私の連絡先情報
郵便メール:
2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
ArrayList 内の任意の位置に要素を挿入または削除する場合、後続の要素全体を前後に移動する必要があるため、時間計算量は O(n) となり、効率が比較的低くなります。そのため、ArrayList は挿入および削除には適していません。どの場面でも。そのため、リンクされたリスト構造である LinkedList が Java コレクションに導入されました。
2.1 リンクリストの概念と構造
リンク リストは物理的に不連続なストレージ構造であり、データ要素の論理的順序はリンク リスト内の参照リンク順序によって実現されます。
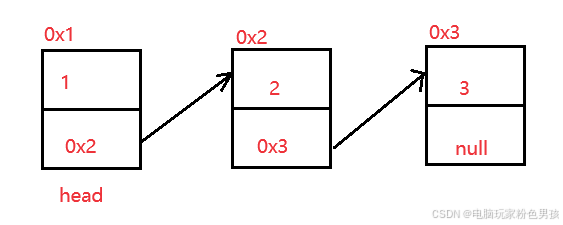
2.2 リンクリストの実装
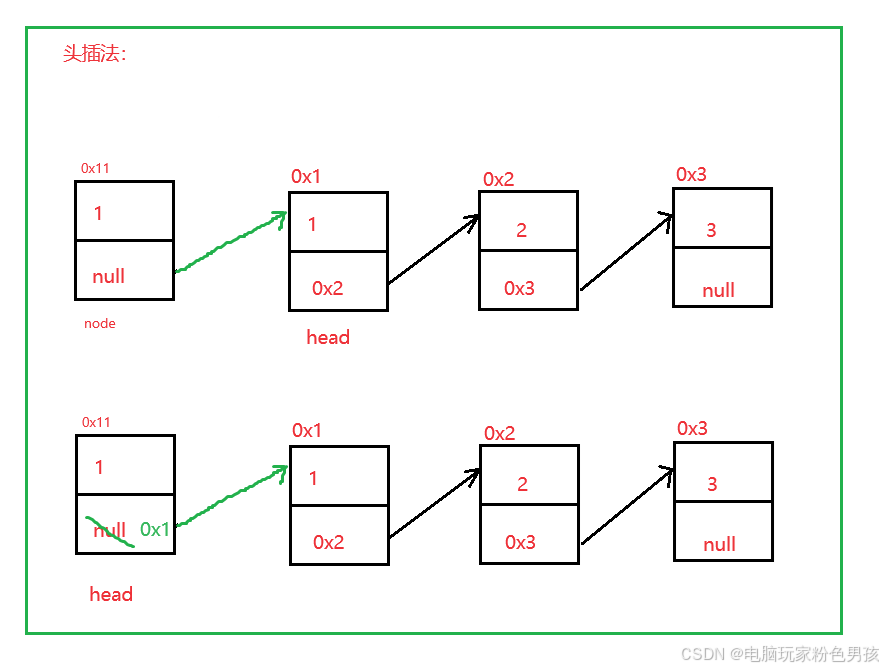
1. ヘッダー挿入メソッド addFirst()
- public void addFirst(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = head;
- head = node;
- }
2.末尾挿入メソッドaddLast()
- public void addList(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- }
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur.next != null) {
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- cur.next = node;
- }
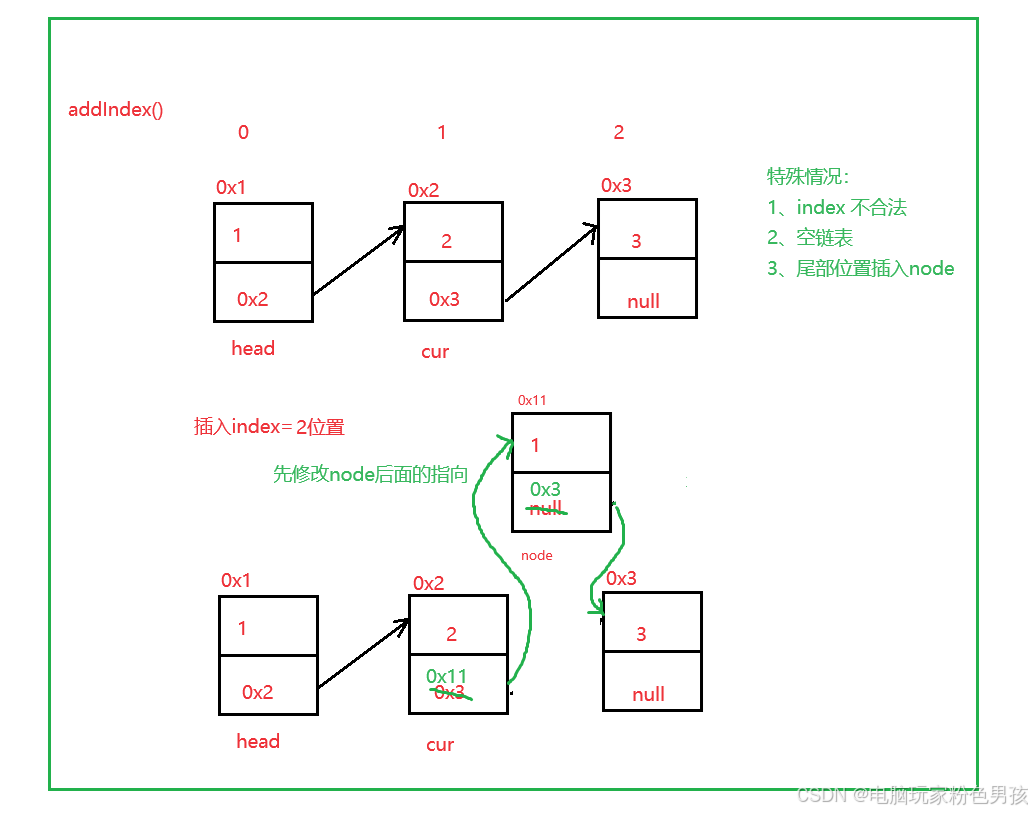
3.インデックスを追加します()
- public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
- int len = size();
- // 不合法
- if (index < 0 || index > len) {
- System.out.println("index不合法");
- return;
- }
- // 空链表
- if (index == 0) {
- addFirst(data);
- return;
- }
- // 尾部插入
- if (index == len) {
- addLast(data);
- return;
- }
-
- //中间位置插入
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (index - 1 != 0) {
- cur = cur.next;
- index--;
- }
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = cur.next;
- cur.next = node;
- }
4. を含む()
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- return true;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
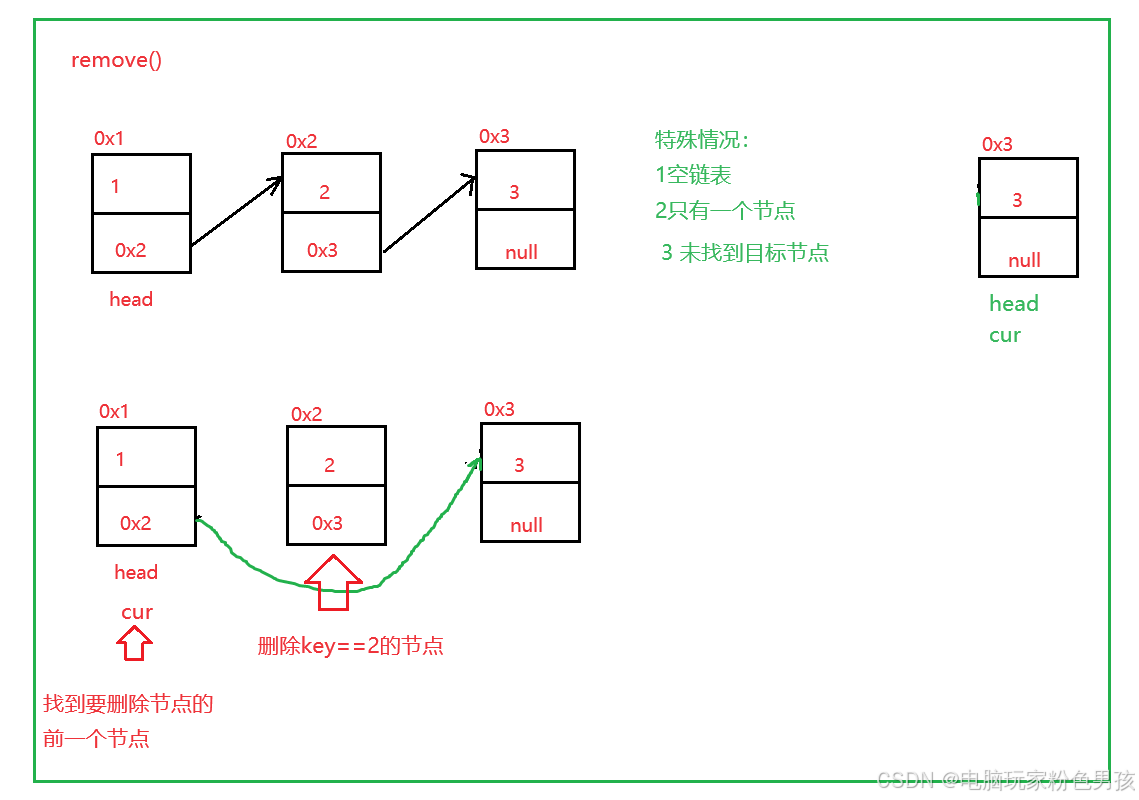
5.削除()
- public void remove(int key) {
- if (head == null) {
- return;
- }
- if (head.val == key) {
- head = head.next;
- }
-
- ListNode cur = findNodeOfKey(key);
- if (cur == null) {
- return;
- }
- ListNode del = cur.next;
- cur.next = del.next;
- }
-
- private ListNode findNodeOfKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur.next != null) {
- if (cur.next.val == key) {
- return cur;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return null;
