2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
Preface: This article provides detailed answers to some of the doubts about the early learning of the quick sort algorithm, and gives an optimized version of the basic quick sort algorithm
The core of the quick sort algorithm is分治思想,The divide and conquer strategy is divided into the following three steps:
Applied to the quick sort algorithm:
The key code of quick sort is如何根据基准元素划分数组区间(parttion)There are many ways to decompose, here we only provide one method挖坑法
Code:
class Solution {
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
quick(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
return nums;
}
private void quick(int[] arr, int start, int end) {
if(start >= end) return;// 递归结束条件
int pivot = parttion(arr, start, end);
// 递归解决子问题
quick(arr, start, pivot - 1);
quick(arr, pivot + 1, end);
}
// 挖坑法进行分解
private int parttion(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
int key = arr[left];
while(left < right) {
while(left < right && arr[right] >= key) right--;
arr[left] = arr[right];
while(left < right && arr[left] <= key) ++left;
arr[right] = arr[left];
}
arr[left] = key;
return left;
}
}
Detailed answer:
1. Whystart>=endIs the recursion end condition?
Continue to decompose sub-problems. The size of the final sub-problem is 1, that is, there is only one element. At this time, there is no need to continue decomposing. The start and end pointers point to this element at the same time.
2. Why should right go first? Instead of left?
Who goes first depends on
基准元素的位置In the above code, the key is the leftmost element. If you moveleft, left first encounters an element larger than the base element, and then executesarr[right] = arr[left], because there is no savearr[right], this element will be lost
If you go right first, right will first encounter an element smaller than the base element. At this time, executearr[left]=arr[right], because left has not moved at this time, it is still pivot, but the pivot has been saved by us using key
3. Why is arr[right]>=key?> not working?
Greater than or equal to is mainly for processing
重复元素问题
For example, there is an array[6,6,6,6,6]If it is >, the right pointer will not move, and the left pointer will not move, and the loop will end in an infinite loop.
4. Why is it called the pit digging method?
When the r pointer encounters the first
arr[r] = arr[l], at this time, the l position is blank, forming a pit
There are two main optimization directions:
O(N*logN), that is, the best time complexity数组分三块At the same time, if we encounter special test cases (sequential array or reverse array), the time complexity will degenerate toO(N^2)First, according to a question (sort by color) Understand what is数组分三块
analyze
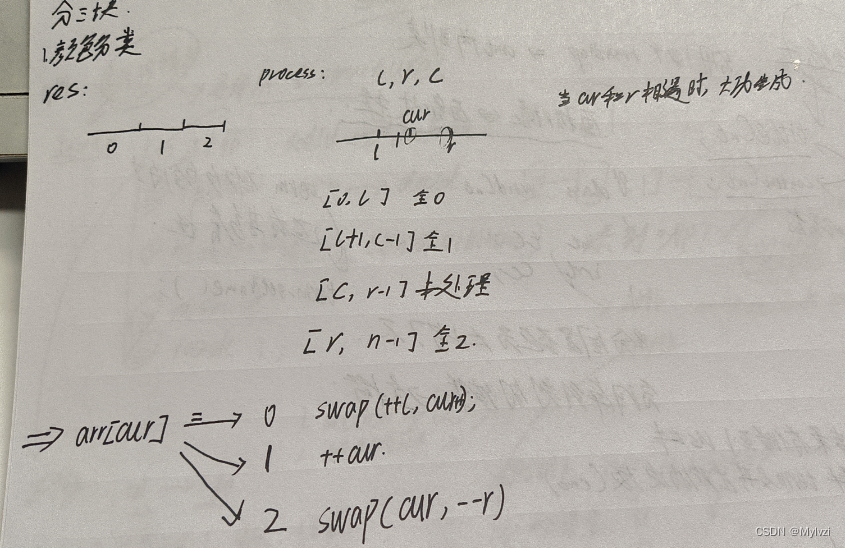
Code:
class Solution {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
// 分治 --
// 1.定义三指针
int i = 0;// 遍历整个数组
int l = -1, r = nums.length;
while(i < r) {
if(nums[i] == 0) swap(nums,++l,i++);
else if(nums[i] == 1) i++;
else swap(nums,--r,i);
}
return;
}
private void swap(int[] nums,int x,int y) {
int tmp = nums[x]; nums[x] = nums[y]; nums[y] = tmp;
}
}
