le mie informazioni di contatto
Posta[email protected]
2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
Quando si inseriscono o si eliminano elementi in qualsiasi posizione in ArrayList, è necessario spostare tutti gli elementi successivi avanti o indietro. La complessità temporale è O(n) e l'efficienza è relativamente bassa Pertanto, ArrayList non è adatto per l'inserimento e l'eliminazione posizione. Pertanto: LinkedList, la struttura dell'elenco collegato, viene introdotta nelle raccolte Java.
2.1 Concetto e struttura di lista concatenata
Un elenco collegato è una struttura di archiviazione fisicamente non continua e l'ordine logico degli elementi di dati viene ottenuto tramite l'ordine dei collegamenti di riferimento nell'elenco collegato.
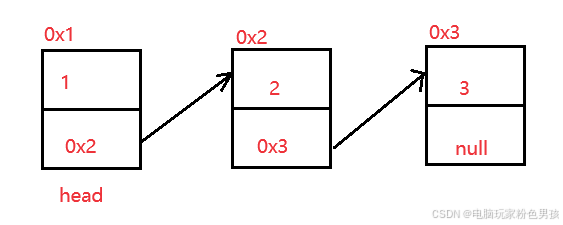
2.2 Implementazione dell'elenco collegato
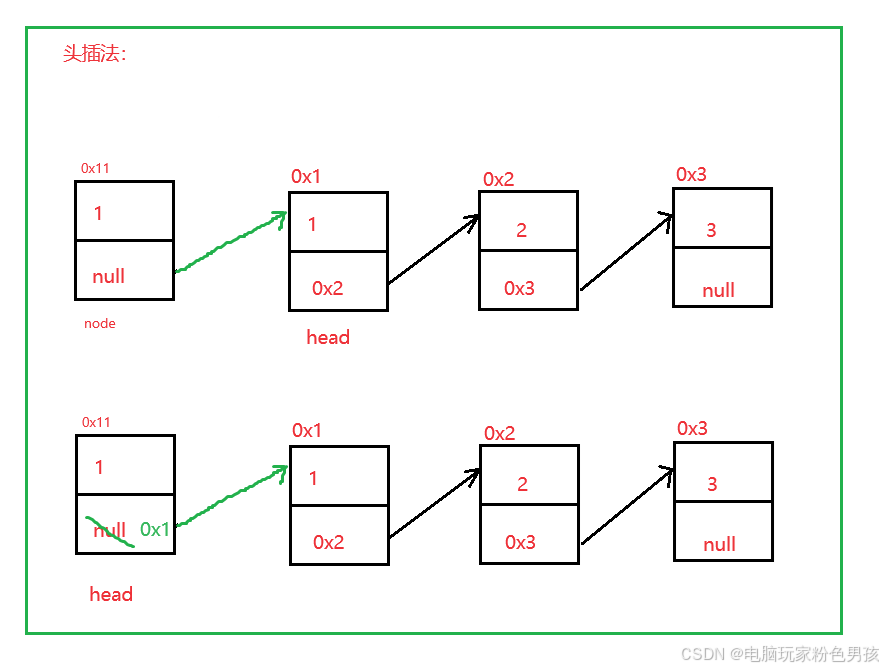
1. Metodo di inserimento dell'intestazione addFirst()
- public void addFirst(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = head;
- head = node;
- }
2. Metodo di inserimento della coda addLast()
- public void addList(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- }
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur.next != null) {
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- cur.next = node;
- }
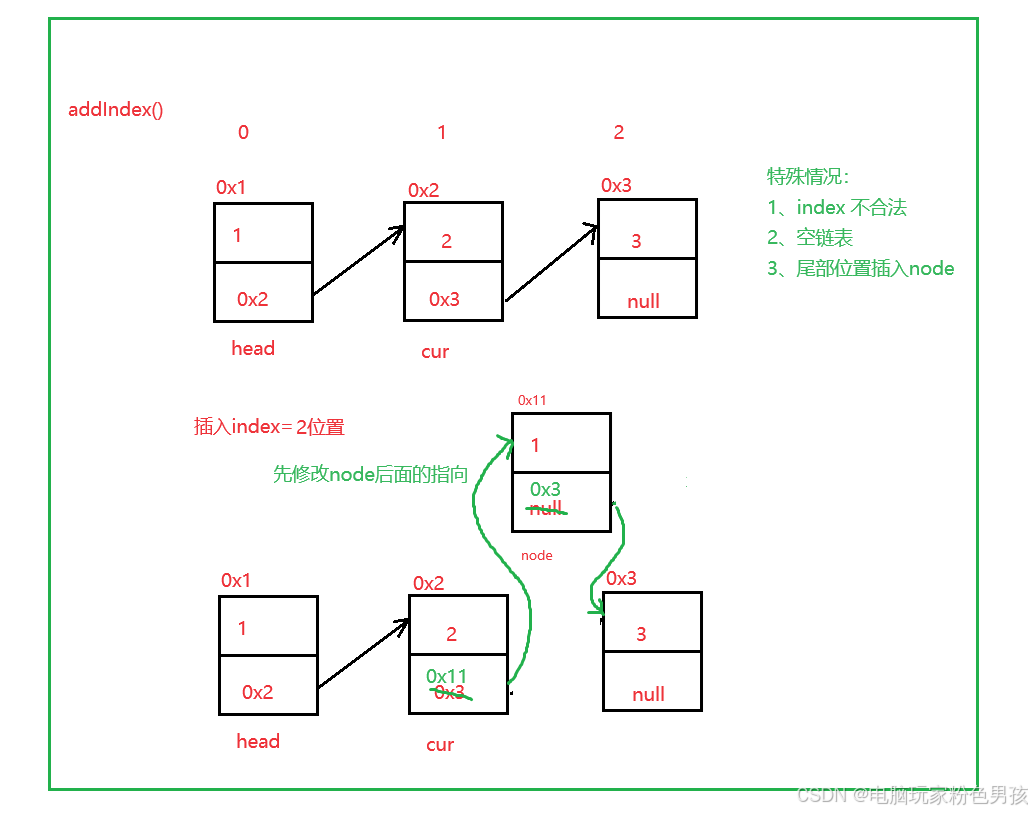
3.addIndex()
- public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
- int len = size();
- // 不合法
- if (index < 0 || index > len) {
- System.out.println("index不合法");
- return;
- }
- // 空链表
- if (index == 0) {
- addFirst(data);
- return;
- }
- // 尾部插入
- if (index == len) {
- addLast(data);
- return;
- }
-
- //中间位置插入
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (index - 1 != 0) {