- }
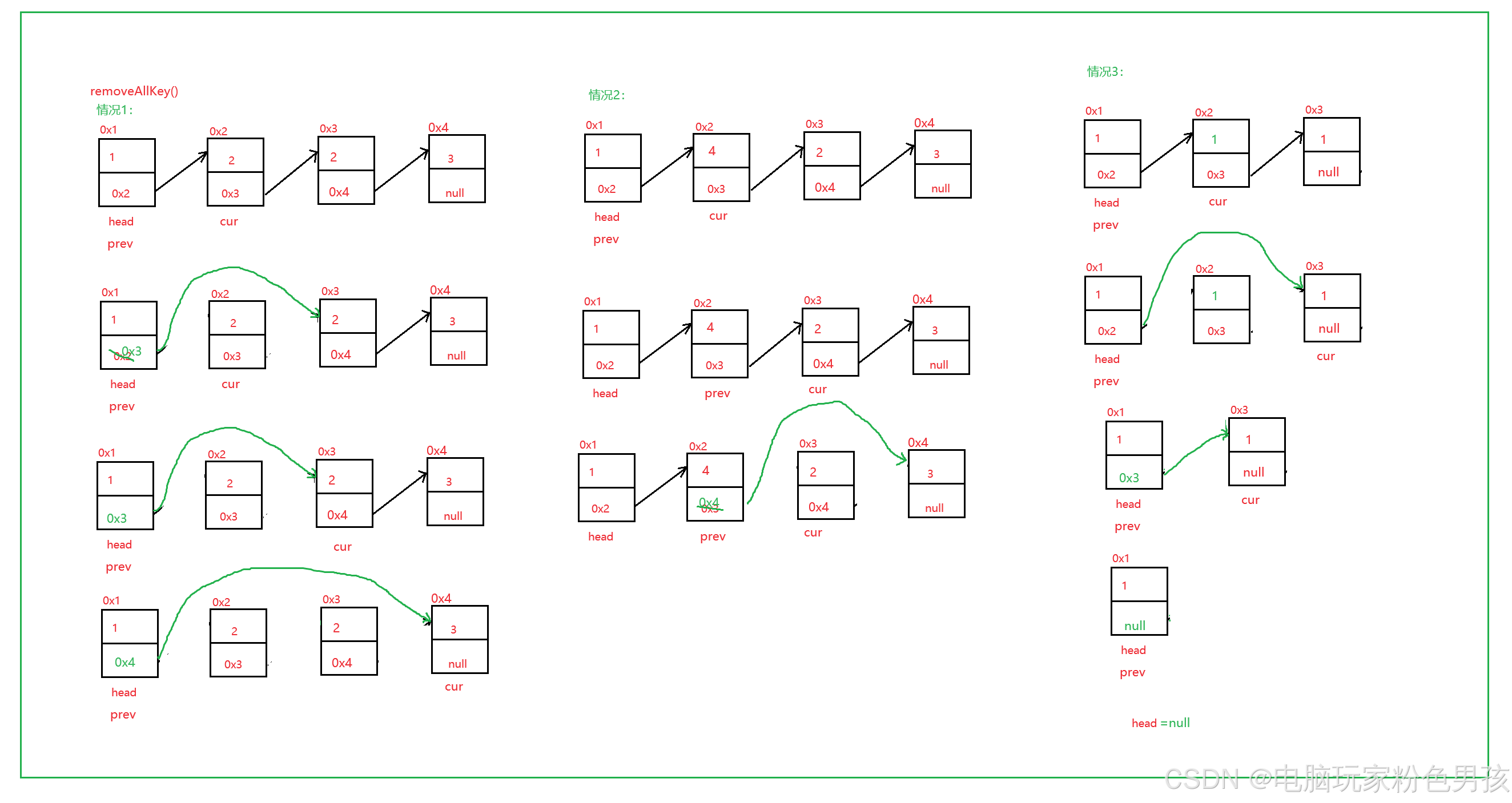
6.すべてのキーを削除します。
- public void removeAllKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head.next;
- ListNode prev = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- prev.next = cur.next;
- } else {
- prev = cur;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- if (head.val == key) {
- head = head.next;
- }
- }
7.クリア()
- public void clear() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- ListNode curNext = cur.next;
- cur.next = null;
- cur = curNext;
- }
- head = null;
- }

8.サイズ()
- public int size() {
- int count = 0;
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- count++;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
9.表示()
- public void display() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- }
- / 2、无头双向链表实现
- public class MyLinkedList {
- //头插法
- public void addFirst(int data){ }
- //尾插法
- public void addLast(int data){}
- //任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
- public void addIndex(int index,int data){}
- //查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
- public boolean contains(int key){}
- //删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
- public void remove(int key){}
- //删除所有值为key的节点
- public void removeAllKey(int key){}
- //得到单链表的长度
- public int size(){}
- public void display(){}
- public void clear(){}
- }
- package DounlyLinkedList;
-
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class MyDoublyLinkedList implements IList {
-
- static class ListNode {
- public int val;
- public ListNode next;
- public ListNode prev;
-
- public ListNode(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
-
- public ListNode head;
- public ListNode last;
-
-
- @Override
- public void addFist(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- last = node;
- } else
- node.next = head;
- head.prev = node;
- head = node;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addLast(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- last = node;
- }
- last.next = node;
- node.prev = last;
- last = node;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
- int len = size();
- if (index < 0 || index > len) {
- System.out.println("index 不合法!");
- }
-
- if (index == 0) {
- addFist(data);
- return;
- }
-
- if (index == len) {
- addLast(data);
- return;
- }
- ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = cur;
- cur.prev.next = node;
- node.prev = cur.prev;
- cur.prev = node;
- }
-
- private ListNode findIndex(int index) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (index != 0) {
- cur = cur.next;
- index--;
- }
- return cur;
- }
-
-
- @Override
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- int count = 0;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- return true;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void remove(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- if (cur == head) {
- head = head.next;
- if (head != null) {
- head.prev = null;
- }
- head.prev = null;
- } else {
- cur.prev.next = cur.next;
- if (cur.next == null) {
- last = last.prev;
- } else {
- cur.next.next = cur.prev;
- }
- }
- return;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
-
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public void removeAllKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- if (cur == head) {
- head = head.next;
- if (head != null) {
- head.prev = null;
- }
- head.prev = null;
- } else {
- cur.prev.next = cur.next;
- if (cur.next == null) {
- last = last.prev;
- } else {
- cur.next.next = cur.prev;
- }
- }
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public int size() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- int count = 0;
- while (cur != null) {
- count++;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void clear() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- ListNode curNext = cur.next;
- cur.next = null;
- cur.prev = null;
