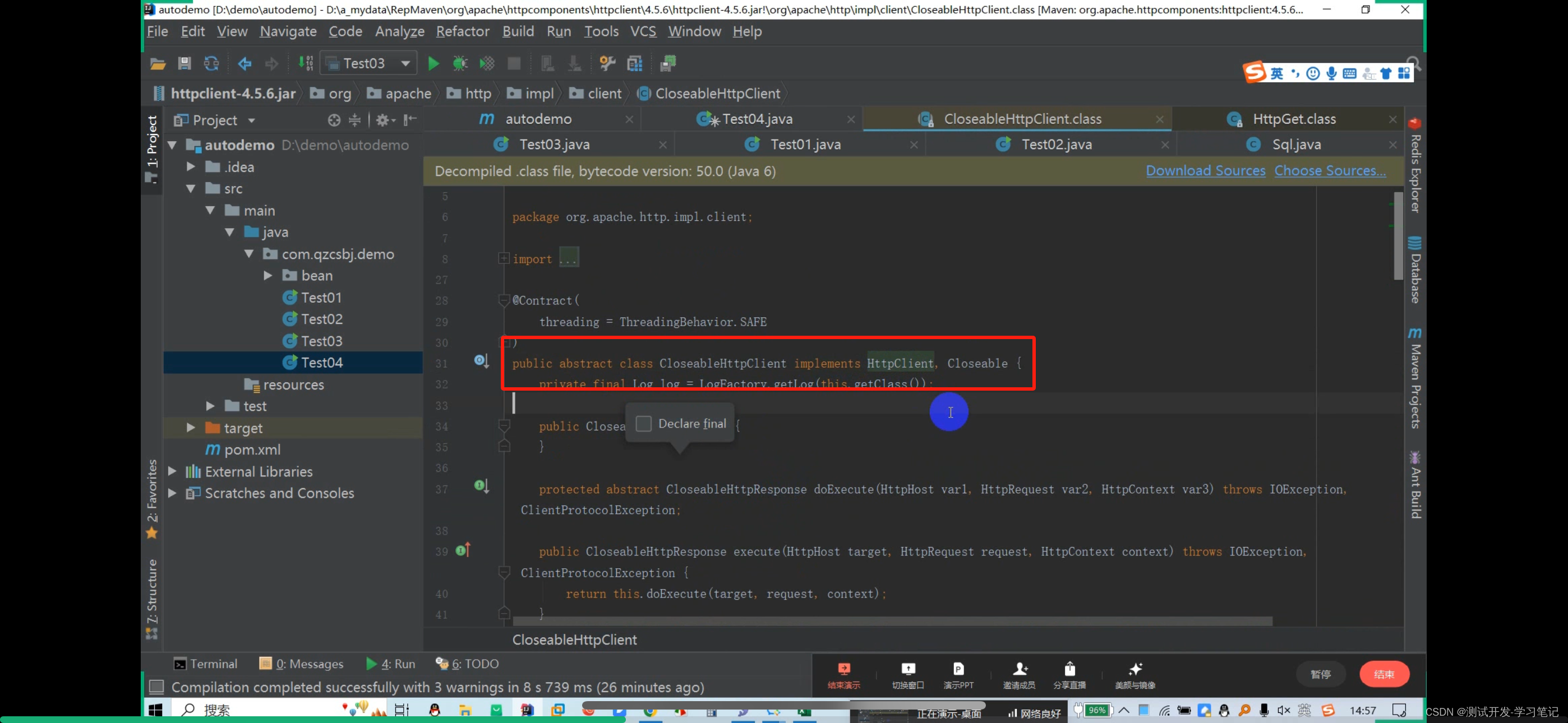
Polymorphism can be used, and the subclass object points to the parent class reference (the interface implemented by the parent class)