- cur = cur.next;
- index--;
- }
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = cur.next;
- cur.next = node;
- }
4. contiene()
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- return true;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
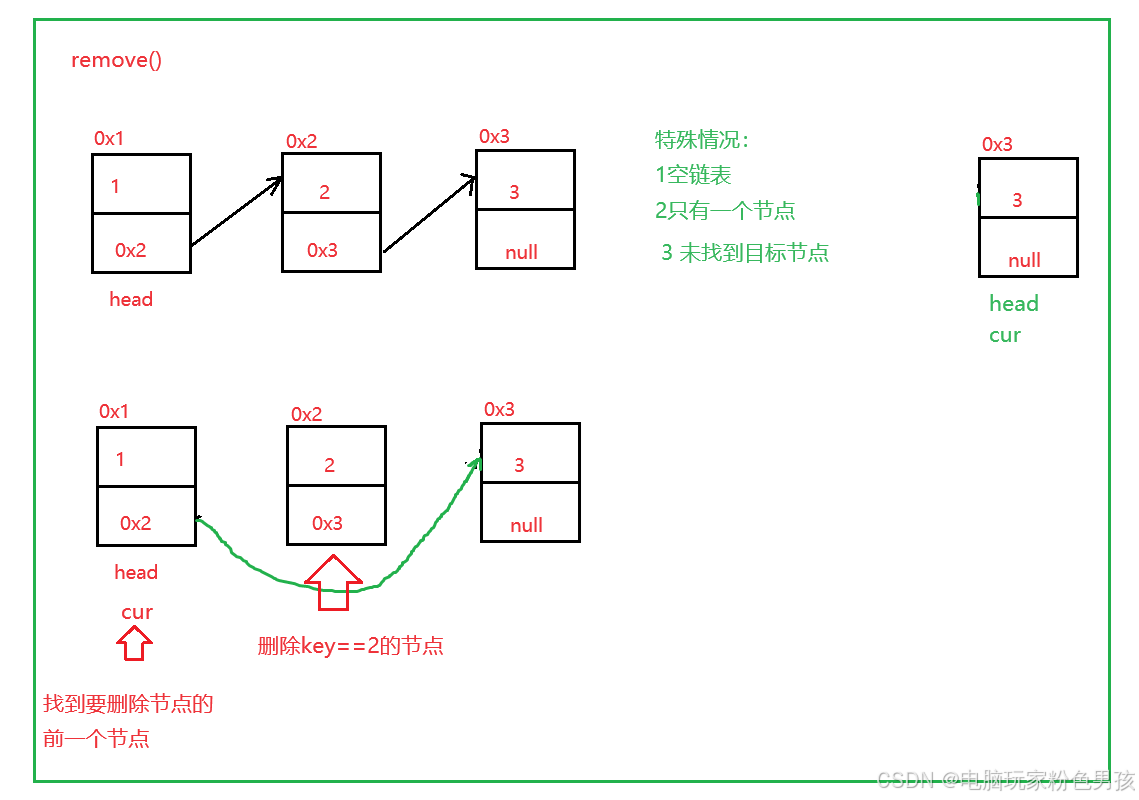
5.rimuovi()
- public void remove(int key) {
- if (head == null) {
- return;
- }
- if (head.val == key) {
- head = head.next;
- }
-
- ListNode cur = findNodeOfKey(key);
- if (cur == null) {
- return;
- }
- ListNode del = cur.next;
- cur.next = del.next;
- }
-
- private ListNode findNodeOfKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur.next != null) {
- if (cur.next.val == key) {
- return cur;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return null;
- }
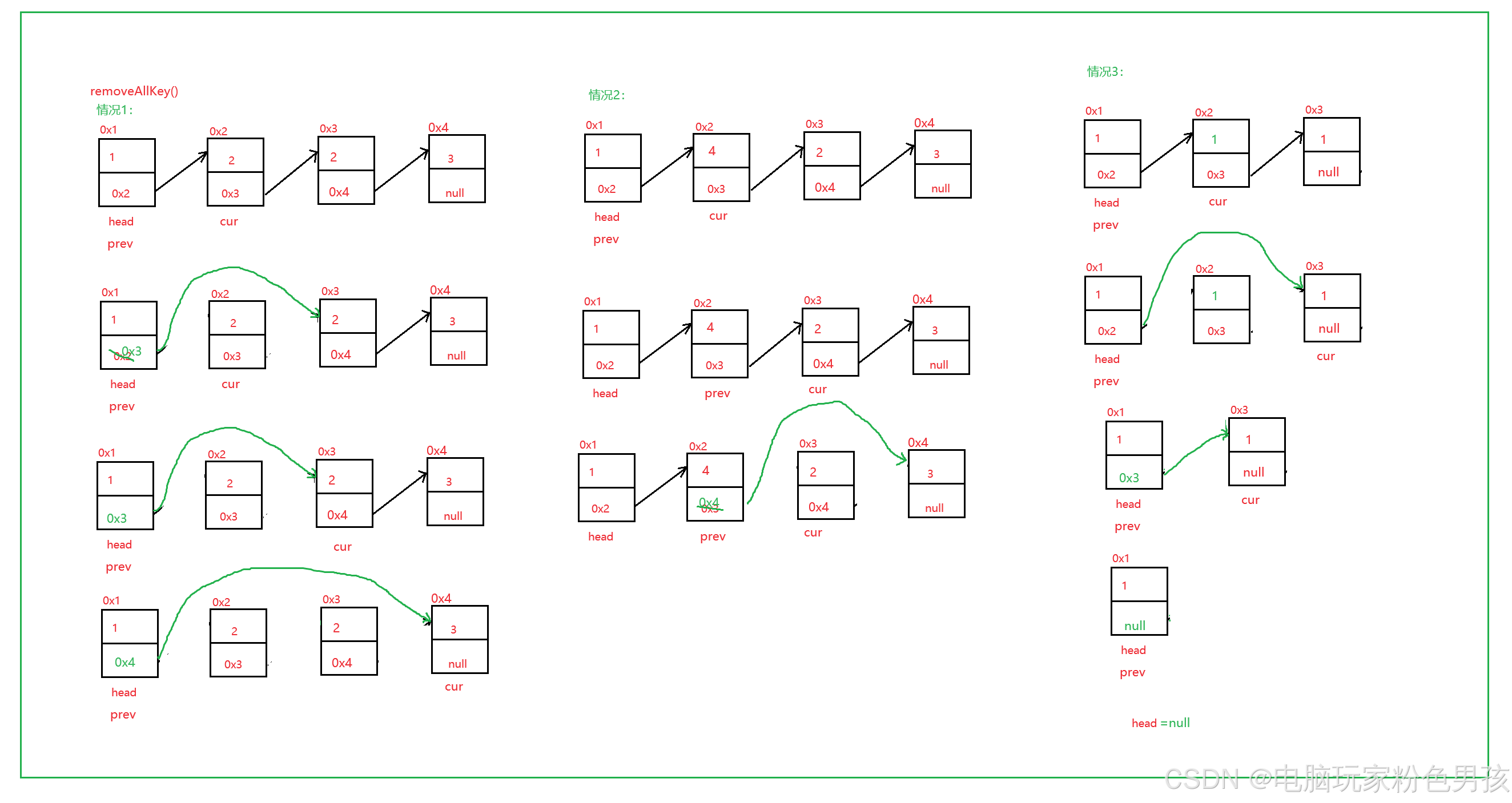
6.rimuoviTutteLeChiavi()
- public void removeAllKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head.next;
- ListNode prev = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- prev.next = cur.next;
- } else {
- prev = cur;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- if (head.val == key) {
- head = head.next;
- }
- }
7.cancella()
- public void clear() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- ListNode curNext = cur.next;
- cur.next = null;
- cur = curNext;
- }
- head = null;
- }

8.dimensione()
- public int size() {
- int count = 0;
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- count++;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
9.visualizza()
- public void display() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- }
- / 2、无头双向链表实现
- public class MyLinkedList {
- //头插法
- public void addFirst(int data){ }
- //尾插法
- public void addLast(int data){}