l,r的起始位置, the first and last elements belong to未处理状态, so `l,r cannot point to these two elements and must be outside the interval三个指针去分别维护四个区间, one of the intervals is未处理区间, as the cur pointer continues to move, all intervals are processed, and finally there are only three intervalsApply the above ideas to快速排序的parttion中, the final result is divided into three intervals
Code:
class Solution {
// 快速排序优化版
// 分解--解决--合并
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
qsort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
return nums;
}
private void qsort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
if(start >= end) return;// 递归结束条件
// 分解
int pivot = nums[start];
int l = start - 1, r = end + 1, i = start;
while(i < r) {
int cur = nums[i];
if(cur < pivot) swap(nums, ++l, i++);
else if(cur == pivot) ++i;
else swap(nums, --r, i);
}
// [start, l] [l+1, r-1] [r, end]
// 递归解决
qsort(nums, start, l);
qsort(nums, r, end);
}
private void swap(int[] nums,int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = tmp;
}
}
2. Randomly select benchmark values
Randomly select the benchmark value using random numbers
int pivot = nums[start + new Random().nextInt(end - start + 1)];
// 起始位置 随机产生的偏移量
The complete improved code:
class Solution {
// 快速排序优化版
// 分解--解决--合并
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
qsort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
return nums;
}
private void qsort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
if(start >= end) return;// 递归结束条件
// 分解
int pivot = nums[start + new Random().nextInt(end - start + 1)];
int l = start - 1, r = end + 1, i = start;
while(i < r) {
int cur = nums[i];
if(cur < pivot) swap(nums, ++l, i++);
else if(cur == pivot) ++i;
else swap(nums, --r, i);
}
// [start, l] [l+1, r-1] [r, end]
// 递归解决
qsort(nums, start, l);
qsort(nums, r, end);
}
private void swap(int[] nums,int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}
The quick selection algorithm is基于快速排序优化版本A time complexity ofO(N)The selection algorithm is used in the following scenarios:第K大/前K大Selection issues such as
01. The Kth largest element in an array
Link: https://leetcode.cn/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/
analyze
sortSort and return the Kth largest one.O(N*logN)O(logN)Recursive call stackNext, we use the fast selection algorithm to implementO(N)The time complexity of
Code:
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
return qsort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, k);
}
private int qsort(int[] nums, int start, int end, int k) {
if(start >= end) return nums[start];
int pivot = nums[start + new Random().nextInt(end - start + 1)];
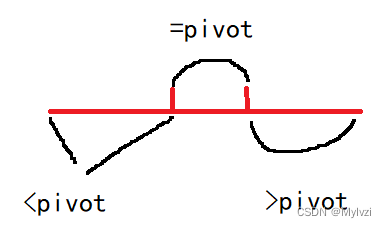
// 数组分三块 <pivot ==pivot >pivot
int l = start - 1, r = end + 1, i = start;
while(i < r) {
if(nums[i] < pivot) swap(nums, ++l, i++);
else if(nums[i] == pivot) ++i;
else swap(nums, --r, i);
}
// [start, l] [l+1, r - 1] [r, end]
int c = end - r + 1, b = r - 1 - (l + 1) + 1, a = l - start + 1;
// 分情况讨论 进行选择
if(c >= k) return qsort(nums, r, end, k);
else if(b + c >= k) return pivot;
else return qsort(nums, start, l, k - b - c);// 找较小区间的第(k-b-c)大
}
private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = tmp;
}
}
O(N)