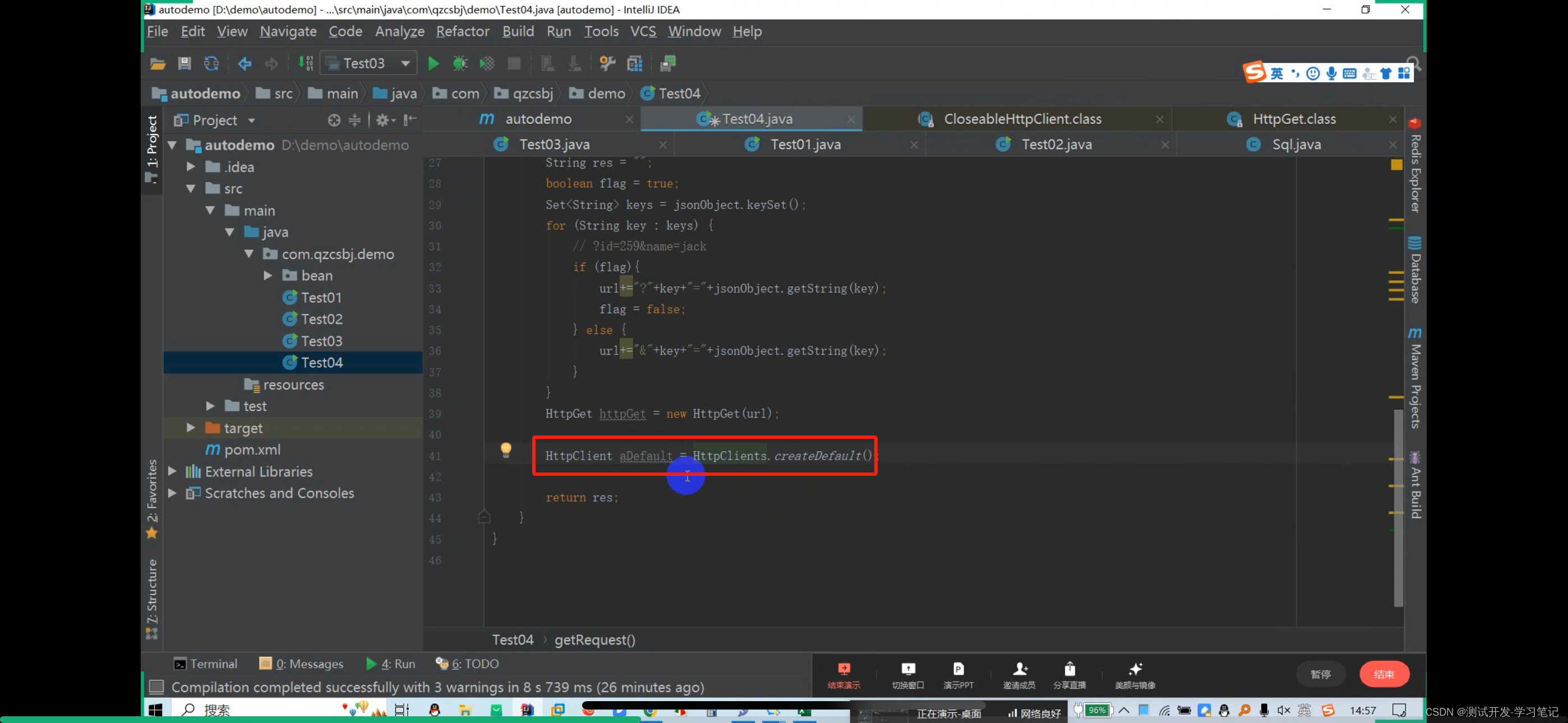
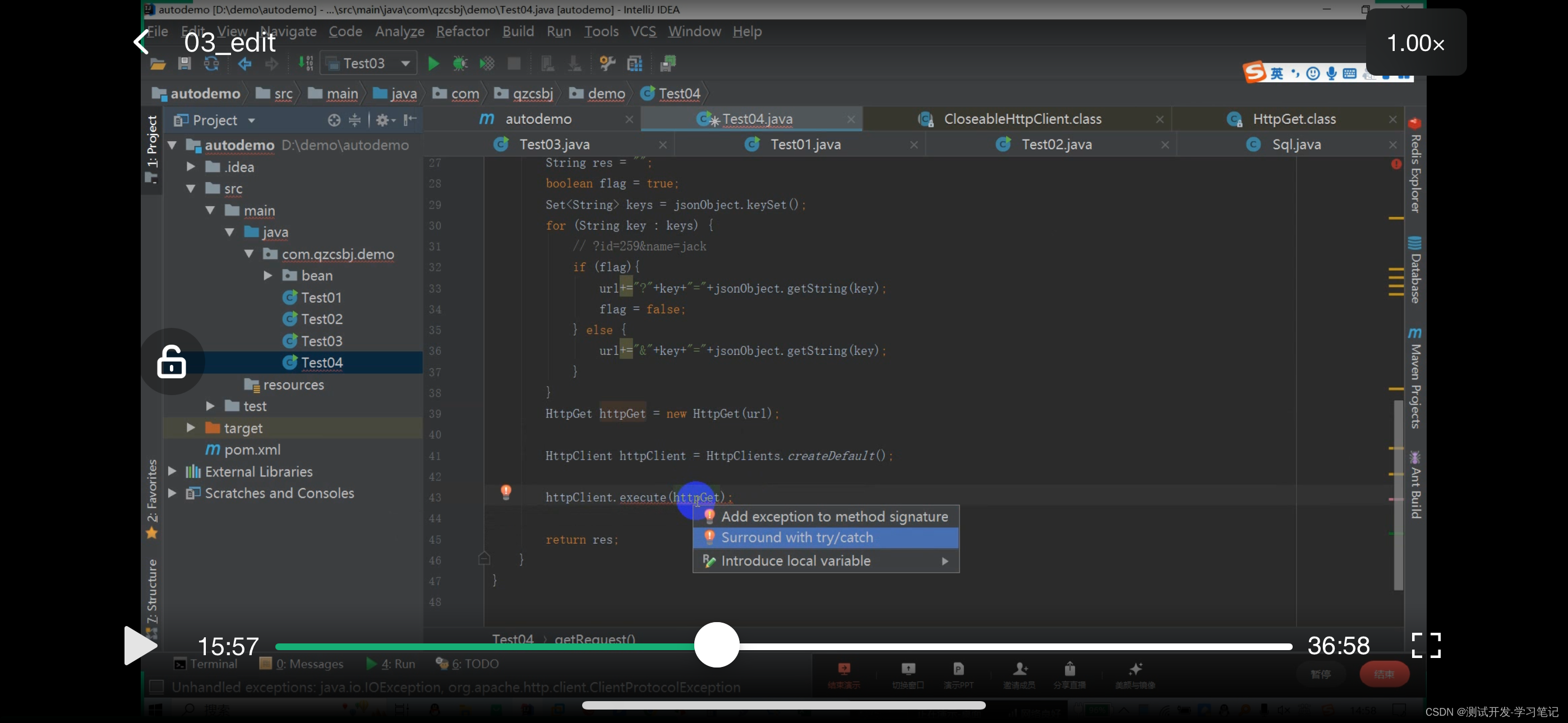
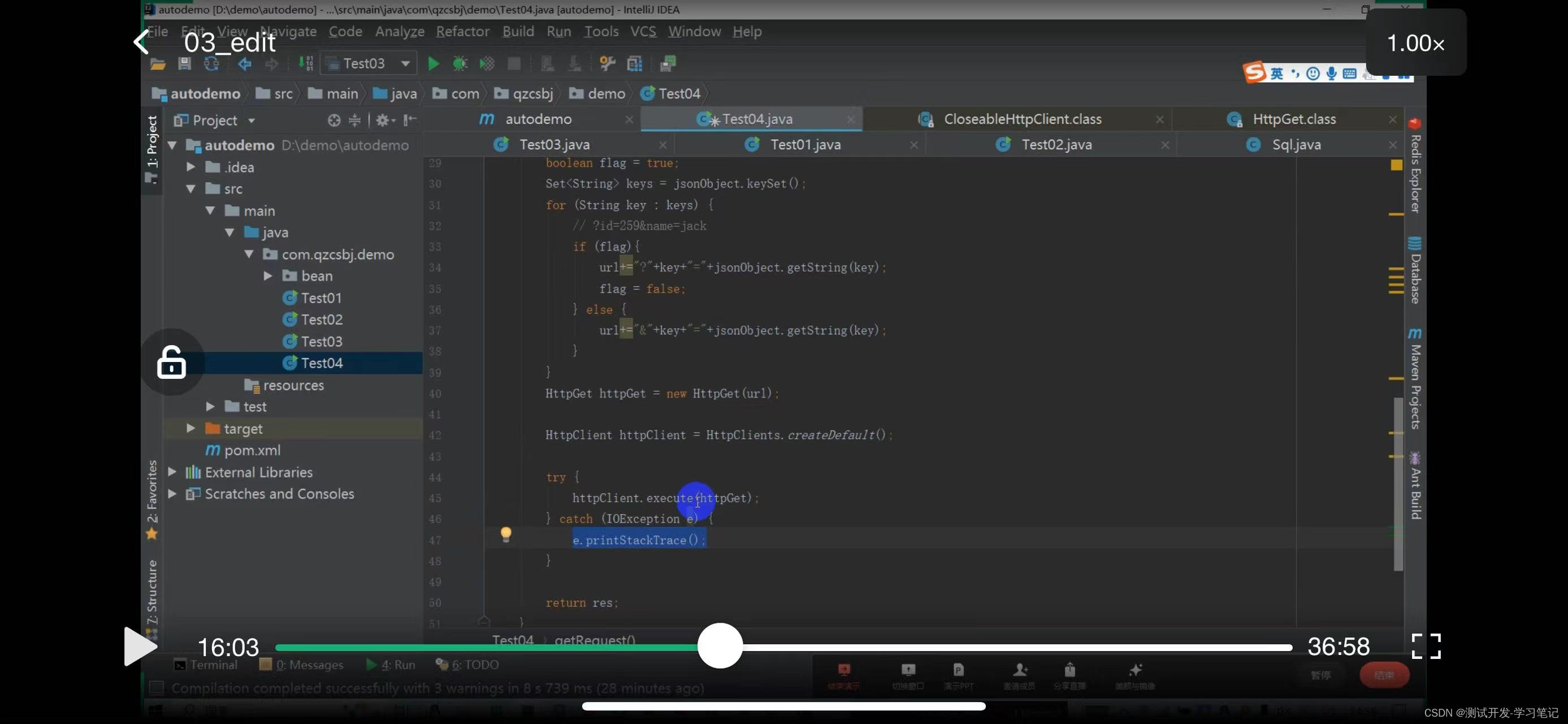
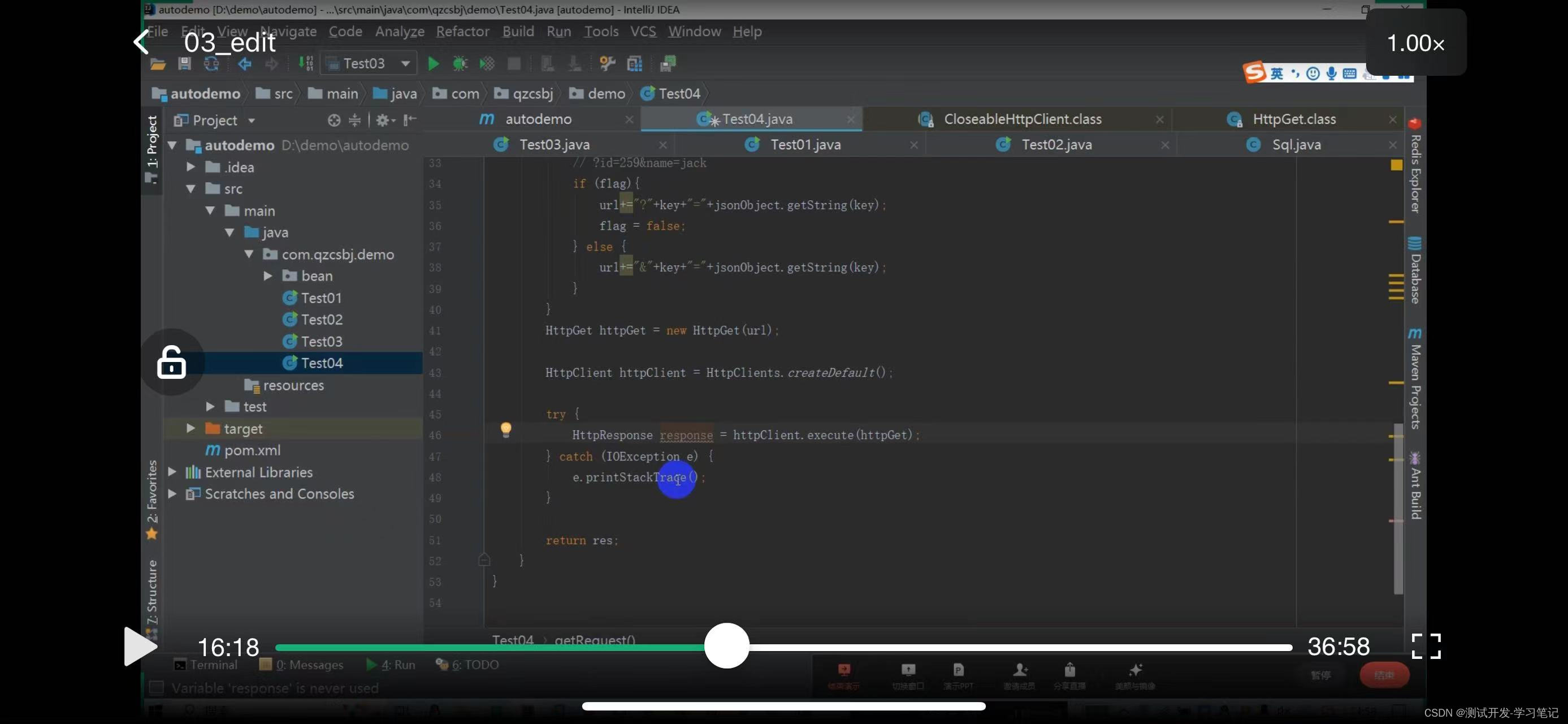
