2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
Focus algorithms can be divided into ranging, phase, and contrast.
Among them, the distance measurement type uses lasers, (TOF, Time of Flight) and other active methods to know the object distance and then focus. The latter two are more commonly used.

As shown in the above picture, the contrast type lens can be seen to push and pull back and forth like a bellows, and the best contrast is obtained through traversal. This focusing method is relatively accurate, but it takes a long time.
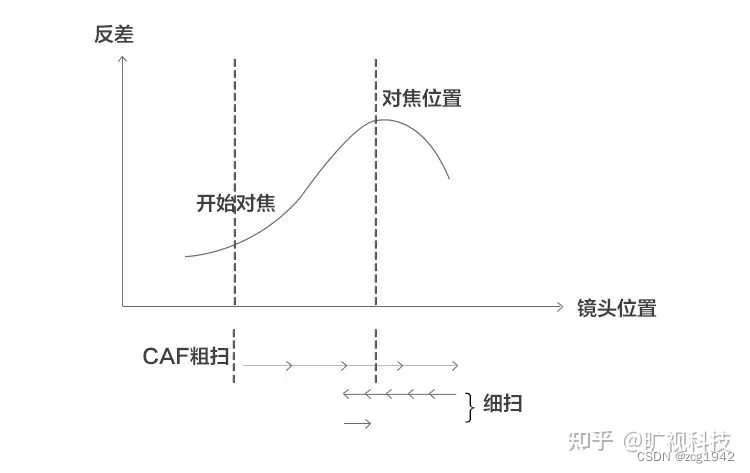
CDAF specifically uses a hill climbing algorithm. The hill climbing algorithm consists of two processes, the first stage is called coarse search, and the second stage is called fine search. When the algorithm controls the motor to move the lens in one direction, the image contrast will gradually increase and then decrease, similar to climbing a mountain.
Let’s first understand the binocular effect and thumb distance measurement.
Because the two eyes are in different positions, their best focus points are different, and they each need light at a specific angle to form the clearest image. So when measuring distance with your thumb, use your two eyes to point at your thumbs, and you can get two different points in the target object along the extension line of this direction. The length of these two points/interpupillary distance = target distance/arm length.

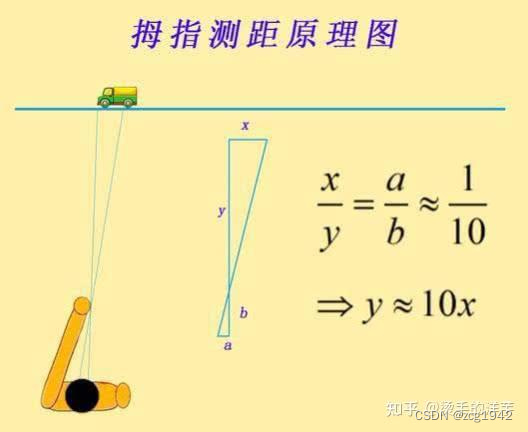
Since the thumb distance measurement can measure the distance, the same principle applies to PDAF. PDAF measures the clarity of the ROI area based on the phase difference of the pixel pair (PD Pixel Pair).
So what is phase difference? How does PDAF use phase difference?
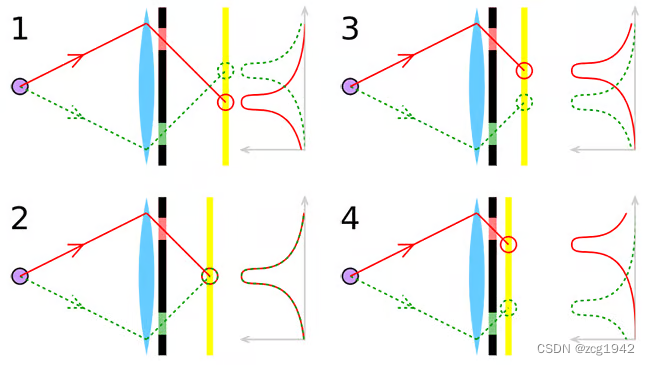
Although only one line of light is drawn in the above figure (symmetrical), in reality, the light is not a single line, so the response on the sensor is a distribution with this line as the peak. If the focus is not good, there will be two peaks. The worse the focus of sub-image 4 is than that of sub-image 3, the farther the distance between the two peaks will be. When the focus is perfect, the two peaks overlap.
Because of symmetry, the shapes of the two waves are the same, but there is a relative offset, which is the phase difference. The phase difference can be positive or negative, and the clarity is highest when the phase is 0.
Because it is calibrated at the factory, the motor only needs to know the phase difference to know which direction to push the lens and how far to push it, which is why PD focusing is faster. PDAF focusing speed is more than twice as fast as CAF and is now the mainstream on mobile phones.
How Phase Detection Autofocus Works
Based on the idea of differentiation, waves can be represented by two different points. How to construct these two points has led to the emergence of various PD sensors. According to the number of PD points, they can be divided into sparse and global. We will take all-pixel as an example.
Dual PD further subdivides each pixel. Dual means "double", because it also belongs to shield PD, but compared with the earlier L and R, which are far apart, the left and right PDs of dual PD are under the same microlens:

