2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
Cum elementa inserendi vel delendi in quovis loco ArrayList, necesse est ut omnia quae sequuntur elementa ante vel retro movere positio. Ideo: LinkedList, indicem coniunctorum structurae, in collectionibus Javae introducitur.
2.1 conceptus et compages indicem coniunctorum
Index coniunctus physice non continuus structurae repositae est, et ordo logicus notitiarum elementorum per ordinem nexus in nexu coniunctionis perficitur.
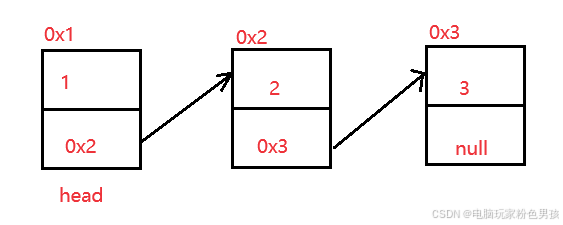
2.2 exsequendam coniunctum album
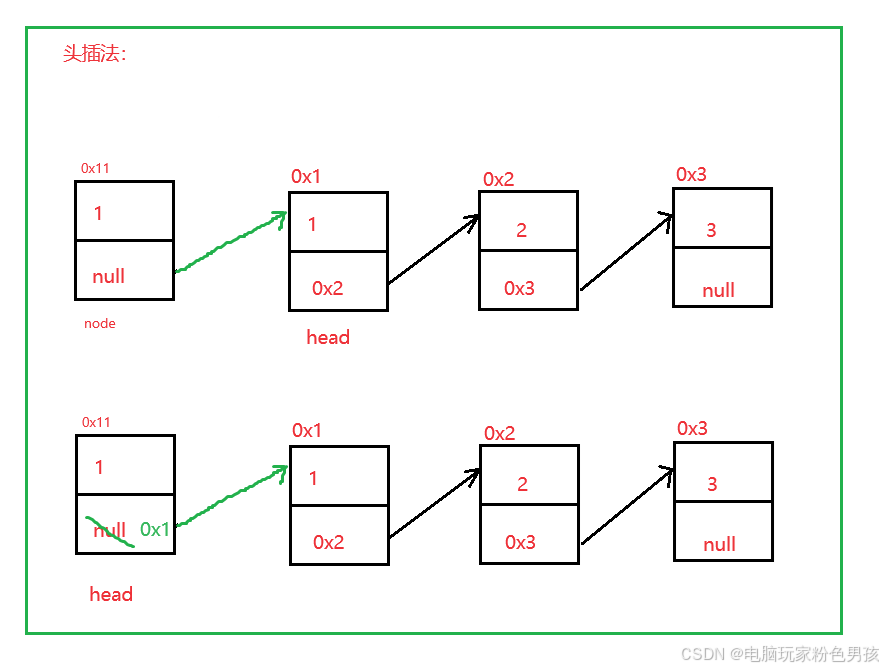
1. Header insertio modum addFirst ()
- public void addFirst(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = head;
- head = node;
- }
2. Cauda insertio modum addLast ()
- public void addList(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- }
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur.next != null) {
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- cur.next = node;
- }
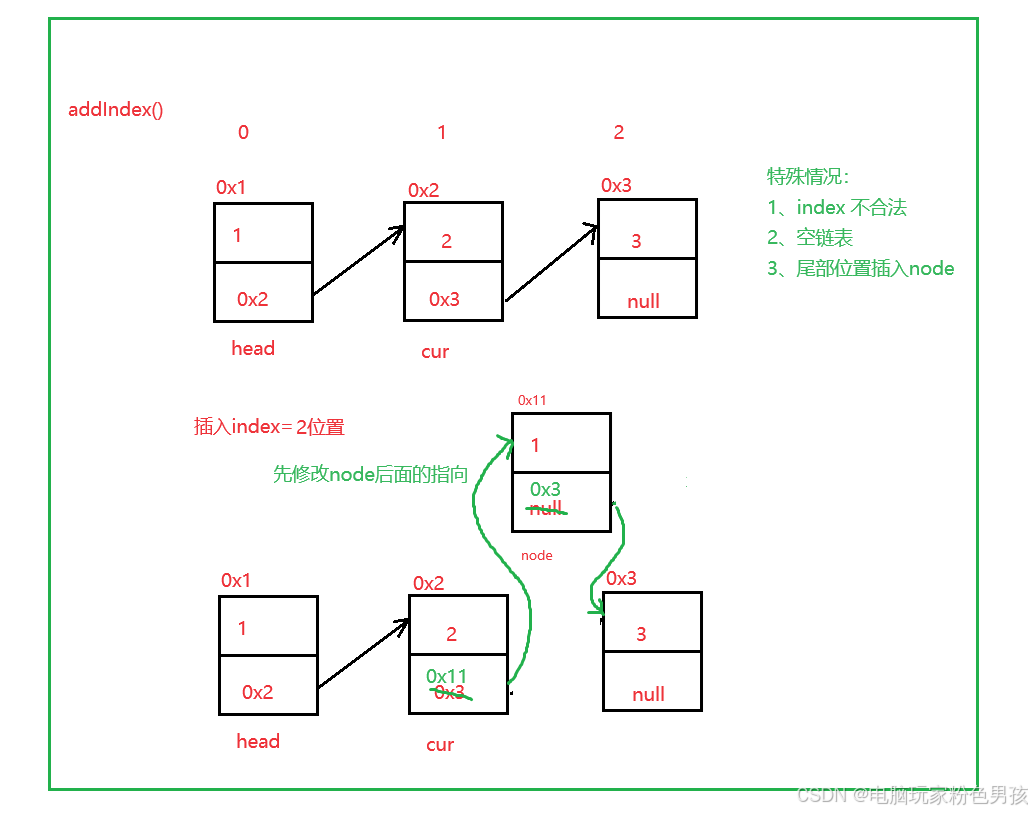
3.addIndex()
- public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
- int len = size();
- // 不合法
- if (index < 0 || index > len) {
- System.out.println("index不合法");
- return;
- }
- // 空链表
- if (index == 0) {
- addFirst(data);
- return;
- }
- // 尾部插入
- if (index == len) {
- addLast(data);
- return;
- }
-
- //中间位置插入
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (index - 1 != 0) {
- cur = cur.next;
- index--;
- }
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = cur.next;
- cur.next = node;
- }
4. continet ()
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- return true;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
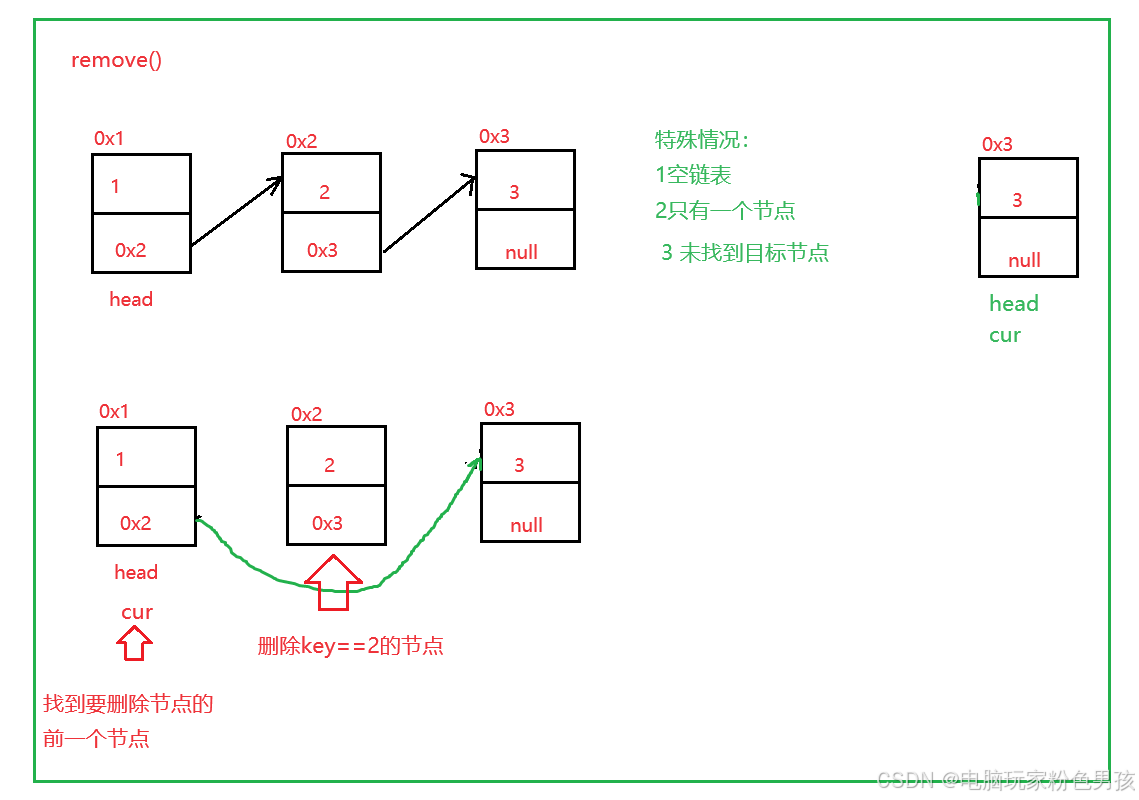