- //任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
- public void addIndex(int index,int data){}
- //查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
- public boolean contains(int key){}
- //删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
- public void remove(int key){}
- //删除所有值为key的节点
- public void removeAllKey(int key){}
- //得到单链表的长度
- public int size(){}
- public void display(){}
- public void clear(){}
- }
- package DounlyLinkedList;
-
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class MyDoublyLinkedList implements IList {
-
- static class ListNode {
- public int val;
- public ListNode next;
- public ListNode prev;
-
- public ListNode(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
-
- public ListNode head;
- public ListNode last;
-
-
- @Override
- public void addFist(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- last = node;
- } else
- node.next = head;
- head.prev = node;
- head = node;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addLast(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- last = node;
- }
- last.next = node;
- node.prev = last;
- last = node;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
- int len = size();
- if (index < 0 || index > len) {
- System.out.println("index 不合法!");
- }
-
- if (index == 0) {
- addFist(data);
- return;
- }
-
- if (index == len) {
- addLast(data);
- return;
- }
- ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = cur;
- cur.prev.next = node;
- node.prev = cur.prev;
- cur.prev = node;
- }
-
- private ListNode findIndex(int index) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (index != 0) {
- cur = cur.next;
- index--;
- }
- return cur;
- }
-
-
- @Override
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- int count = 0;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- return true;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void remove(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- if (cur == head) {
- head = head.next;
- if (head != null) {
- head.prev = null;
- }
- head.prev = null;
- } else {
- cur.prev.next = cur.next;
- if (cur.next == null) {
- last = last.prev;
- } else {
- cur.next.next = cur.prev;
- }
- }
- return;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
-
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public void removeAllKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- if (cur == head) {
- head = head.next;
- if (head != null) {
- head.prev = null;
- }
- head.prev = null;
- } else {
- cur.prev.next = cur.next;
- if (cur.next == null) {
- last = last.prev;
- } else {
- cur.next.next = cur.prev;
- }
- }
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public int size() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- int count = 0;
- while (cur != null) {
- count++;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void clear() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- ListNode curNext = cur.next;
- cur.next = null;
- cur.prev = null;
- cur = curNext;
- }
- head = null;
- last = null;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void dispaly() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- package DounlyLinkedList;
-
- public interface IList {
- void addFist(int data);
-
- void addLast(int data);
-
- void addIndex(int index, int data);
-
- boolean contains(int key);
-
- void remove(int key);
-
- void removeAllKey(int key);
-
- int size();
-
- void clear();
-
- void dispaly();
- }
4.1 Cos'è LinkedLis

