Mi informacion de contacto
Correo[email protected]
2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
¿Alguna vez se ha encontrado con una situación en la que el servidor necesita transmitir datos activamente al cliente? Actualmente existen tres soluciones.
Comparación de varias opciones:
votación:
El cliente solicita datos del servidor a través de solicitudes frecuentes para lograr un efecto similar a las actualizaciones en tiempo real. La ventaja del sondeo es que es fácil de implementar, pero ejercerá una presión adicional sobre el servidor y la red, y el retraso será alto.
Conexión WebSocket:
El servidor establece una conexión Socket con el cliente para la transmisión de datos. El método de transmisión Socket es full-duplex. WebSocket es una conexión larga basada en TCP. En comparación con el protocolo HTTP, puede lograr una transmisión de datos liviana y de baja latencia. Es muy adecuada para escenarios de comunicación en tiempo real y se utiliza principalmente para comunicaciones bidireccionales altamente interactivas.
Empuje SSE:
SSE (Server-Sent Events) es una tecnología push basada en el protocolo HTTP que solo permite la comunicación unidireccional. En comparación con WebSocket, SSE es más simple y liviano.
Los siguientes son los pasos y el código de muestra para usar SSE con SpringBoot
Dependencias de configuración
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
SSE se ha integrado en spring-web, por lo que se puede utilizar directamente.
código de fondo
import com.wry.wry_test.service.SseService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.SseEmitter;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/sse")
@Slf4j
@Validated
public class SseTestController {
@Autowired
private SseService service;
@GetMapping("/testSse")
public SseEmitter testSse(@RequestParam("clientId") @NotBlank(message = "客户端id不能为空") String clientId) {
final SseEmitter emitter = service.getConn(clientId);
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
service.send(clientId);
log.info("建立连接成功!clientId = {}", clientId);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("推送数据异常");
}
});
return emitter;
}
@GetMapping("/sseConection")
public SseEmitter createConnection(@RequestParam("clientId") @NotBlank(message = "客户端id不能为空") String clientId) {
return service.getConn(clientId);
}
@GetMapping("/sendMsg")
public void sendMsg(@RequestParam("clientId") String clientId) {
try {
// 异步发送消息
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
service.send(clientId);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("推送数据异常");
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@GetMapping("/sendMsgToAll")
public void sendMsgToAll() {
try {
//异步发送消息
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
service.sendToAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@GetMapping("closeConn/{clientId}")
public String closeConn(@PathVariable("clientId") @NotBlank(message = "客户端id不能为空") String clientId) {
service.closeConn(clientId);
return "连接已关闭";
}
}
package com.wry.wry_test.service;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.SseEmitter;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
public interface SseService {
/**
* 获取连接
* @param clientId 客户端id
* @return
*/
SseEmitter getConn(String clientId);
/**
* 发送消息到指定客户端
* @param clientId 客户端id
* @throws Exception
*/
void send(String clientId);
/**
* 发送消息到所有SSE客户端
* @throws Exception
*/
void sendToAll() throws Exception;
/**
* 关闭指定客户端的连接
* @param clientId 客户端id
*/
void closeConn(String clientId);
}
package com.wry.wry_test.service.impl;
import com.wry.wry_test.service.SseService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.SseEmitter;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
@Service
@Slf4j
public class SseServiceImpl implements SseService {
private static final Map<String, SseEmitter> SSE_CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public SseEmitter getConn(@NotBlank String clientId) {
final SseEmitter sseEmitter = SSE_CACHE.get(clientId);
if (sseEmitter != null) {
return sseEmitter;
} else {
// 设置连接超时时间,需要配合配置项 spring.mvc.async.request-timeout: 600000 一起使用
final SseEmitter emitter = new SseEmitter(600_000L);
// 注册超时回调,超时后触发
emitter.onTimeout(() -> {
log.info("连接已超时,正准备关闭,clientId = {}", clientId);
SSE_CACHE.remove(clientId);
});
// 注册完成回调,调用 emitter.complete() 触发
emitter.onCompletion(() -> {
log.info("连接已关闭,正准备释放,clientId = {}", clientId);
SSE_CACHE.remove(clientId);
log.info("连接已释放,clientId = {}", clientId);
});
// 注册异常回调,调用 emitter.completeWithError() 触发
emitter.onError(throwable -> {
log.error("连接已异常,正准备关闭,clientId = {}", clientId, throwable);
SSE_CACHE.remove(clientId);
});
SSE_CACHE.put(clientId, emitter);
log.info("建立连接成功!clientId = {}", clientId);
return emitter;
}
}
/**
* 模拟类似于 chatGPT 的流式推送回答
*
* @param clientId 客户端 id
* @throws IOException 异常
*/
@Override
public void send(@NotBlank String clientId) {
final SseEmitter emitter = SSE_CACHE.get(clientId);
if (emitter == null) return;
// 开始推送数据
// todo 模拟推送数据
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
String msg = "SSE 测试数据";
try {
this.sseSend(emitter, msg, clientId);
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("推送数据异常", e);
break;
}
}
log.info("推送数据结束,clientId = {}", clientId);
// 结束推流
emitter.complete();
}
/**
* 发送数据给所有连接
*/
public void sendToAll() {
List<SseEmitter> emitters = new ArrayList<>(SSE_CACHE.values());
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
String msg = "SSE 测试数据";
this.sseSend(emitters, msg);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void closeConn(@NotBlank String clientId) {
final SseEmitter sseEmitter = SSE_CACHE.get(clientId);
if (sseEmitter != null) {
sseEmitter.complete();
}
}
/**
* 推送数据封装
*
* @param emitter sse长连接
* @param data 发送数据
* @param clientId 客户端id
*/
private void sseSend(SseEmitter emitter, Object data, String clientId) {
try {
emitter.send(data);
log.info("推送数据成功,clientId = {}", clientId);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("推送数据异常", e);
throw new RuntimeException("推送数据异常");
}
}
/**
* 推送数据封装
*
* @param emitter sse长连接
* @param data 发送数据
*/
private void sseSend(List<SseEmitter> emitter, Object data) {
emitter.forEach(e -> {
try {
e.send(data);
} catch (IOException ioException) {
log.error("推送数据异常", ioException);
}
});
log.info("推送数据成功");
}
}
El efecto de implementación es el siguiente: el servidor envía datos continuamente al front-end, y el front-end también puede llamar a la interfaz para cerrar activamente la conexión.