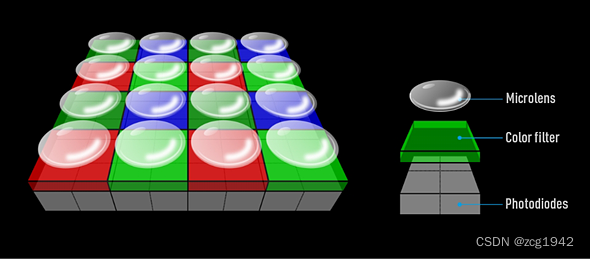
There are two diodes under each color filter:

During the focusing stage, the two photodiodes form images separately. After the focusing is completed and the actual imaging stage comes, the two photodiodes are merged together, so there will be no interference from the phase difference.
When dual PD technology is combined with quad bayer, it is Octa PD:
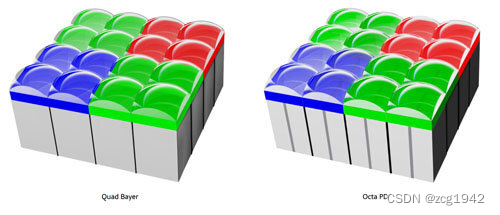
OCL is the abbreviation of "On-Chip Lens", which refers to the microlens on the photosensitive element shared by several adjacent pixels. There are 2x1 OCL and 2x2 OCL.
2x2OCL refers to the combination of OCL technology and Quad Bayer. The four quadrants of the same color channel share one lens:
When the lighting conditions are good, high-resolution images can be obtained by remoisc, and better image quality can be obtained through binning when the lighting conditions are poor.

