내 연락처 정보
우편메소피아@프로톤메일.com
2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
ArrayList의 임의 위치에 요소를 삽입하거나 삭제하려면 이후의 요소 전체를 앞으로 또는 뒤로 이동해야 하며 시간 복잡도가 O(n)이므로 효율성이 상대적으로 낮습니다. 위치. 따라서 연결된 목록 구조인 LinkedList가 Java 컬렉션에 도입되었습니다.
2.1 연결리스트의 개념과 구조
연결리스트(linked list)는 물리적으로 비연속적인 저장 구조로, 연결리스트의 참조 링크 순서에 따라 데이터 요소의 논리적 순서가 결정된다.
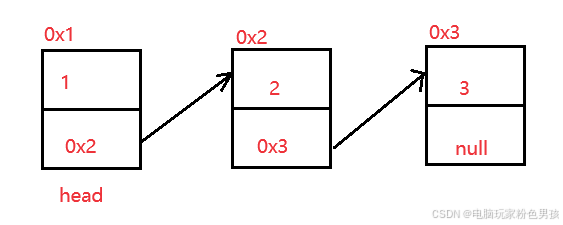
2.2 연결리스트 구현
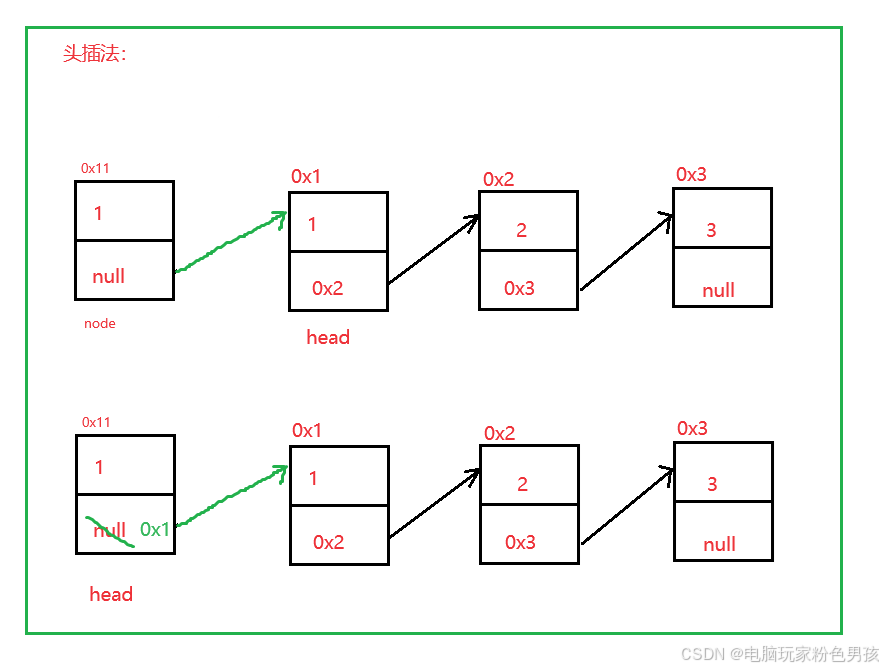
1. 헤더 삽입 메소드 addFirst()
- public void addFirst(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = head;
- head = node;
- }
2. 테일 삽입 메소드 addLast()
- public void addList(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- }
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur.next != null) {
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- cur.next = node;
- }
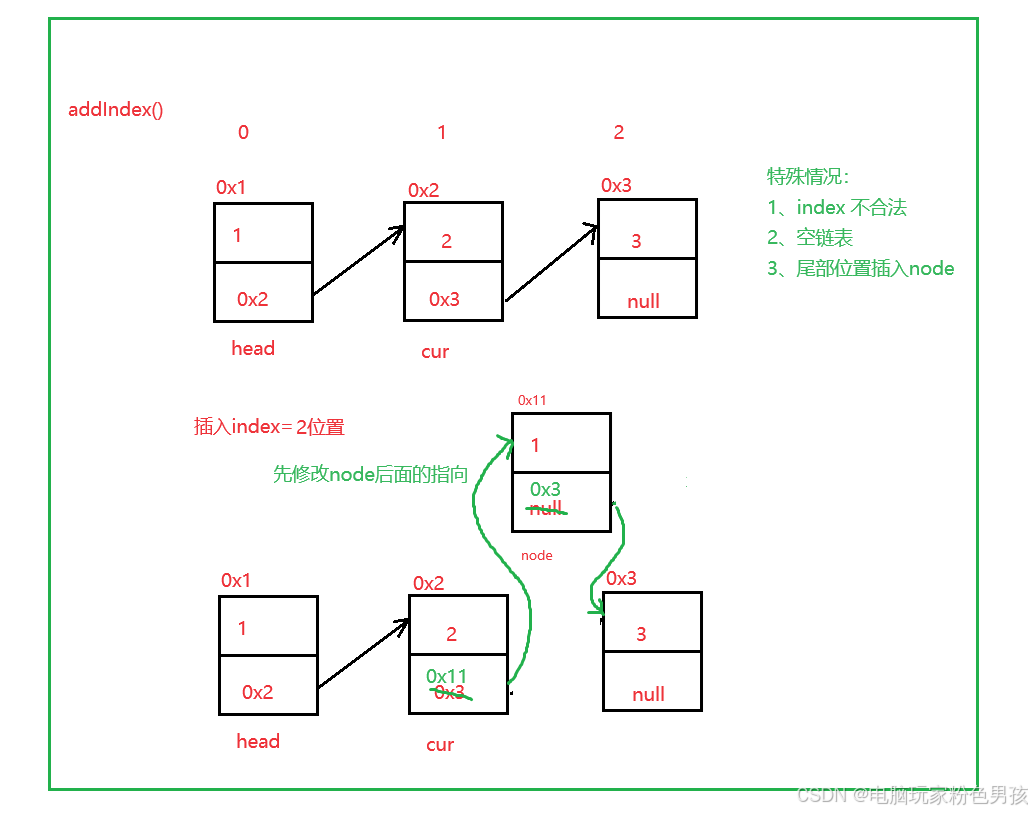
3.인덱스 추가()
- public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
- int len = size();
- // 不合法
- if (index < 0 || index > len) {
- System.out.println("index不合法");
- return;
- }
- // 空链表
- if (index == 0) {
- addFirst(data);
- return;
- }
- // 尾部插入
- if (index == len) {
- addLast(data);
- return;
- }
-
- //中间位置插入
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (index - 1 != 0) {
- cur = cur.next;
- index--;
- }
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = cur.next;
- cur.next = node;
- }
4.포함()
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- return true;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
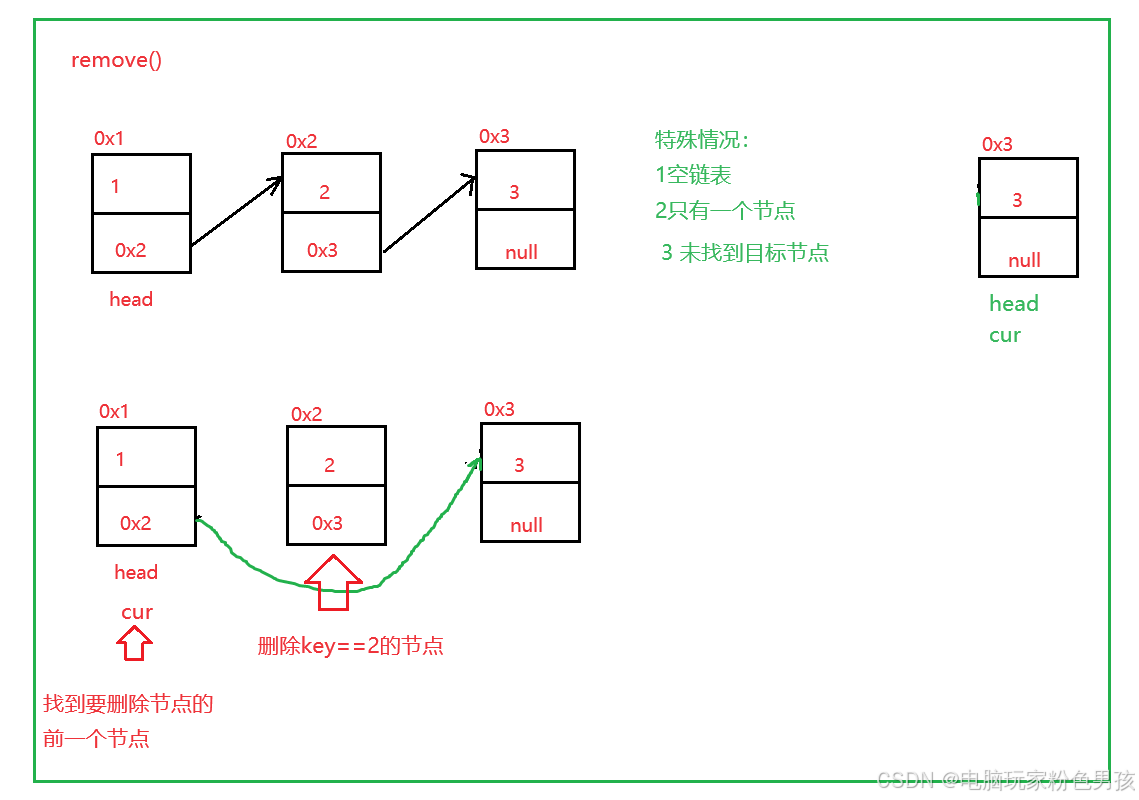
5.제거()
- public void remove(int key) {
- if (head == null) {
- return;
- }
- if (head.val == key) {