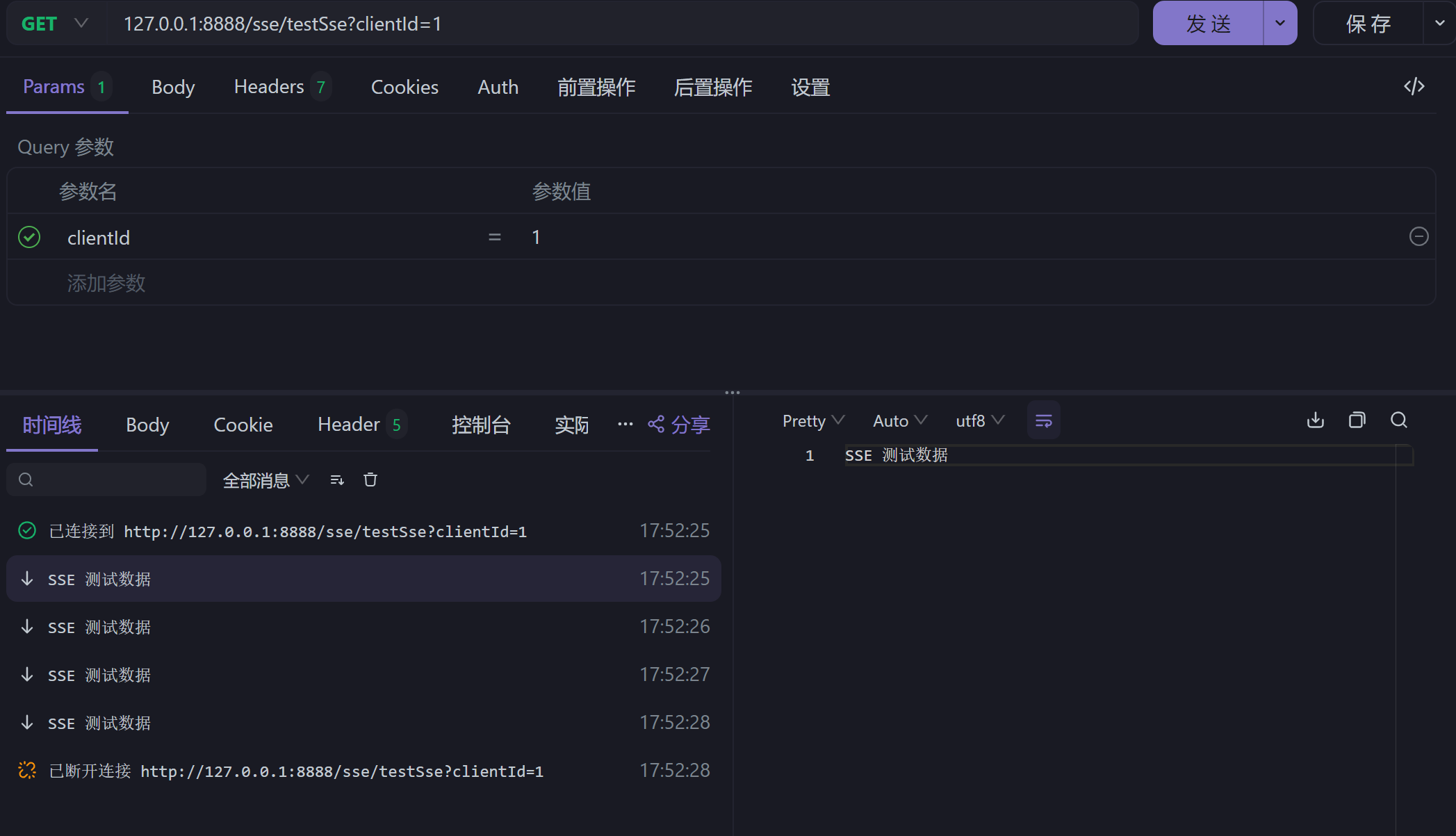
Escenarios aplicables: dado que SSE es una comunicación unidireccional entre el servidor y el servidor, es adecuada para conexiones que requieren persistencia unidireccional. Por ejemplo: