моя контактная информация
Почтамезофия@protonmail.com
2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
При вставке или удалении элементов в любой позиции ArrayList необходимо переместить все последующие элементы вперед или назад. Временная сложность равна O(n), а эффективность относительно низкая. Поэтому ArrayList не подходит для вставки и удаления. в любой позиции. Поэтому: LinkedList, структура связанного списка, представлена в коллекциях Java.
2.1 Понятие и структура связанного списка
Связанный список представляет собой физически прерывистую структуру хранения, а логический порядок элементов данных достигается за счет порядка ссылочных ссылок в связанном списке.
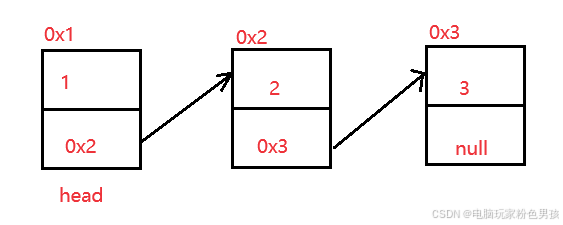
2.2 Реализация связанного списка
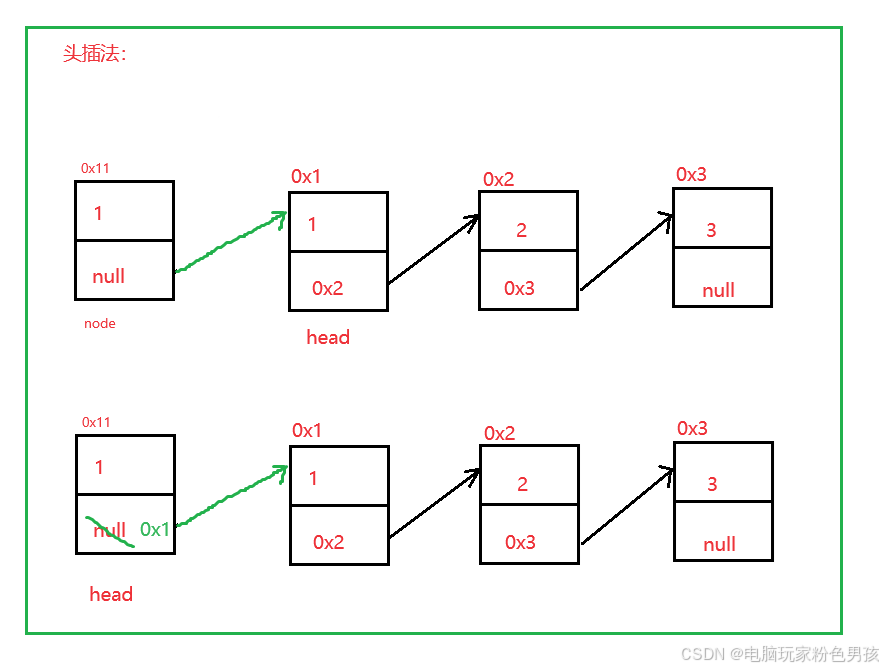
1. Метод вставки заголовка addFirst()
- public void addFirst(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = head;
- head = node;
- }
2. Метод вставки хвоста addLast()
- public void addList(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- }
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur.next != null) {
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- cur.next = node;
- }
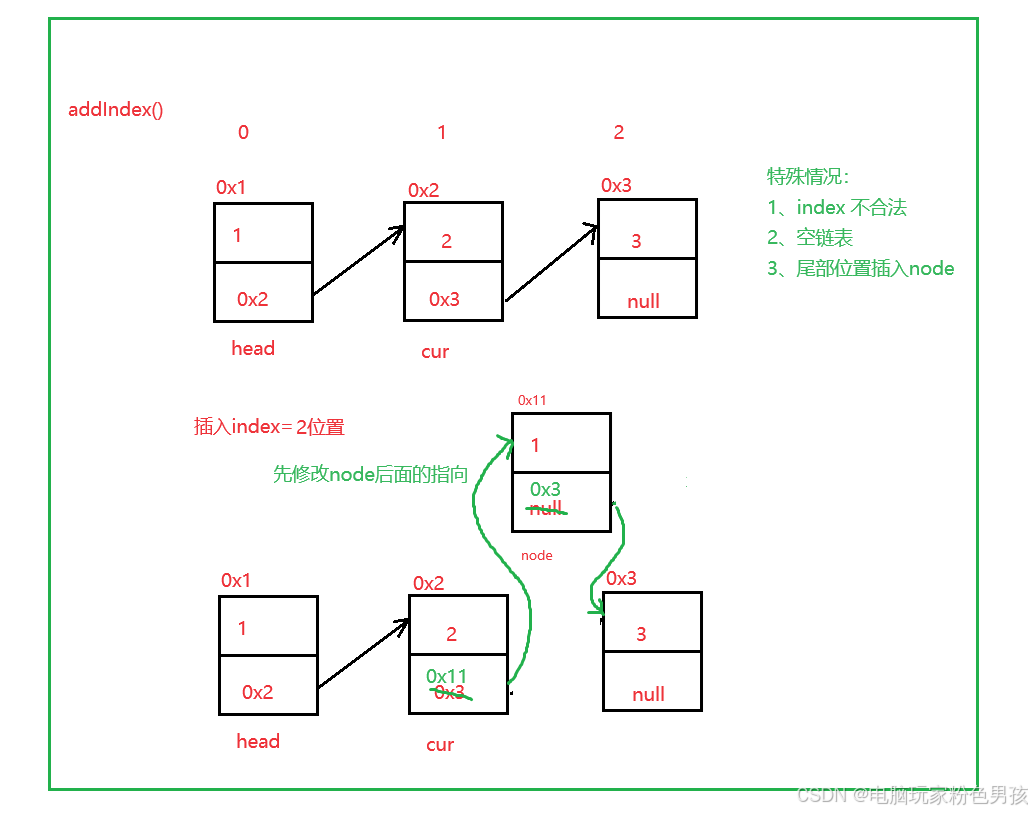
3.addIndex()
- public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
- int len = size();
- // 不合法
- if (index < 0 || index > len) {
- System.out.println("index不合法");
- return;
- }
- // 空链表
- if (index == 0) {
- addFirst(data);
- return;
- }
- // 尾部插入
- if (index == len) {
- addLast(data);
- return;
- }
-
- //中间位置插入
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (index - 1 != 0) {
- cur = cur.next;
- index--;
- }
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = cur.next;