- cur = curNext;
- }
- head = null;
- last = null;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void dispaly() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- package DounlyLinkedList;
-
- public interface IList {
- void addFist(int data);
-
- void addLast(int data);
-
- void addIndex(int index, int data);
-
- boolean contains(int key);
-
- void remove(int key);
-
- void removeAllKey(int key);
-
- int size();
-
- void clear();
-
- void dispaly();
- }
4.1 LinkedLisとは

【イラスト】
1. LinkedList は List インターフェイスを実装します。
2. LinkedList の基礎となる層は二重リンク リストを使用します
3. LinkedList は RandomAccess インターフェイスを実装していないため、LinkedList はランダム アクセスをサポートしません。
4. LinkedList 内の任意の位置での要素の挿入と削除は比較的効率的であり、時間計算量は O(1) です。
5. LinkedList は、あらゆる場所での挿入シナリオにより適しています。
4.2 LinkedListの使用
1. LinkedListの構築
| 方法 | 説明する |
| リンクリスト() | 引数なしの構築 |
| パブリックLinkedList(コレクション | 他のコレクションコンテナの要素を使用してリストを構築する |
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
- List<String> list2 = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
-
- list2.add("javaSE");
- list2.add("javaWeb");
- list2.add("javaEE");
-
- List<String> list3 = new LinkedList<>(list2);
-
- }
- }
-
-
2. LinkedList の他の一般的なメソッドの紹介
| 方法 | 説明する |
| ブール加算(E e) | テールプラグe |
| void add(int インデックス、E 要素) | インデックス位置に e を挿入します |
| ブール型addAll(コレクションc) | cの最後に要素を挿入します |
| E 削除(int インデックス) | インデックス位置要素を削除する |
| ブール値削除(オブジェクトo) | 最初に見つかった o を削除します |
| E get(int インデックス) | 添え字のインデックス位置要素を取得します |
| E セット(int インデックス、E 要素) | 添字インデックス位置要素を要素に設定します |
| void をクリアする() | クリア |
| ブール値を含む(オブジェクト o) | o が線形表にあるかどうかを判断します |
| int インデックス(オブジェクト o) | 最初の o が位置するインデックスを返します |
| int lastIndexOf(オブジェクトo) | 最後の o の添え字を返します |
| リストのサブリスト(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | リストの一部をインターセプトする |
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
- list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(4);
- list.add(5);
- list.add(6);
- list.add(7);
- System.out.println(list.size());
- System.out.println(list);
- // 在起始位置插入0