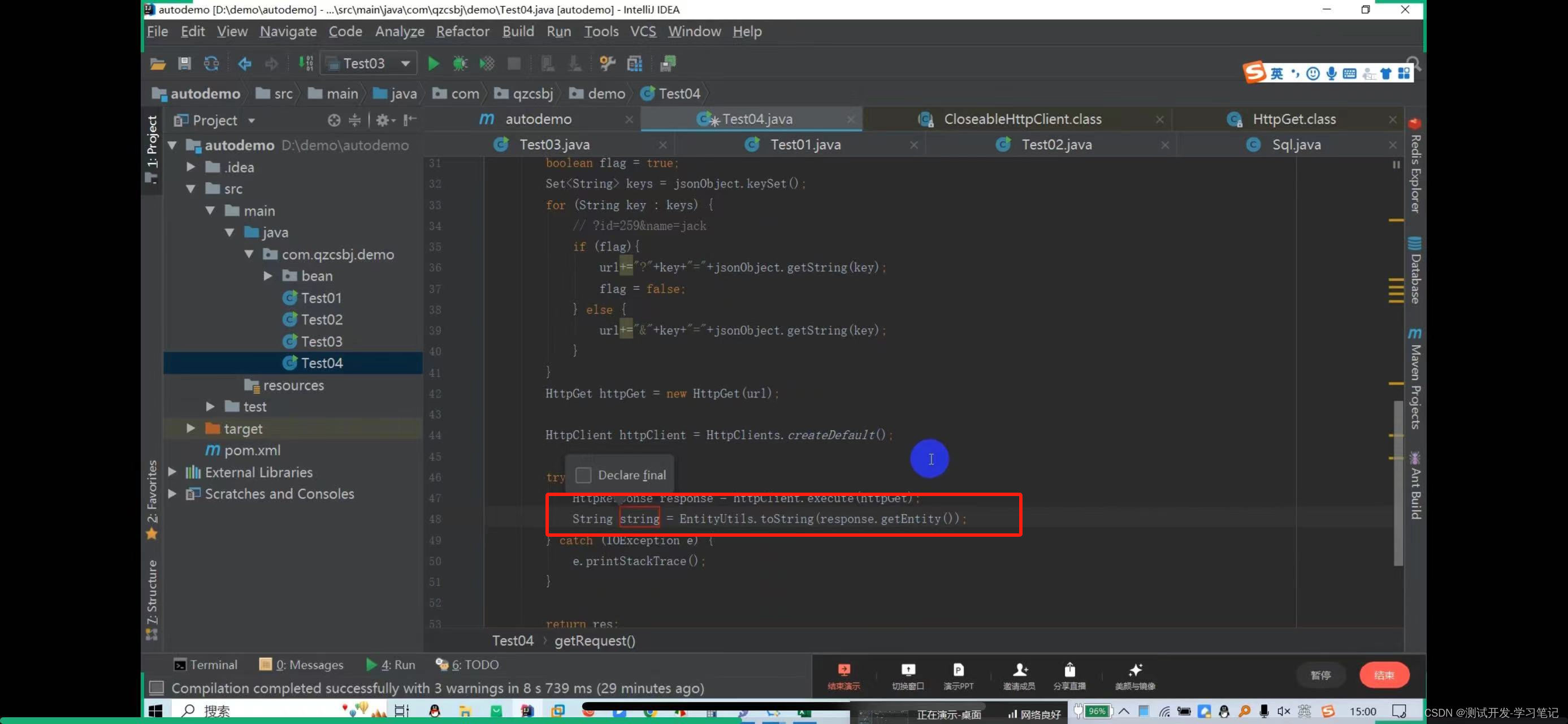
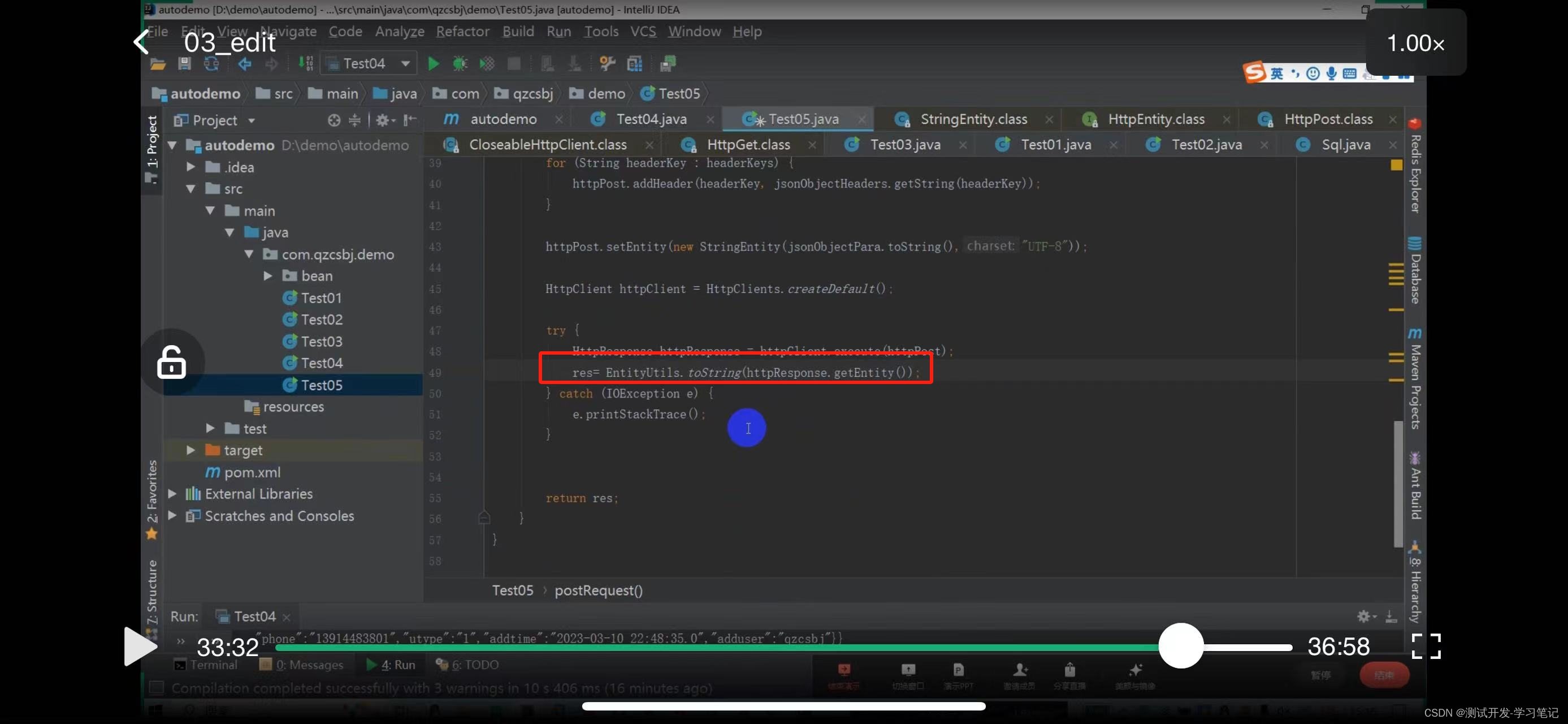
The result res is defined above
Right now
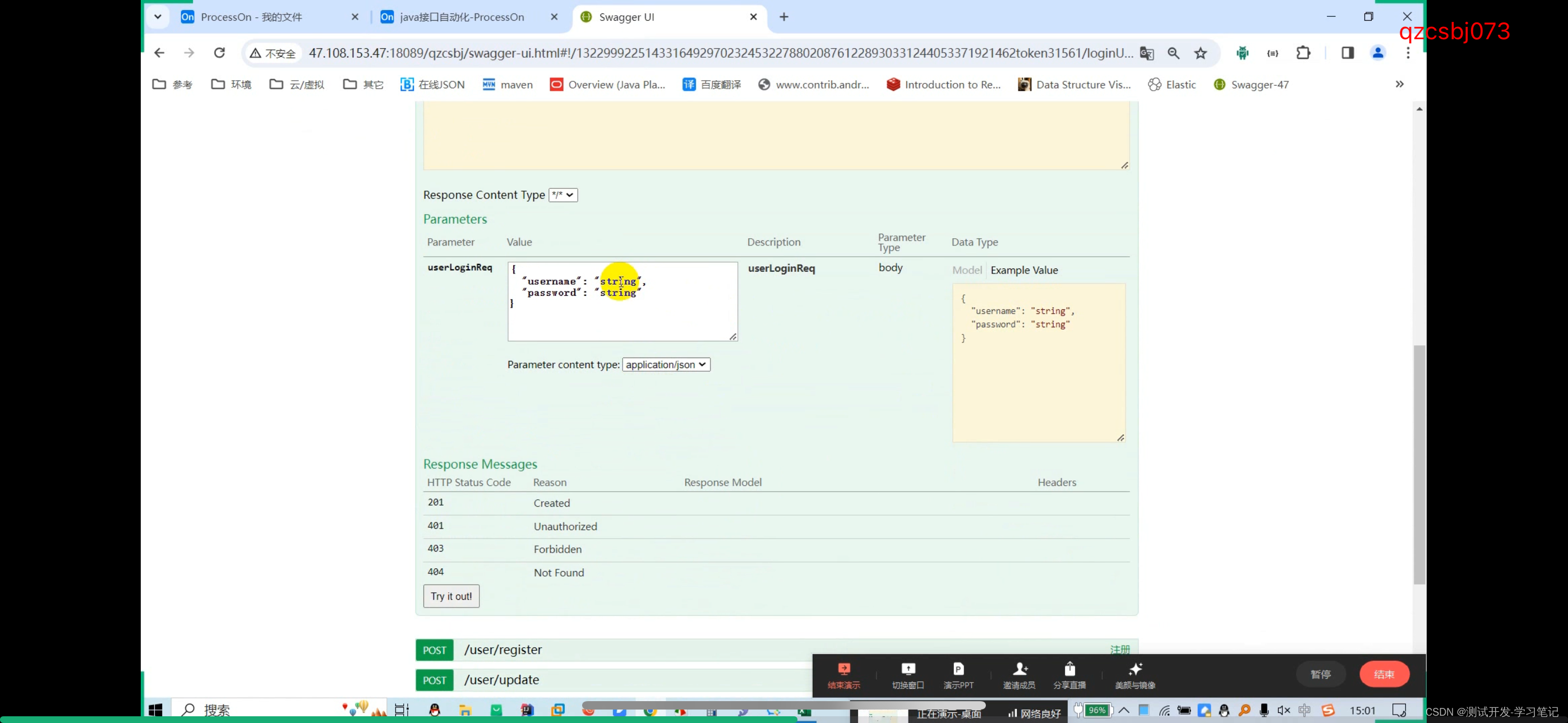