- cur.next = node;
- }
4.содержит()
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- return true;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
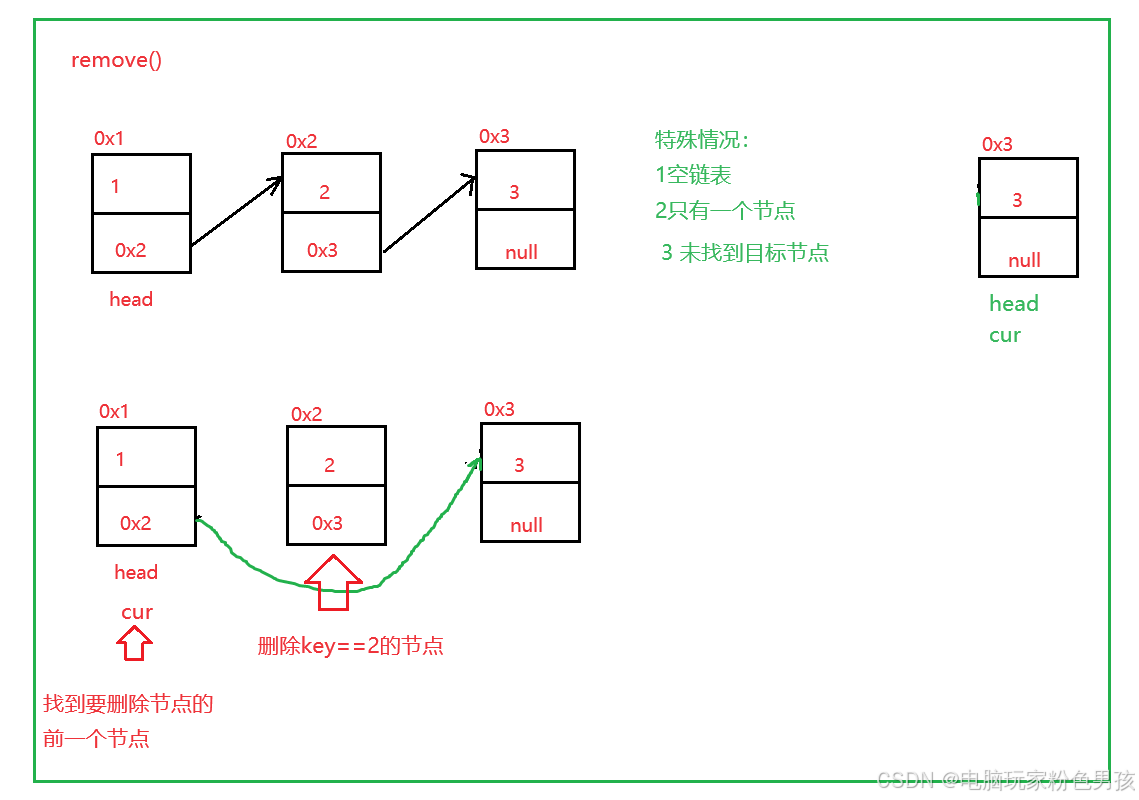
5.удалить()
- public void remove(int key) {
- if (head == null) {
- return;
- }
- if (head.val == key) {
- head = head.next;
- }
-
- ListNode cur = findNodeOfKey(key);
- if (cur == null) {
- return;
- }
- ListNode del = cur.next;
- cur.next = del.next;
- }
-
- private ListNode findNodeOfKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur.next != null) {
- if (cur.next.val == key) {
- return cur;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return null;
- }
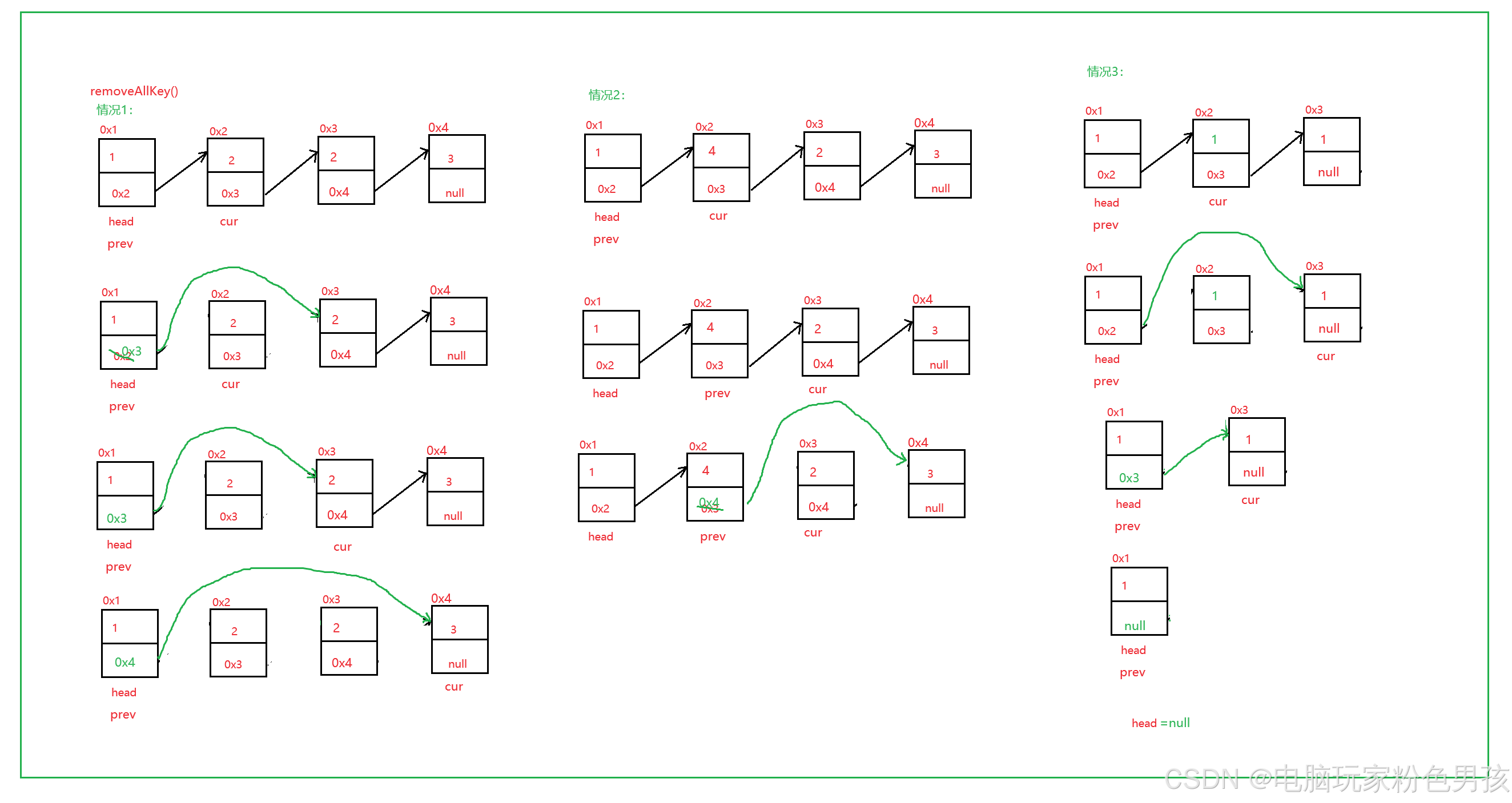
6.removeAllKey()
- public void removeAllKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head.next;
- ListNode prev = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- prev.next = cur.next;
- } else {
- prev = cur;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- if (head.val == key) {
- head = head.next;
- }
- }
7.очистить()
- public void clear() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- ListNode curNext = cur.next;
- cur.next = null;
- cur = curNext;
- }
- head = null;
- }

8.размер()
- public int size() {
- int count = 0;
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- count++;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
9.дисплей()
- public void display() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- }
- / 2、无头双向链表实现
- public class MyLinkedList {
- //头插法
- public void addFirst(int data){ }
- //尾插法
- public void addLast(int data){}
- //任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
- public void addIndex(int index,int data){}
- //查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
- public boolean contains(int key){}
- //删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
- public void remove(int key){}
- //删除所有值为key的节点
- public void removeAllKey(int key){}
- //得到单链表的长度
- public int size(){}
- public void display(){}
- public void clear(){}
- }
- package DounlyLinkedList;
-
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class MyDoublyLinkedList implements IList {
-
- static class ListNode {
- public int val;
- public ListNode next;
- public ListNode prev;
-
- public ListNode(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
-
- public ListNode head;
- public ListNode last;
-
-
- @Override
- public void addFist(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- last = node;
- } else
- node.next = head;
- head.prev = node;
- head = node;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addLast(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- last = node;
- }
- last.next = node;
- node.prev = last;
- last = node;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
- int len = size();
- if (index < 0 || index > len) {
- System.out.println("index 不合法!");
- }
-
- if (index == 0) {
- addFist(data);
- return;
- }
-
- if (index == len) {
- addLast(data);
- return;
- }
- ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = cur;
- cur.prev.next = node;
- node.prev = cur.prev;
- cur.prev = node;
- }
-
- private ListNode findIndex(int index) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (index != 0) {
- cur = cur.next;
- index--;
- }
- return cur;
- }
-
-
- @Override
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- int count = 0;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- return true;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void remove(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- if (cur == head) {
- head = head.next;
- if (head != null) {
- head.prev = null;
- }
- head.prev = null;
- } else {
- cur.prev.next = cur.next;
- if (cur.next == null) {
- last = last.prev;
- } else {
- cur.next.next = cur.prev;
- }
- }
- return;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
-
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public void removeAllKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- if (cur == head) {
- head = head.next;
- if (head != null) {
- head.prev = null;
- }
- head.prev = null;
- } else {
- cur.prev.next = cur.next;
- if (cur.next == null) {
- last = last.prev;
- } else {
- cur.next.next = cur.prev;
- }
- }
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public int size() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- int count = 0;
- while (cur != null) {
- count++;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void clear() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- ListNode curNext = cur.next;
- cur.next = null;
- cur.prev = null;
- cur = curNext;
- }
- head = null;
- last = null;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void dispaly() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- package DounlyLinkedList;
-
- public interface IList {
- void addFist(int data);
-
- void addLast(int data);
-
- void addIndex(int index, int data);
-
- boolean contains(int key);
-
- void remove(int key);
-
- void removeAllKey(int key);
-
- int size();
-
- void clear();
-
- void dispaly();
- }
4.1 Что такое LinkedLis

【иллюстрировать】
1. LinkedList реализует интерфейс списка.
2. Базовый уровень LinkedList использует двусвязный список.