Both use full-pixel PD focusing. The only difference is the source of the phase difference. Octa PD is a more traditional dual PD, while 2x2OCL is the difference in four quadrants brought by a shared lens.
The former benefits from having two diodes when actually imaging, so they can be merged to eliminate the phase difference, so that the four values of the same color channel of quad raw are more uniform. However, the phase difference of 2x2OCL cannot be eliminated, and the four quadrants of the same color channel will change regularly with the image gradient during imaging, which is not conducive to subsequent image processing.
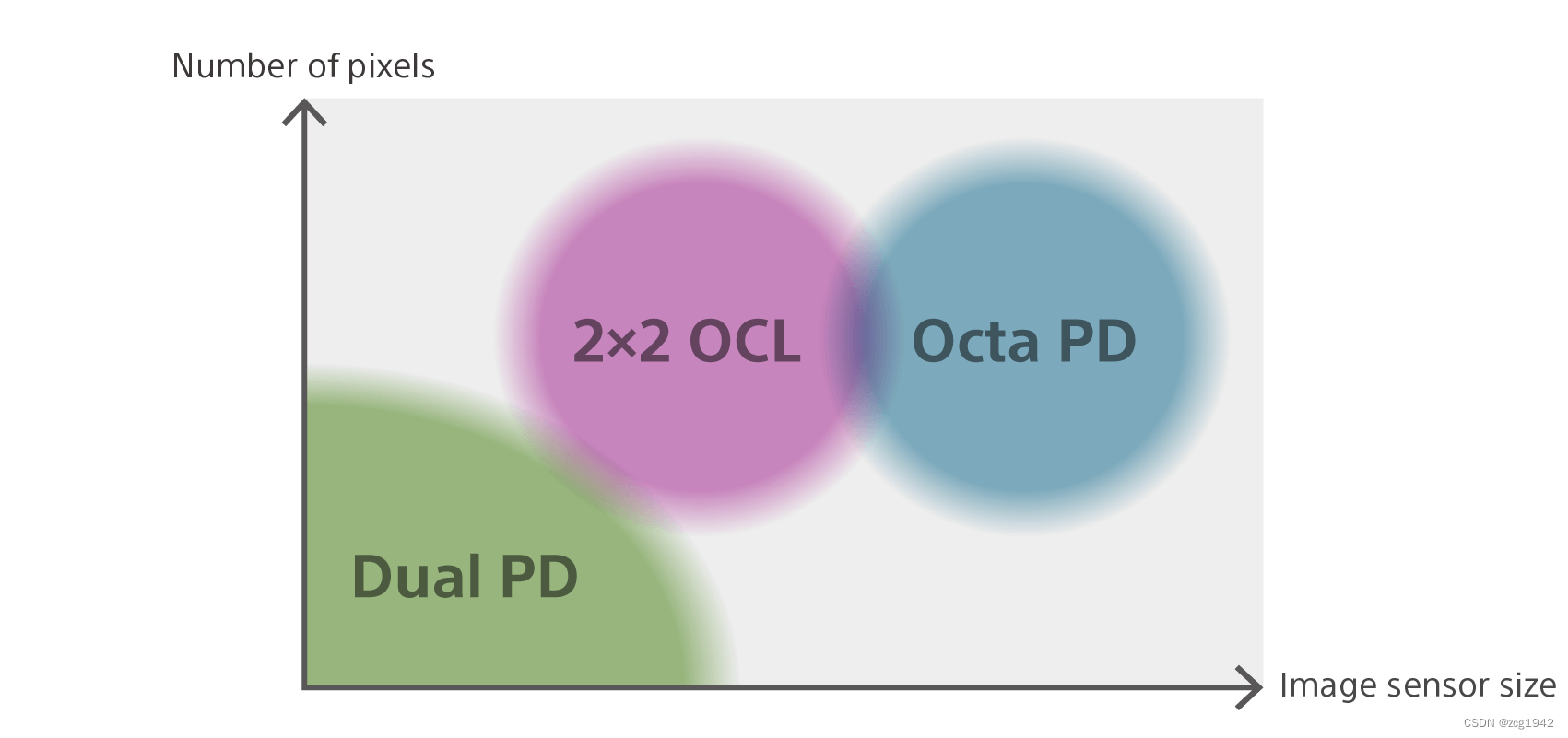
Octa PD integrates two diodes and has more micro lenses, so this technology is generally used when the sensor is large; OCL is used on medium-sized sensors. As shown in the following figure:
In practice, PD focus is usually used first to quickly push the lens to a roughly accurate position, and then contrast focus is performed to allow the image to truly reach an ideal state with high contrast.
reference:
All-pixel Auto Focus (AF) Technology | Image Sensor for Mobile | Technology | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Grouphttps://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=8993499All-pixel Auto Focus (AF) Technology | Image Sensor for Mobile | Technology | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Group