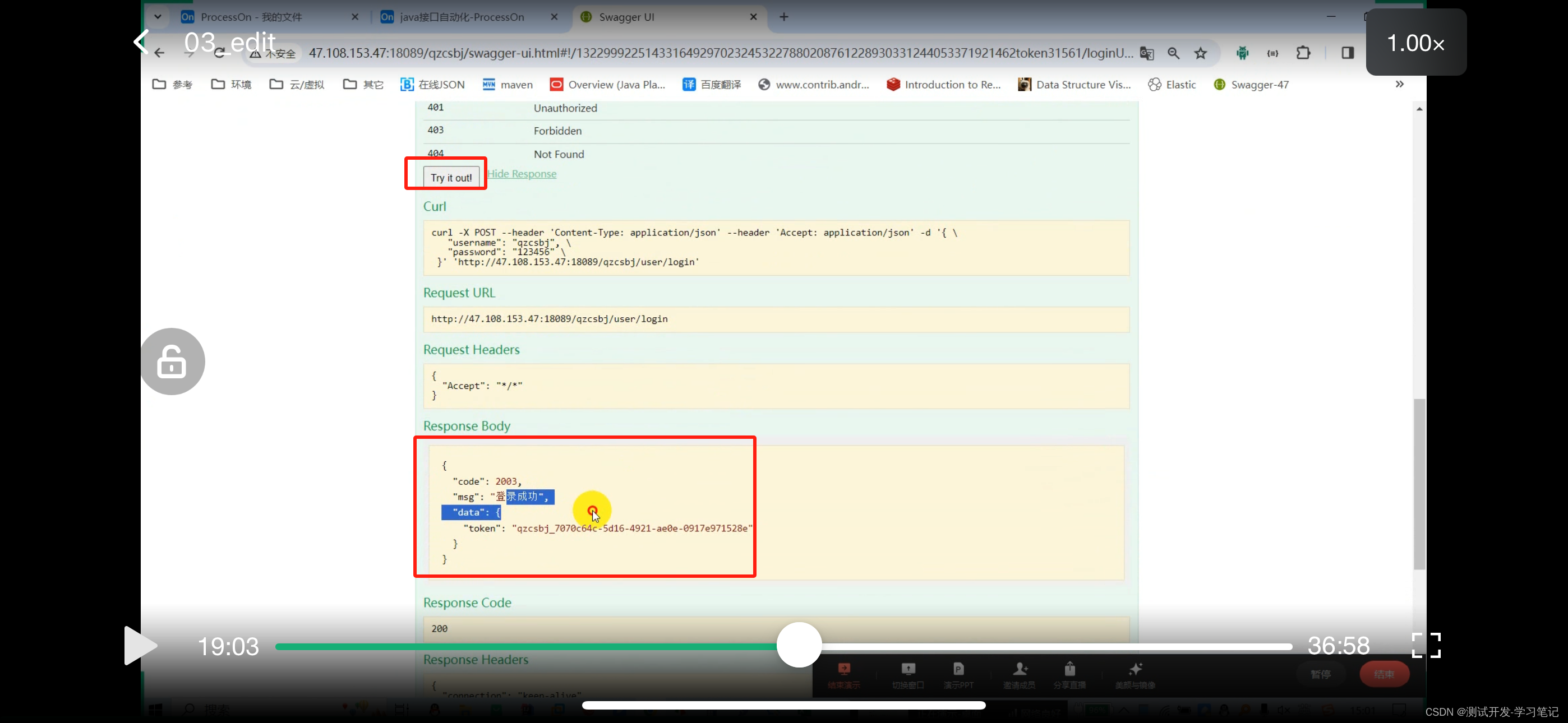
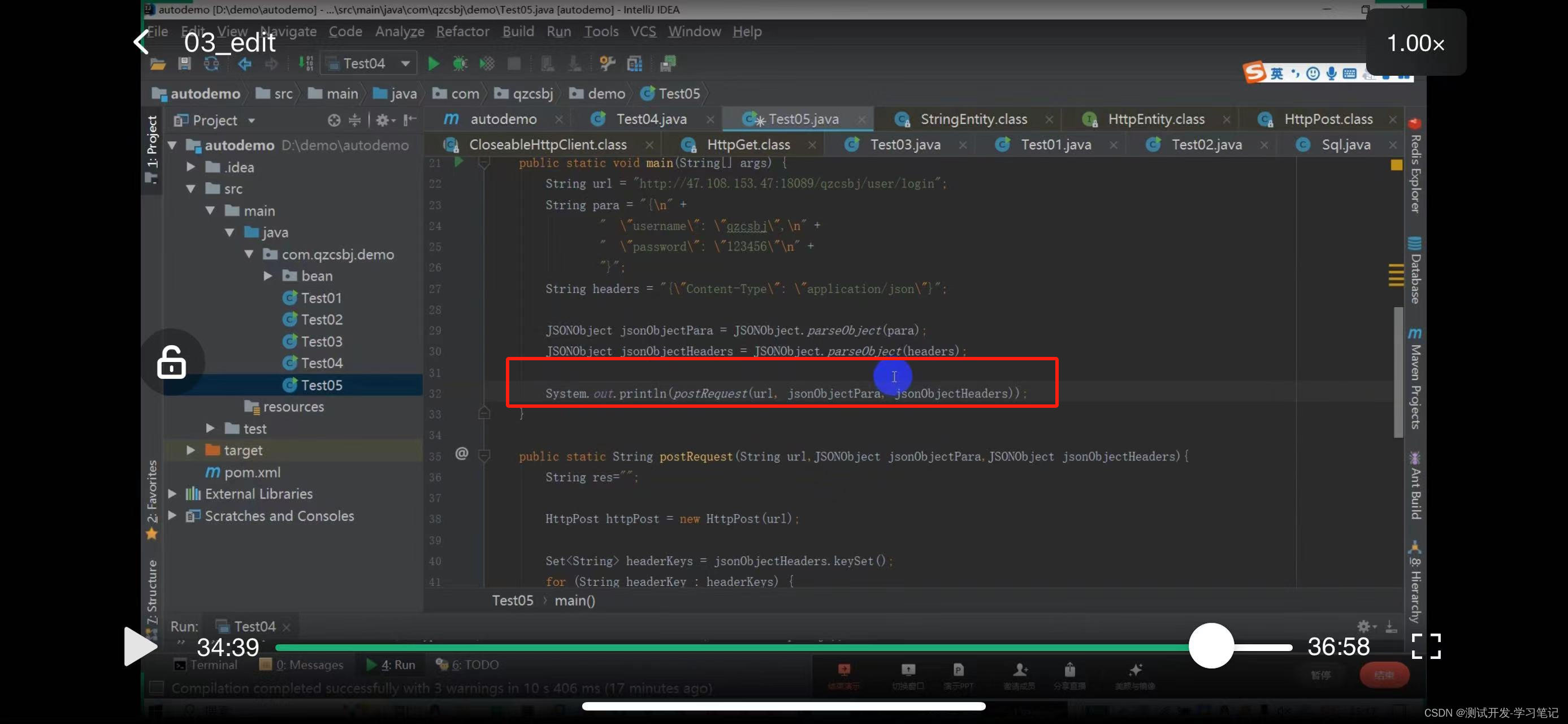
http://47.108.153.47:18089/qzcsbj/user/login
url, request parameters, request header