- list.add(0, 0); // add(index, elem): 在index位置插入元素elem
- System.out.println(list);
- list.remove(); // remove(): 删除第一个元素,内部调用的是removeFirst()
- list.removeFirst(); // removeFirst(): 删除第一个元素
- list.removeLast(); // removeLast(): 删除最后元素
- list.remove(1); // remove(index): 删除index位置的元素
- System.out.println(list);
- // contains(elem): 检测elem元素是否存在,如果存在返回true,否则返回false
- if(!list.contains(1)){
- list.add(0, 1);
- }
- list.add(1);
- System.out.println(list);
- System.out.println(list.indexOf(1)); // indexOf(elem): 从前往后找到第一个elem的位置
- System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1)); // lastIndexOf(elem): 从后往前找第一个1的位置
- int elem = list.get(0); // get(index): 获取指定位置元素
- list.set(0, 100); // set(index, elem): 将index位置的元素设置为elem
- System.out.println(list);
- // subList(from, to): 用list中[from, to)之间的元素构造一个新的LinkedList返回
- List<Integer> copy = list.subList(0, 3);
- System.out.println(list);
- System.out.println(copy);
- list.clear(); // 将list中元素清空
- System.out.println(list.size());
- }
3. LinkedList の走査
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
- list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(4);
- list.add(5);
- list.add(6);
- list.add(7);
- System.out.println(list.size());
- // foreach遍历
- for (int e:list) {
- System.out.print(e + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
- ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
- while(it.hasNext()){
- System.out.print(it.next()+ " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
- ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
- while (rit.hasPrevious()){
- System.out.print(rit.previous() +" ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
| 違い | 配列リスト | リンクリスト |
| 収納スペースについて | 物理的に連続していなければならない | 論理的には連続的ですが、物理的には必ずしも連続的ではありません |
| ランダムアクセス | サポートO(1) | サポートされていない: O(N) |
| ヘッドプラグ | 要素を移動する必要があり、効率が低い O(N) | 参照のポインタを変更するだけで、時間計算量は O(1) になります。 |
| 入れる | スペースが足りない場合は増設が必要 | 容量という概念がない |
| アプリケーションシナリオ | 要素の効率的な保管 + 頻繁なアクセス | あらゆる場所での頻繁な挿入と削除 |