2024-07-08
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
당신이 빅 데이터 개발 엔지니어로서 "디지털 혁신"을 겪고 있다고 주장하는 대기업에 막 합류했다고 상상해 보십시오. 입사 첫 주에는 열정이 넘치고 근육을 풀고 기술을 사용하여 회사에서 데이터 기반 의사 결정을 내리고 싶습니다.

그러나 회사의 데이터 인프라와 프로세스를 더 깊이 파고들기 시작하면 앞으로의 과제가 예상보다 훨씬 더 크다는 것을 깨닫게 됩니다.
이러한 과제에 직면한 귀하는 이 회사에서 진정한 데이터 기반 의사 결정을 달성하기 위해 아직 갈 길이 멀다는 것을 깨달았습니다. 문제를 더 잘 이해하고 해결하기 위해 이러한 문제를 체계적으로 분류하기로 결정합니다.

데이터 사일로는 정보 시스템이나 조직 단위 간에 데이터를 효과적으로 공유할 수 없는 상황입니다. 이는 개발의 중복과 자원의 낭비로 이어진다.
예:
코드 예(Python):
# 销售部门的数据库
sales_db = {
"product_a": {"sales": 1000, "revenue": 50000},
"product_b": {"sales": 800, "revenue": 40000}
}
# 库存部门的数据库
inventory_db = {
"product_a": {"stock": 500},
"product_b": {"stock": 200}
}
# 由于数据孤岛,我们无法直接获取销售和库存的综合信息
# 需要手动整合数据
def get_product_info(product):
if product in sales_db and product in inventory_db:
return {
"sales": sales_db[product]["sales"],
"revenue": sales_db[product]["revenue"],
"stock": inventory_db[product]["stock"]
}
return None
print(get_product_info("product_a"))

데이터 가치사슬의 결함은 데이터 수집부터 최종 활용까지의 과정이 중단되어 데이터의 가치를 완전히 실현하지 못하는 것을 의미합니다.
예:
코드 예(Python):
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# 假设我们有用户浏览数据
df = pd.DataFrame({
'user_id': range(1000),
'page_views': np.random.randint(1, 100, 1000),
'time_spent': np.random.randint(10, 3600, 1000),
'purchases': np.random.randint(0, 5, 1000)
})
# 尝试建立一个预测模型
X = df[['page_views', 'time_spent']]
y = df['purchases']
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 模型评分
print(f"Model Score: {model.score(X_test, y_test)}")
# 但是,如果分析团队不理解这个模型或不知道如何解释结果,
# 那么这个模型就无法为业务决策提供有价值的指导
이 문제는 통일된 표준, 데이터 거버넌스 메커니즘, 필요한 데이터, 표준화된 프로세스, 전문 조직 및 관리 시스템 등의 부족을 포함하여 데이터 관리의 여러 측면과 관련이 있습니다.