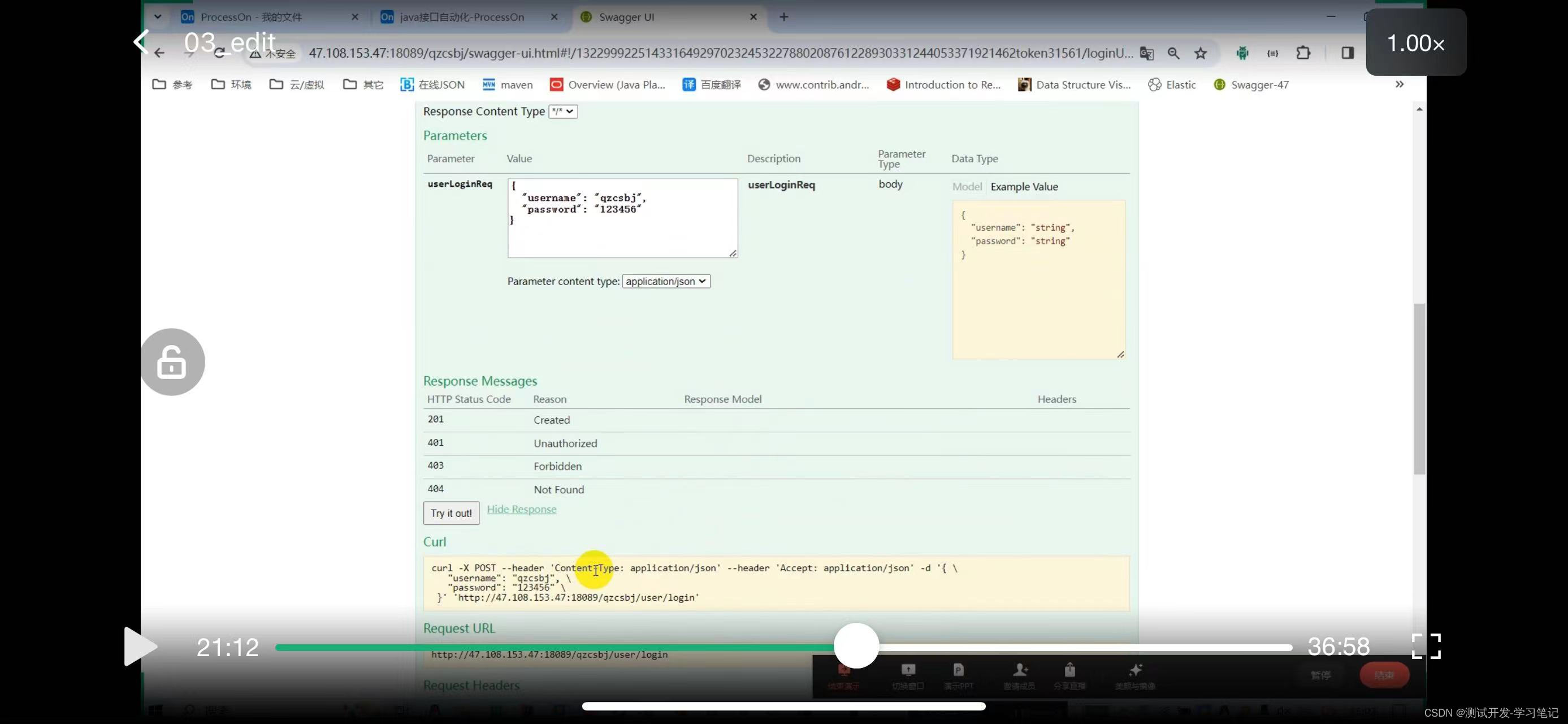
These parameters are obtained from data files in the automation framework
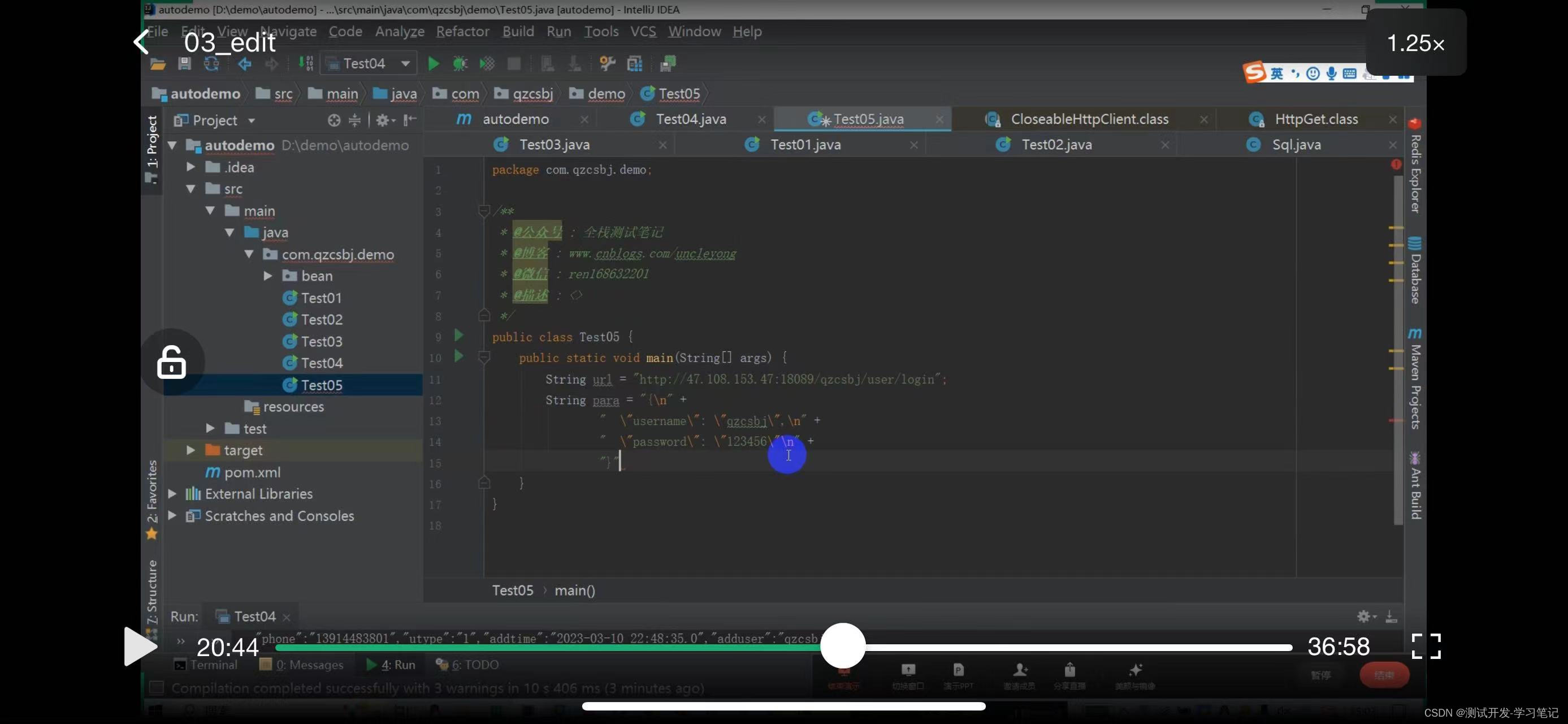