- head = head.next;
- }
-
- ListNode cur = findNodeOfKey(key);
- if (cur == null) {
- return;
- }
- ListNode del = cur.next;
- cur.next = del.next;
- }
-
- private ListNode findNodeOfKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur.next != null) {
- if (cur.next.val == key) {
- return cur;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return null;
- }
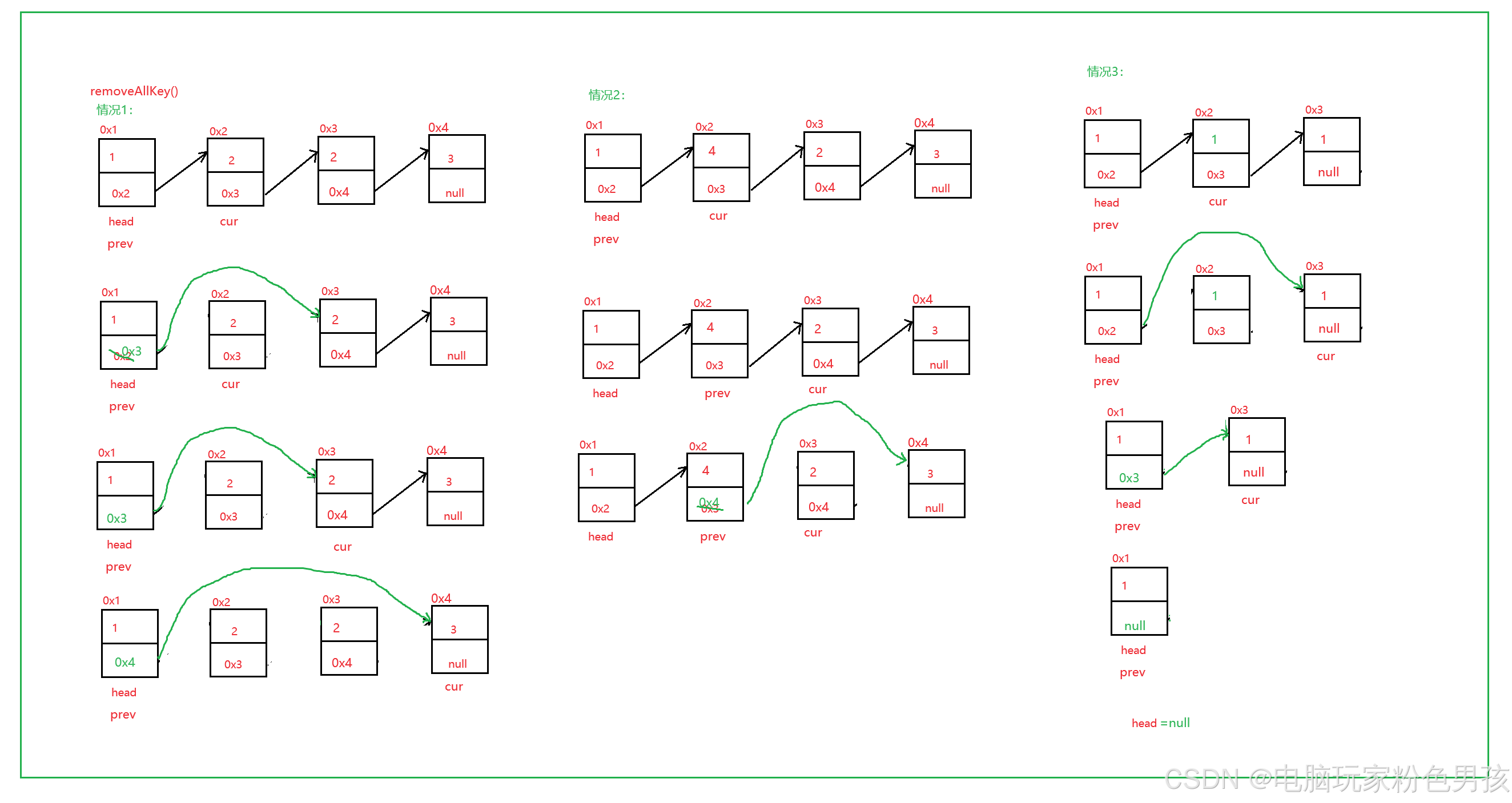
6.모든키제거()
- public void removeAllKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head.next;
- ListNode prev = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- prev.next = cur.next;
- } else {
- prev = cur;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- if (head.val == key) {
- head = head.next;
- }
- }
7.지우기()
- public void clear() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- ListNode curNext = cur.next;
- cur.next = null;
- cur = curNext;
- }
- head = null;
- }

8.크기()
- public int size() {
- int count = 0;
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- count++;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
9.디스플레이()
- public void display() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- }
- / 2、无头双向链表实现
- public class MyLinkedList {
- //头插法
- public void addFirst(int data){ }
- //尾插法
- public void addLast(int data){}
- //任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
- public void addIndex(int index,int data){}
- //查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
- public boolean contains(int key){}
- //删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
- public void remove(int key){}
- //删除所有值为key的节点
- public void removeAllKey(int key){}
- //得到单链表的长度
- public int size(){}
- public void display(){}
- public void clear(){}
- }
- package DounlyLinkedList;
-
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class MyDoublyLinkedList implements IList {
-
- static class ListNode {
- public int val;
- public ListNode next;
- public ListNode prev;
-
- public ListNode(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
-
- public ListNode head;
- public ListNode last;
-
-
- @Override
- public void addFist(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- last = node;
- } else
- node.next = head;
- head.prev = node;
- head = node;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addLast(int data) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- if (head == null) {
- head = node;
- last = node;
- }
- last.next = node;
- node.prev = last;
- last = node;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
- int len = size();
- if (index < 0 || index > len) {
- System.out.println("index 不合法!");
- }
-
- if (index == 0) {
- addFist(data);
- return;
- }
-
- if (index == len) {
- addLast(data);
- return;
- }
- ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
- ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
- node.next = cur;
- cur.prev.next = node;
- node.prev = cur.prev;
- cur.prev = node;
- }
-
- private ListNode findIndex(int index) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (index != 0) {
- cur = cur.next;
- index--;
- }
- return cur;
- }
-
-
- @Override
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- int count = 0;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- return true;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void remove(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- if (cur == head) {
- head = head.next;
- if (head != null) {
- head.prev = null;
- }
- head.prev = null;
- } else {
- cur.prev.next = cur.next;
- if (cur.next == null) {
- last = last.prev;
- } else {
- cur.next.next = cur.prev;
- }
- }
- return;
- }
- cur = cur.next;
-
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public void removeAllKey(int key) {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == key) {
- if (cur == head) {
- head = head.next;
- if (head != null) {
- head.prev = null;
- }
- head.prev = null;
- } else {
- cur.prev.next = cur.next;
- if (cur.next == null) {
- last = last.prev;
- } else {
- cur.next.next = cur.prev;
- }
- }
- }
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public int size() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- int count = 0;
- while (cur != null) {
- count++;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void clear() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- ListNode curNext = cur.next;
- cur.next = null;
- cur.prev = null;
- cur = curNext;
- }
- head = null;
- last = null;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void dispaly() {
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- package DounlyLinkedList;
-
- public interface IList {
- void addFist(int data);
-
- void addLast(int data);
-
- void addIndex(int index, int data);
-
- boolean contains(int key);
-
- void remove(int key);
-
- void removeAllKey(int key);
-
- int size();
-
- void clear();
-
- void dispaly();
- }
4.1 LinkedLis란 무엇입니까?

【그림을 그리다】
1. LinkedList는 List 인터페이스를 구현합니다.
2. LinkedList의 기본 레이어는 이중 연결 목록을 사용합니다.
3. LinkedList는 RandomAccess 인터페이스를 구현하지 않으므로 LinkedList는 임의 액세스를 지원하지 않습니다.
4. LinkedList의 임의 위치에 요소를 삽입하고 삭제하는 것은 상대적으로 효율적이며 시간 복잡도는 O(1)입니다.
5. LinkedList는 모든 위치의 삽입 시나리오에 더 적합합니다.
4.2 LinkedList의 사용
1. LinkedList 구축
| 방법 | 설명하다 |
| 연결 리스트() | 무인수 건설 |
| 공개 LinkedList(컬렉션 | 다른 컬렉션 컨테이너의 요소를 사용하여 목록 구성 |
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
- List<String> list2 = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
-
- list2.add("javaSE");
- list2.add("javaWeb");
- list2.add("javaEE");
-
- List<String> list3 = new LinkedList<>(list2);
-
- }
- }
-
-
2. LinkedList의 다른 일반적인 방법 소개
| 방법 | 설명하다 |
| 불리언 추가(E e) | 테일 플러그 e |
| void add(int 인덱스, E 요소) | 인덱스 위치에 e 삽입 |
| boolean addAll(컬렉션 c) | c의 끝에 요소 삽입 |
| E 제거(int index) | 인덱스 위치 요소 삭제 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 처음 발생한 o 삭제 |
| E get(int 인덱스) | 아래 첨자 색인 위치 요소를 가져옵니다. |
| E set(int 인덱스, E 요소) | 아래 첨자 색인 위치 요소를 요소로 설정 |
| 무효 지우기() | 분명한 |
| boolean 포함(Object o) | o가 선형 테이블에 있는지 확인 |
| int indexOf(객체 o) | 첫 번째 o가 위치한 인덱스를 반환합니다. |
| int lastIndexOf(객체 o) | 마지막 o의 첨자를 반환합니다. |
| 리스트 subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 목록의 일부를 가로채기 |
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
- list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(4);
- list.add(5);
- list.add(6);
- list.add(7);
- System.out.println(list.size());
- System.out.println(list);
- // 在起始位置插入0
- list.add(0, 0); // add(index, elem): 在index位置插入元素elem
- System.out.println(list);
- list.remove(); // remove(): 删除第一个元素,内部调用的是removeFirst()
- list.removeFirst(); // removeFirst(): 删除第一个元素
- list.removeLast(); // removeLast(): 删除最后元素
- list.remove(1); // remove(index): 删除index位置的元素
- System.out.println(list);
- // contains(elem): 检测elem元素是否存在,如果存在返回true,否则返回false
- if(!list.contains(1)){
- list.add(0, 1);
- }
- list.add(1);
- System.out.println(list);
- System.out.println(list.indexOf(1)); // indexOf(elem): 从前往后找到第一个elem的位置
- System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1)); // lastIndexOf(elem): 从后往前找第一个1的位置
- int elem = list.get(0); // get(index): 获取指定位置元素
- list.set(0, 100); // set(index, elem): 将index位置的元素设置为elem
- System.out.println(list);
- // subList(from, to): 用list中[from, to)之间的元素构造一个新的LinkedList返回
- List<Integer> copy = list.subList(0, 3);
- System.out.println(list);
- System.out.println(copy);
- list.clear(); // 将list中元素清空
- System.out.println(list.size());
- }
3. LinkedList 순회
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
- list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(4);
- list.add(5);
- list.add(6);
- list.add(7);
- System.out.println(list.size());
- // foreach遍历
- for (int e:list) {
- System.out.print(e + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
- ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
- while(it.hasNext()){
- System.out.print(it.next()+ " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
- ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
- while (rit.hasPrevious()){
- System.out.print(rit.previous() +" ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
| 차이점 | 배열 목록 | 연결 리스트 |
| 저장 공간에 | 물리적으로 연속적이어야 함 | 논리적으로 연속적이지만 반드시 물리적으로 연속적일 필요는 없음 |
| 무작위 액세스 | 지원 O(1) | 지원되지 않음: O(N) |
| 헤드 플러그 | 요소 이동 필요, 효율성 낮음 O(N) | 참조 포인터를 수정하면 시간 복잡도는 O(1)입니다. |
| 끼워 넣다 | 공간이 부족할 경우 확장이 필요함 | 용량 개념이 없음 |
| 애플리케이션 시나리오 | 효율적인 요소 저장 + 빈번한 액세스 | 어느 위치에서나 자주 삽입 및 삭제됨 |