5.remove()
- public void remove(int key) {
- if (head == null) {
- return;
- }
- if (head.val == key) {
- head = head.next;
- }
-
- ListNode cur = findNodeOfKey(key);
- if (cur == null) {
- return;
- }
- ListNode del = cur.next;
- cur.next = del.next;
- }
-
- private ListNode findNodeOfKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur.next != null) {
- if (cur.next.val == key) {
- return cur;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return null;
- }
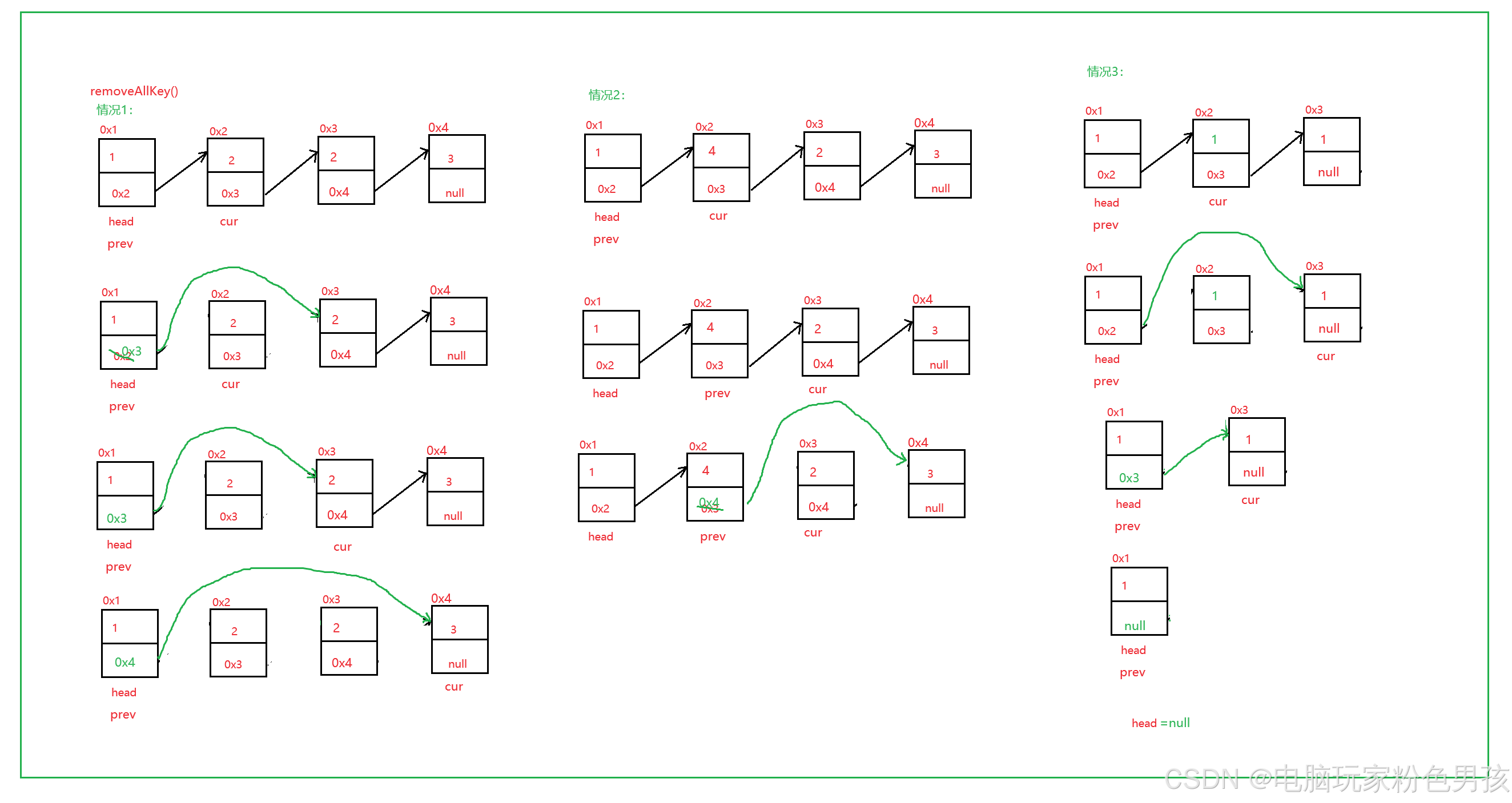
6.removeAllKey ()
- public void removeAllKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head.next;
- ListNode prev = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- prev.next = cur.next;
- } else {
- prev = cur;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- if (head.val == key) {
- head = head.next;
- }
- }
7.clear()
- public void clear() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- ListNode curNext = cur.next;
- cur.next = null;
- cur = curNext;
- }
- head = null;
- }

8.size()
- public int size() {
- int count = 0;
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- count++;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
9.display()
- public void display() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- }
- / 2、无头双向链表实现
- public class MyLinkedList {
- //头插法
- public void addFirst(int data){ }
- //尾插法
- public void addLast(int data){}
- //任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
- public void addIndex(int index,int data){}
- //查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
- public boolean contains(int key){}
- //删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
- public void remove(int key){}
- //删除所有值为key的节点
- public void removeAllKey(int key){}