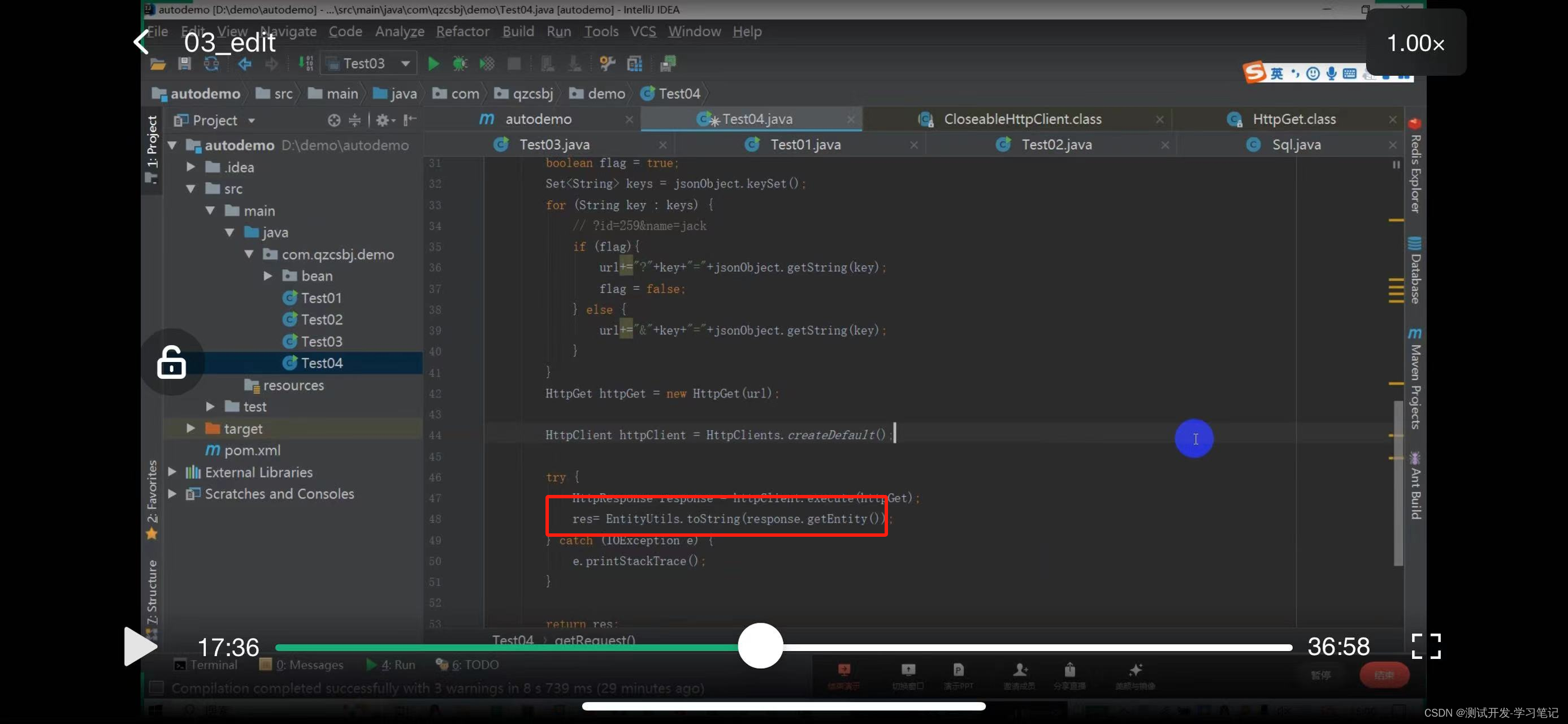
Define res
Return res
Pass URL
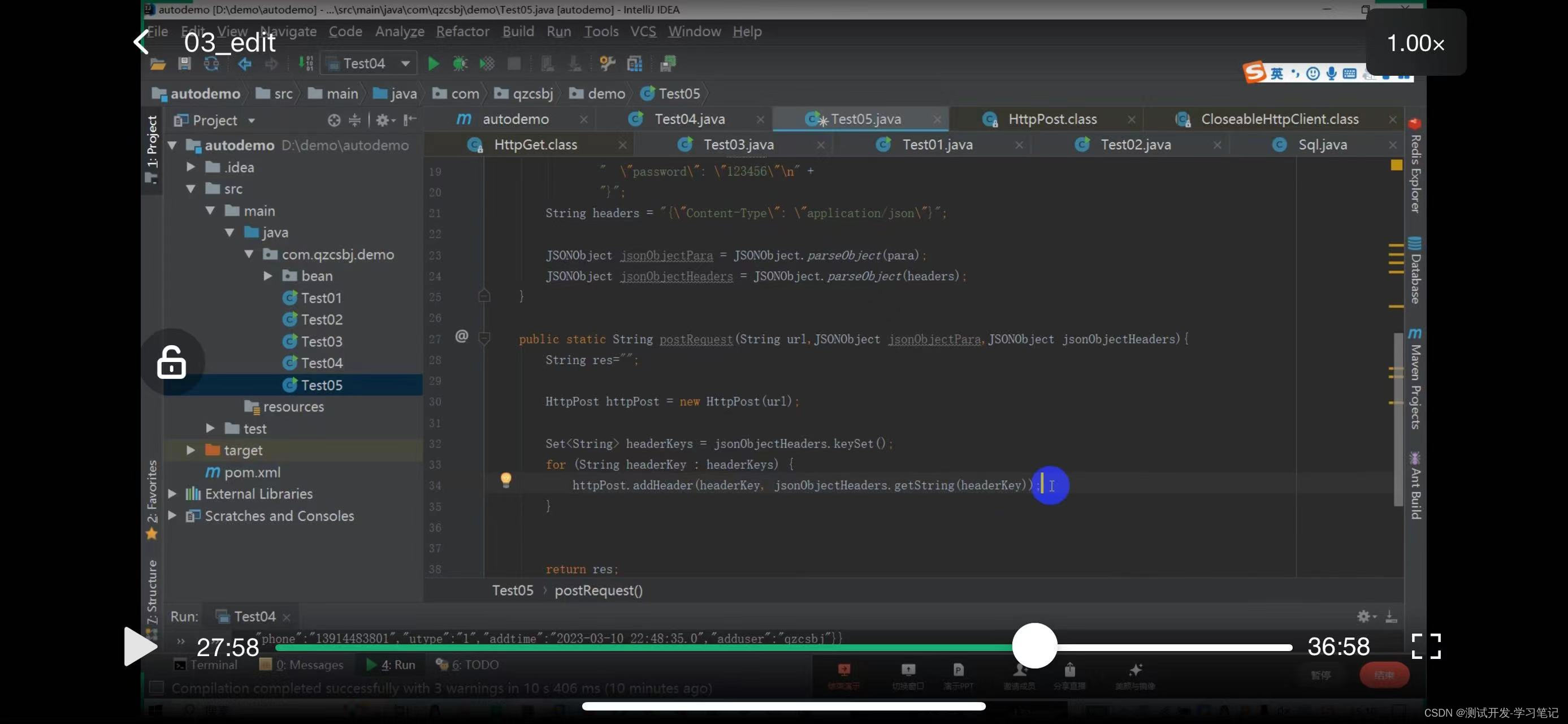
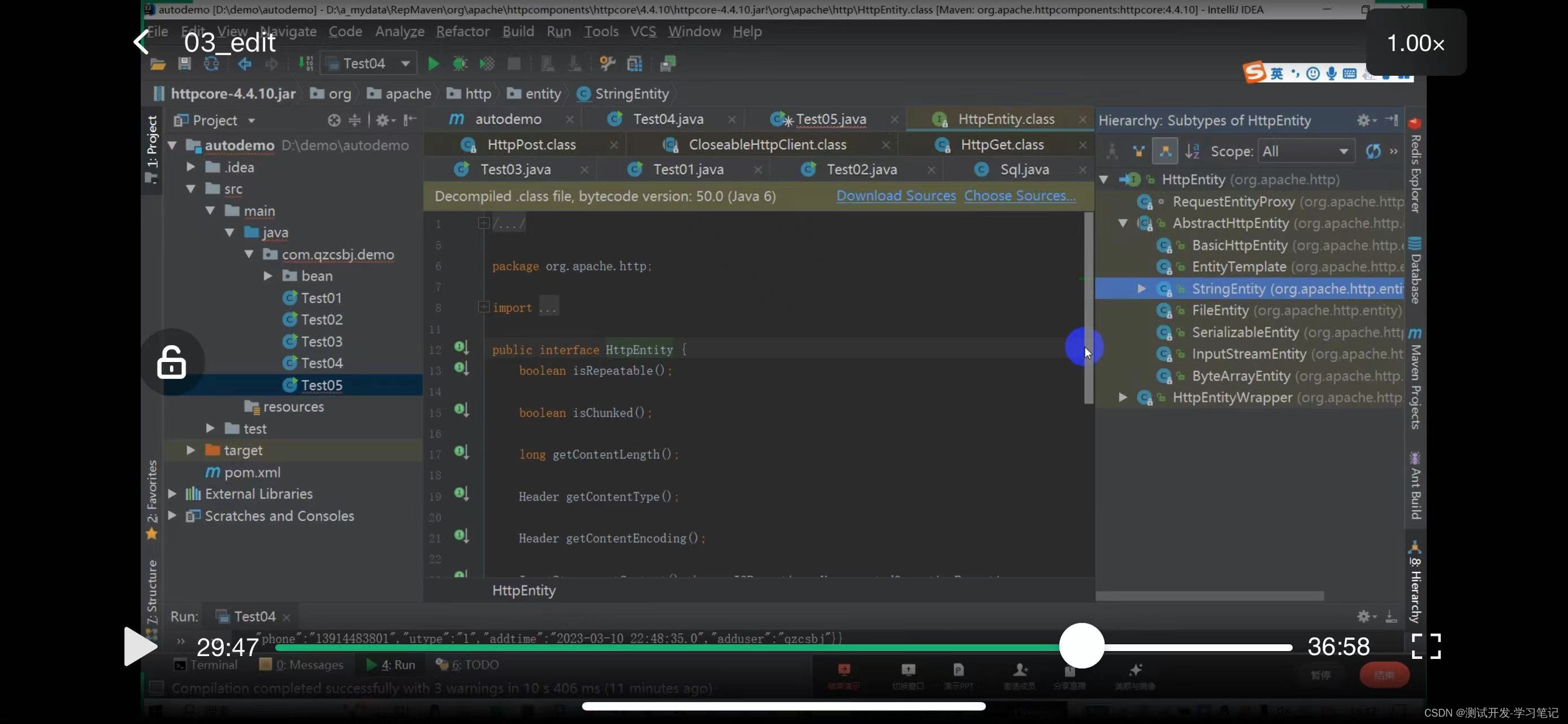