【illustrare】
1. LinkedList implementa l'interfaccia Elenco
2. Il livello sottostante di LinkedList utilizza un elenco doppiamente collegato
3. LinkedList non implementa l'interfaccia RandomAccess, quindi LinkedList non supporta l'accesso casuale.
4. L'inserimento e l'eliminazione di elementi in qualsiasi posizione in LinkedList è relativamente efficiente e la complessità temporale è O (1)
5. LinkedList è più adatto per scenari di inserimento in qualsiasi posizione
4.2 Utilizzo di LinkedList
1. Costruzione di LinkedList
| metodo | spiegare |
| Lista collegata() | Costruzione senza argomenti |
| pubblico LinkedList(Collezione | Costruisci un elenco utilizzando elementi di altri contenitori di raccolta |
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
- List<String> list2 = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
-
- list2.add("javaSE");
- list2.add("javaWeb");
- list2.add("javaEE");
-
- List<String> list3 = new LinkedList<>(list2);
-
- }
- }
-
-
2. Introduzione ad altri metodi comuni di LinkedList
| metodo | spiegare |
| booleano add(E e) | tappo di coda e |
| void add(int indice, E elemento) | Inserire e nella posizione dell'indice |
| booleano addAll(Collezione c) | Inserisci gli elementi in c alla fine |
| E rimuovi(int indice) | Elimina l'elemento della posizione dell'indice |
| booleano rimuovi(Oggetto o) | Elimina la prima o incontrata |
| E get(int indice) | Ottieni l'elemento di posizione dell'indice in pedice |
| E set(int indice, E elemento) | Imposta l'elemento di posizione dell'indice del pedice su element |
| vuoto cancella() | Chiaro |
| booleano contiene(Oggetto o) | Determina se o è nella tavola lineare |
| int indiceOf(Oggetto o) | Restituisce l'indice in cui si trova la prima o |
| int lastIndexOf(Oggetto o) | Restituisce il pedice dell'ultima o |
| Elenco subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Intercetta parte della lista |
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
- list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(4);
- list.add(5);
- list.add(6);
- list.add(7);
- System.out.println(list.size());
- System.out.println(list);
- // 在起始位置插入0
- list.add(0, 0); // add(index, elem): 在index位置插入元素elem
- System.out.println(list);
- list.remove(); // remove(): 删除第一个元素,内部调用的是removeFirst()
- list.removeFirst(); // removeFirst(): 删除第一个元素
- list.removeLast(); // removeLast(): 删除最后元素
- list.remove(1); // remove(index): 删除index位置的元素
- System.out.println(list);
- // contains(elem): 检测elem元素是否存在,如果存在返回true,否则返回false
- if(!list.contains(1)){
- list.add(0, 1);
- }
- list.add(1);
- System.out.println(list);
- System.out.println(list.indexOf(1)); // indexOf(elem): 从前往后找到第一个elem的位置
- System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1)); // lastIndexOf(elem): 从后往前找第一个1的位置
- int elem = list.get(0); // get(index): 获取指定位置元素
- list.set(0, 100); // set(index, elem): 将index位置的元素设置为elem
- System.out.println(list);
- // subList(from, to): 用list中[from, to)之间的元素构造一个新的LinkedList返回
- List<Integer> copy = list.subList(0, 3);
- System.out.println(list);
- System.out.println(copy);
- list.clear(); // 将list中元素清空
- System.out.println(list.size());
- }
3. Attraversamento della LinkedList
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
- list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(4);
- list.add(5);
- list.add(6);
- list.add(7);
- System.out.println(list.size());
- // foreach遍历
- for (int e:list) {
- System.out.print(e + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
- ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
- while(it.hasNext()){
- System.out.print(it.next()+ " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
- ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
- while (rit.hasPrevious()){
- System.out.print(rit.previous() +" ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
| differenza | Lista di array | Lista collegata |
| Sullo spazio di archiviazione | deve essere fisicamente continua | Logicamente continuo, non necessariamente fisicamente continuo |
| accesso casuale | Supporto O(1) | Non supportato: O(N) |
| Tappo di testa | Necessità di spostare elementi, bassa efficienza O(N) | Basta modificare il puntatore del riferimento, la complessità temporale è O(1) |
| inserire | Quando lo spazio è insufficiente, è necessaria l'espansione | Nessun concetto di capacità |
| Scenari applicativi | Stoccaggio efficiente degli elementi + accesso frequente | Inserimento ed eliminazione frequenti in qualsiasi posizione |