- //得到单链表的长度
- public int size(){}
- public void display(){}
- public void clear(){}
- }
- package DounlyLinkedList;
-
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class MyDoublyLinkedList implements IList {
-
- static class ListNode {
- public int val;
- public ListNode next;
- public ListNode prev;
-
- public ListNode(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
-
- public ListNode head;
- public ListNode last;
-
-
- @Override
- public void addFist(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- last = node;
- } else
- node.next = head;
- head.prev = node;
- head = node;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addLast(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- last = node;
- }
- last.next = node;
- node.prev = last;
- last = node;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
- int len = size();
- if (index < 0 || index > len) {
- System.out.println("index 不合法!");
- }
-
- if (index == 0) {
- addFist(data);
- return;
- }
-
- if (index == len) {
- addLast(data);
- return;
- }
- ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = cur;
- cur.prev.next = node;
- node.prev = cur.prev;
- cur.prev = node;
- }
-
- private ListNode findIndex(int index) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (index != 0) {
- cur = cur.next;
- index--;
- }
- return cur;
- }
-
-
- @Override
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- int count = 0;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- return true;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void remove(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- if (cur == head) {
- head = head.next;
- if (head != null) {
- head.prev = null;
- }
- head.prev = null;
- } else {
- cur.prev.next = cur.next;
- if (cur.next == null) {
- last = last.prev;
- } else {
- cur.next.next = cur.prev;
- }
- }
- return;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
-
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public void removeAllKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- if (cur == head) {
- head = head.next;
- if (head != null) {
- head.prev = null;
- }
- head.prev = null;
- } else {
- cur.prev.next = cur.next;
- if (cur.next == null) {
- last = last.prev;
- } else {
- cur.next.next = cur.prev;
- }
- }
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public int size() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- int count = 0;
- while (cur != null) {
- count++;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void clear() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- ListNode curNext = cur.next;
- cur.next = null;
- cur.prev = null;
- cur = curNext;
- }
- head = null;
- last = null;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void dispaly() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- package DounlyLinkedList;
-
- public interface IList {
- void addFist(int data);
-
- void addLast(int data);
-
- void addIndex(int index, int data);
-
- boolean contains(int key);
-
- void remove(int key);
-
- void removeAllKey(int key);
-
- int size();
-
- void clear();
-
- void dispaly();
- }
4.1 Quid est LinkedLis

illustrate】
1. LinkedList utensilia List interface
2. Ratio iacuit LinkedList utitur duplici coniunctione list
3. LinkedList in instrumento RandomAccess non adducit, ideo LinkedList aditum non adiuvat.
4. Elementa inserentes et delentes in quovis positione in LinkedList est relative efficiens, et tempus multiplicitas est O (1).