예:
코드 예(Python):
# 假设我们有来自不同国家的客户数据,格式不统一
us_customers = [
{"name": "John Doe", "phone": "1234567890"},
{"name": "Jane Smith", "phone": "0987654321"}
]
uk_customers = [
{"full_name": "David Brown", "tel": " 44 1234567890"},
{"full_name": "Emma Wilson", "tel": " 44 0987654321"}
]
# 由于缺乏统一标准,我们需要手动处理数据
def standardize_customer(customer, country):
if country == "US":
return {
"full_name": customer["name"],
"phone_number": " 1 " customer["phone"]
}
elif country == "UK":
return {
"full_name": customer["full_name"],
"phone_number": customer["tel"]
}
# 标准化数据
standardized_customers = (
[standardize_customer(c, "US") for c in us_customers]
[standardize_customer(c, "UK") for c in uk_customers]
)
print(standardized_customers)
이 문제는 데이터 접근성, 이해성 및 추적성과 관련이 있습니다.
예:
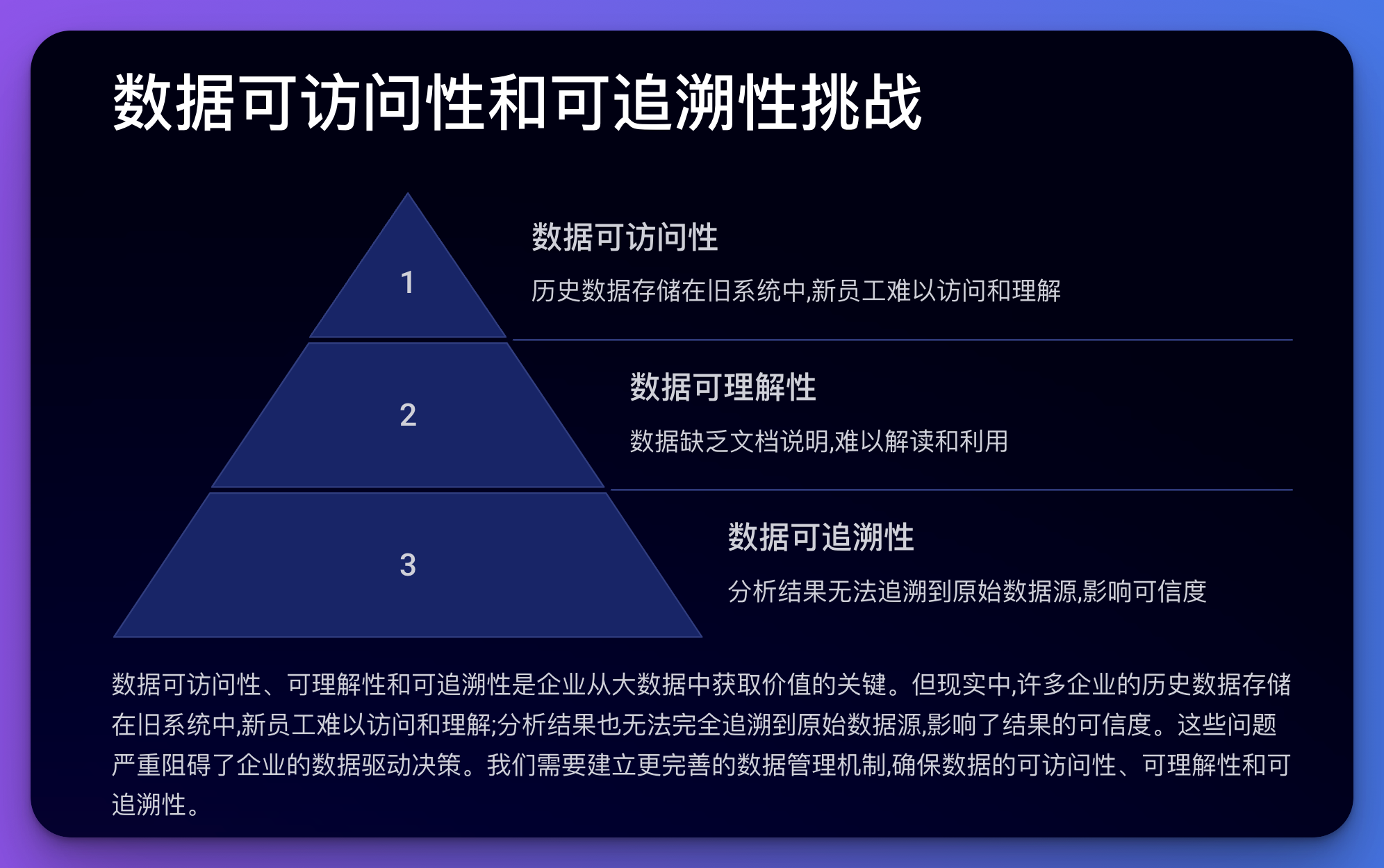
코드 예(Python):
import hashlib
import json
from datetime import datetime
class DataRecord:
def __init__(self, data, source):
self.data = data
self.source = source
self.timestamp = datetime.now().isoformat()
self.hash = self._calculate_hash()
def _calculate_hash(self):
record = json.dumps({"data": self.data, "source": self.source, "timestamp": self.timestamp})
return hashlib.sha256(record.encode()).hexdigest()
def __str__(self):
return f"Data: {self.data}, Source: {self.source}, Timestamp: {self.timestamp}, Hash: {self.hash}"
# 创建一些数据记录
record1 = DataRecord("User A purchased Product X", "Sales System")
record2 = DataRecord("Product X inventory decreased by 1", "Inventory System")
print(record1)
print(record2)
# 这种方法可以帮助追踪数据的来源和变化,但仍然需要额外的系统来管理这些记录
데이터 품질 문제에는 부정확성, 불완전성, 불일치, 중복 등이 포함됩니다.

예:
코드 예(Python):
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 创建一个包含一些"脏"数据的DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'name': ['John', 'Jane', 'John', 'Bob', 'Alice', np.nan],
'age': [30, 25, 30, -5, 200, 35],
'email': ['[email protected]', 'jane@example', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', 'invalid']
})
print("Original data:")
print(df)
# 数据清洗
def clean_data(df):
# 删除重复行
df = df.drop_duplicates()
# 处理缺失值
df['name'] = df['name'].fillna('Unknown')
# 修正异常值
df.loc[df['age']