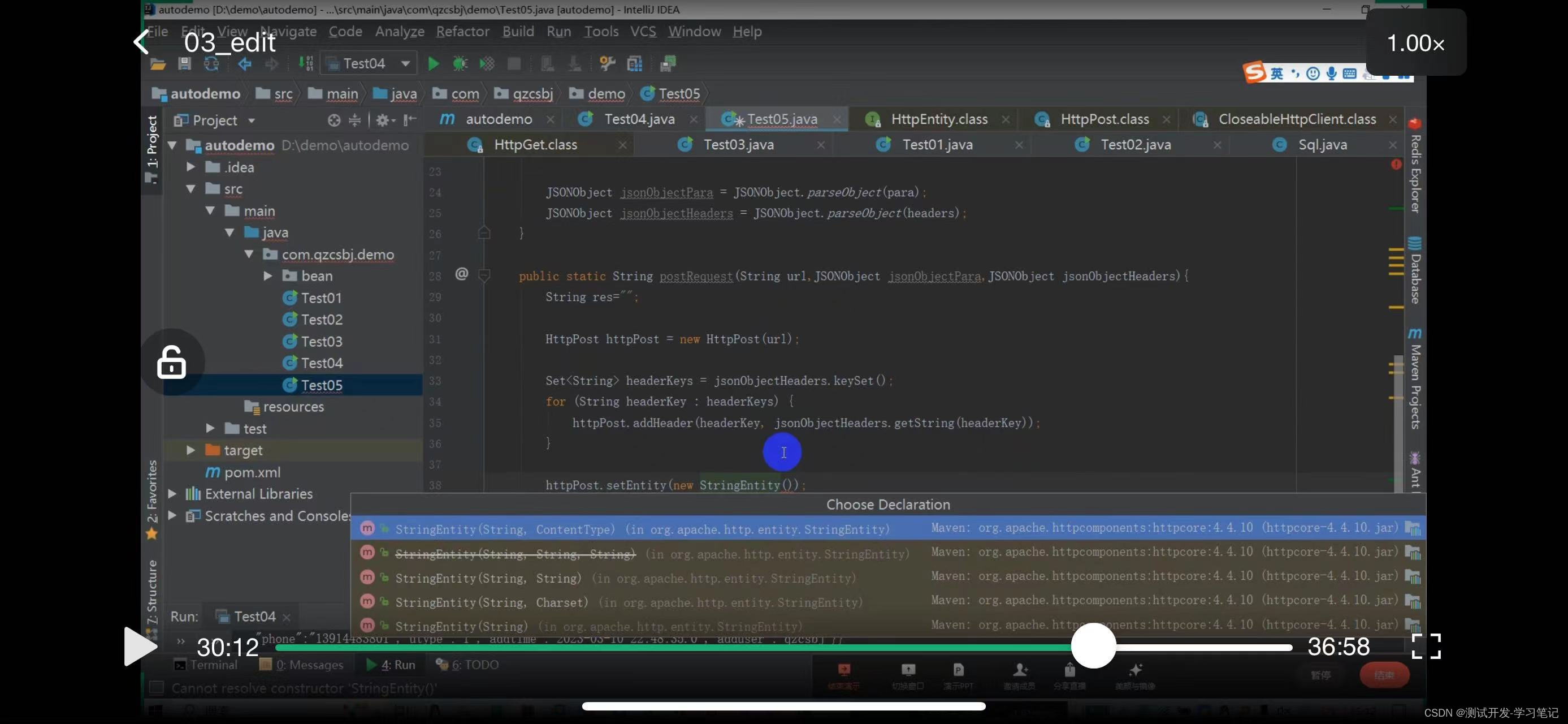
Look at the constructor method can pass String, specify the second constructor
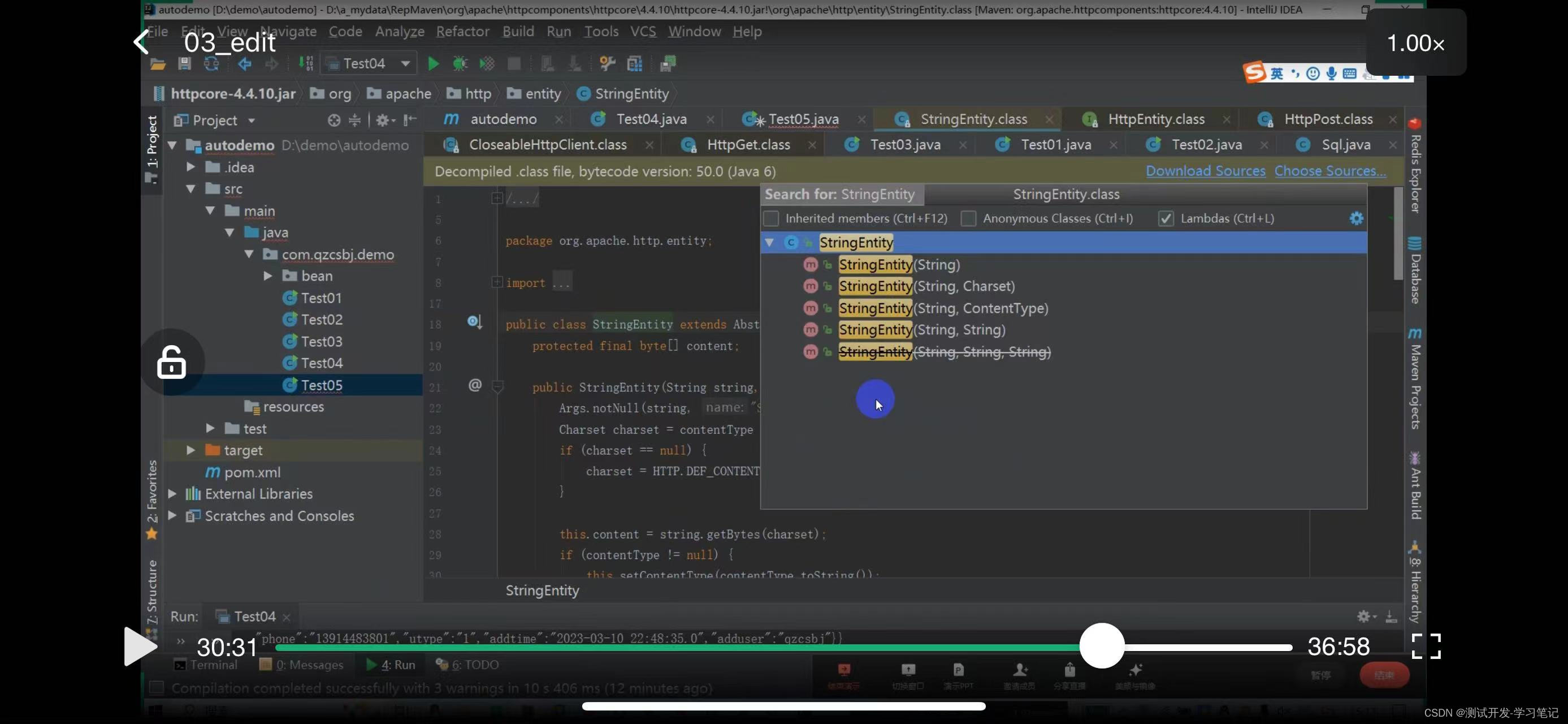