5. LinkedList aptior est ad missiones inserendas in aliquo loco
4.2 Usus LinkedList
1. Constructio LinkedList
| methodo | explicare " |
| LinkedList () | Nulla ratio constructionis |
| publica LinkedList (Collection | Construe Indicem elementorum ex aliis vasis collectum |
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
- List<String> list2 = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
-
- list2.add("javaSE");
- list2.add("javaWeb");
- list2.add("javaEE");
-
- List<String> list3 = new LinkedList<>(list2);
-
- }
- }
-
-
2. Introductio ad alios modos communes de LinkedList
| methodo | explicare " |
| Boolean add(E e) | cauda obturaculum e * |
| void add (int index, E element) | Inserta e in indice positionis |
| Boolean addAll (Collectio c) | In c inserere elementa in fine |
| E remove (int index) | Delere indicem positio elementum |
| Boolean distantiam (Object o) | Delere primum o offendit |
| E get (int index) | Adepto subscript index loco elementi |
| E set(int index, E elementum) | Constitue subscript in indice loco elementum est elementum |
| inanis patet () | Patet |
| Boolean continet (O Object) | Utrum o sit in mensa lineari |
| int indexOf (Object o) | Redde indicem ubi primum o situm est |
| int lastIndexOf (Object o) | Refert subscript in ultimis o* |
| Index subList (int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Intercipere partem album |
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
- list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(4);
- list.add(5);
- list.add(6);
- list.add(7);
- System.out.println(list.size());
- System.out.println(list);
- // 在起始位置插入0
- list.add(0, 0); // add(index, elem): 在index位置插入元素elem
- System.out.println(list);
- list.remove(); // remove(): 删除第一个元素,内部调用的是removeFirst()
- list.removeFirst(); // removeFirst(): 删除第一个元素
- list.removeLast(); // removeLast(): 删除最后元素
- list.remove(1); // remove(index): 删除index位置的元素
- System.out.println(list);
- // contains(elem): 检测elem元素是否存在,如果存在返回true,否则返回false
- if(!list.contains(1)){
- list.add(0, 1);
- }
- list.add(1);
- System.out.println(list);
- System.out.println(list.indexOf(1)); // indexOf(elem): 从前往后找到第一个elem的位置
- System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1)); // lastIndexOf(elem): 从后往前找第一个1的位置
- int elem = list.get(0); // get(index): 获取指定位置元素
- list.set(0, 100); // set(index, elem): 将index位置的元素设置为elem
- System.out.println(list);
- // subList(from, to): 用list中[from, to)之间的元素构造一个新的LinkedList返回
- List<Integer> copy = list.subList(0, 3);
- System.out.println(list);
- System.out.println(copy);
- list.clear(); // 将list中元素清空
- System.out.println(list.size());
- }
3. Traversal de LinkedList
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
- list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(4);
- list.add(5);
- list.add(6);
- list.add(7);
- System.out.println(list.size());
- // foreach遍历
- for (int e:list) {
- System.out.print(e + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
- ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
- while(it.hasNext()){
- System.out.print(it.next()+ " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
- ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
- while (rit.hasPrevious()){
- System.out.print(rit.previous() +" ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
| differentia | ArrayList | LinkedList |
| In repono spatium | oportet esse corporaliter continua | Logice continua, non necessario physice continua |
| temere accessum | Suscipe Domine (1) | Non praebetur: O (N) |
| Caput obturaculum | Oportet elementa movere, humilis efficientiam O (N) | Modo regulam modificandi relationis, tempus multiplicitatis est O (1). |
| inserta | Cum spatium insufficiens est, dilatatio requiritur | Nulla conceptio capacitatis |
| Application missiones | Efficiens repono elementorum + frequentes accessus | Crebra insertio et deletio in aliquo loco |