3. LinkedList не реализует интерфейс RandomAccess, поэтому LinkedList не поддерживает произвольный доступ.
4. Вставка и удаление элементов в любой позиции LinkedList относительно эффективна, а временная сложность равна O(1).
5. LinkedList больше подходит для сценариев вставки в любом месте.
4.2 Использование LinkedList
1. Создание LinkedList
| метод | объяснять |
| СвязанныйСписок() | Конструкция без аргументов |
| публичный СвязанныйСписок(Коллекция | Создайте список, используя элементы из других контейнеров коллекций. |
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
- List<String> list2 = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
-
- list2.add("javaSE");
- list2.add("javaWeb");
- list2.add("javaEE");
-
- List<String> list3 = new LinkedList<>(list2);
-
- }
- }
-
-
2. Знакомство с другими распространенными методами LinkedList.
| метод | объяснять |
| логическое сложение (E e) | хвостовая заглушка e |
| void add(int index, E элемент) | Вставьте e в индексную позицию |
| логическое addAll(Коллекция c) | Вставьте элементы в c в конце |
| E удалить(целый индекс) | Удалить элемент позиции индекса |
| логическое удаление (Объект o) | Удалить первое встреченное o |
| E получить(целый индекс) | Получить элемент позиции индекса нижнего индекса |
| E set(целый индекс, элемент E) | Установите элемент позиции индекса нижнего индекса в элемент |
| пустота очистить() | Прозрачный |
| логическое значение содержит (Объект o) | Определите, находится ли o в линейной таблице |
| int indexOf(Объект o) | Вернуть индекс, в котором находится первый символ o. |
| int lastIndexOf(Объект o) | Возвращает нижний индекс последнего o |
| Список subList(целое число fromIndex, целое число toIndex) | Перехватить часть списка |
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
- list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(4);
- list.add(5);
- list.add(6);
- list.add(7);
- System.out.println(list.size());
- System.out.println(list);
- // 在起始位置插入0
- list.add(0, 0); // add(index, elem): 在index位置插入元素elem
- System.out.println(list);
- list.remove(); // remove(): 删除第一个元素,内部调用的是removeFirst()
- list.removeFirst(); // removeFirst(): 删除第一个元素
- list.removeLast(); // removeLast(): 删除最后元素
- list.remove(1); // remove(index): 删除index位置的元素
- System.out.println(list);
- // contains(elem): 检测elem元素是否存在,如果存在返回true,否则返回false
- if(!list.contains(1)){
- list.add(0, 1);
- }
- list.add(1);
- System.out.println(list);
- System.out.println(list.indexOf(1)); // indexOf(elem): 从前往后找到第一个elem的位置
- System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1)); // lastIndexOf(elem): 从后往前找第一个1的位置
- int elem = list.get(0); // get(index): 获取指定位置元素
- list.set(0, 100); // set(index, elem): 将index位置的元素设置为elem
- System.out.println(list);
- // subList(from, to): 用list中[from, to)之间的元素构造一个新的LinkedList返回
- List<Integer> copy = list.subList(0, 3);
- System.out.println(list);
- System.out.println(copy);
- list.clear(); // 将list中元素清空
- System.out.println(list.size());
- }
3. Обход LinkedList
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
- list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(4);
- list.add(5);
- list.add(6);
- list.add(7);
- System.out.println(list.size());
- // foreach遍历
- for (int e:list) {
- System.out.print(e + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
- ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
- while(it.hasNext()){
- System.out.print(it.next()+ " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
- ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
- while (rit.hasPrevious()){
- System.out.print(rit.previous() +" ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
| разница | ArrayList | СвязанныйСписок |
| На складском месте | должен быть физически непрерывным | Логически непрерывный, не обязательно физически непрерывный |
| произвольный доступ | Поддержка О (1) | Не поддерживается: O(N) |
| Головная пробка | Необходимость перемещения элементов, низкая эффективность O(N) | Просто измените указатель ссылки, временная сложность равна O (1). |
| вставлять | Когда места недостаточно, требуется расширение. | Нет понятия мощности |
| Сценарии применения | Эффективное хранение элементов + частый доступ | Частая вставка и удаление в любом месте |