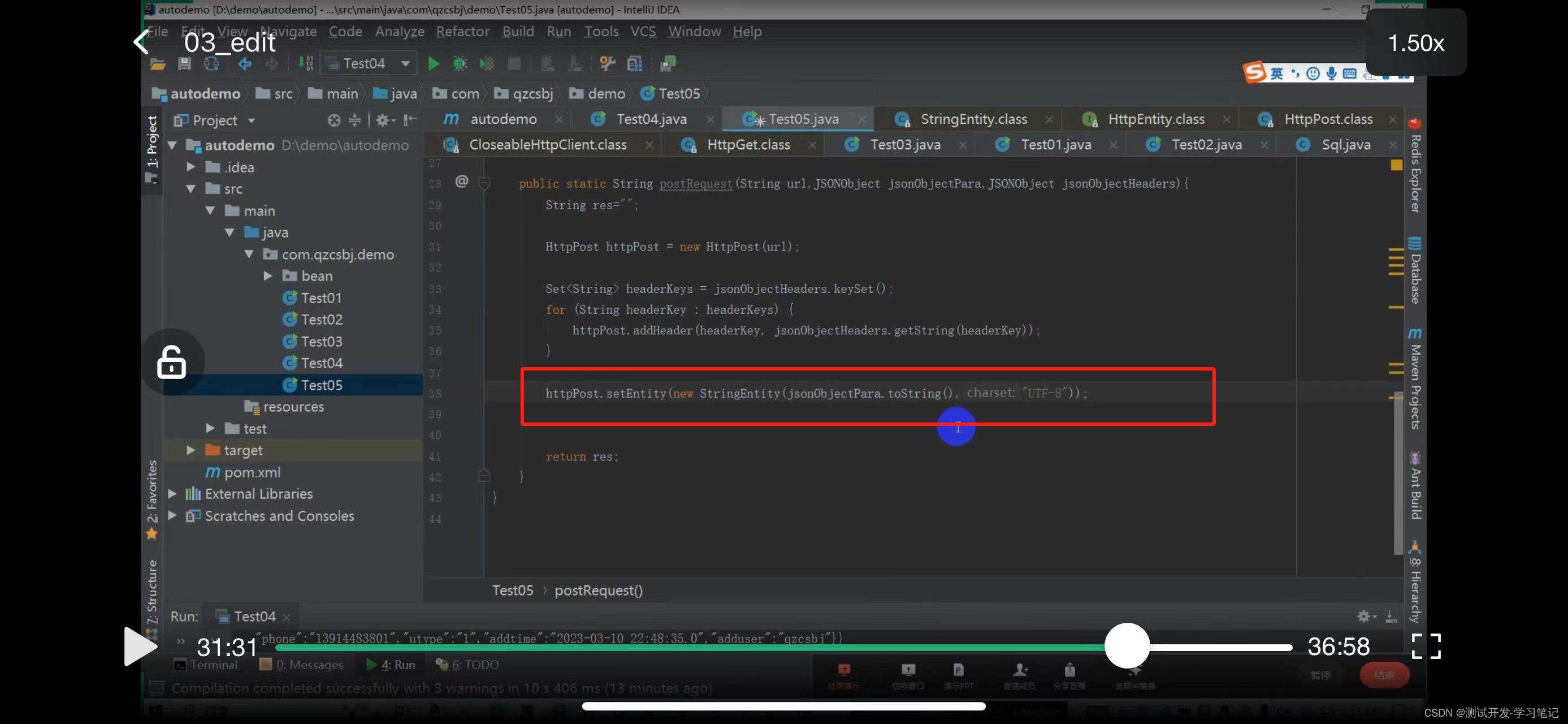
The above defines the post request: the request header and the data to be sent.
Subclass object points to parent class reference