2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
Table of contents
3. Define direction calculation function
4. Extract required information from txt file
5. Calculate the target’s direction change angle between adjacent photos
6. Calculate the moving distance and speed of the target between adjacent photos
- //字符串分割
- vector<string> split(const string &s, char delimiter) {
- vector<string> tokens;
- string token;
- istringstream tokenStream(s);
- while (getline(tokenStream, token, delimiter)) {
- tokens.push_back(token);
- }
- return tokens;
- }
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846 // piIn order to obtain the moving direction of the target in the plane, this paper adopts the 360° direction method commonly used in the military field. That is, the north is 0°, and the clockwise direction is 0-360°. For example, the east direction is 90° in our direction system.
some of,
double lon1_rad = lon1 * M_PI / 180.0;
double lat1_rad = lat1 * M_PI / 180.0;
double lon2_rad = lon2 * M_PI / 180.0;
double lat2_rad = lat2 * M_PI / 180.0;
Measured in radians.
- //方向函数
- double calculateDirectionAngle(double lon1, double lat1, double lon2, double lat2) {
- // Convert degrees to radians
- double lon1_rad = lon1 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lat1_rad = lat1 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lon2_rad = lon2 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lat2_rad = lat2 * M_PI / 180.0;
-
- // Calculate delta longitude and convert to radians
- double delta_lon_rad = (lon2 - lon1) * M_PI / 180.0;
-
- // Calculate y and x components
- double y = sin(delta_lon_rad) * cos(lat2_rad);
- double x = cos(lat1_rad) * sin(lat2_rad) - sin(lat1_rad) * cos(lat2_rad) * cos(delta_lon_rad);
-
- // Calculate direction angle in radians
- double direction_rad = atan2(y, x);
-
- // Convert direction angle to degrees
- double direction_deg = direction_rad * 180.0 / M_PI;
-
- // Ensure direction angle is within [0, 360) degrees
- if (direction_deg < 0) {
- direction_deg += 360.0;
- }
-
- return direction_deg;
- }
-
- ifstream file("LBH.txt");
- if (!file.is_open()) {
- cerr << "Could not open the file!" << endl;
- return 1;
- }
-
- string line;
- // Skip the header line
- getline(file, line);
-
- vector<vector<string>> extractedData;
-
- // Read each line from the file
- while (getline(file, line)) {
- vector<string> columns = split(line, 't');
- if (columns.size() < 16) {
- cerr << "Invalid line format" << endl;
- continue;
- }
-
- // Extract the required columns: 0, 13, 14, 15
- vector<string> extractedColumns;
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[0]); // Image Name
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[13]); // Longitude
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[14]); // Latitude
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[15]); // Altitude
-
- extractedData.push_back(extractedColumns);
- }
-
- file.close();
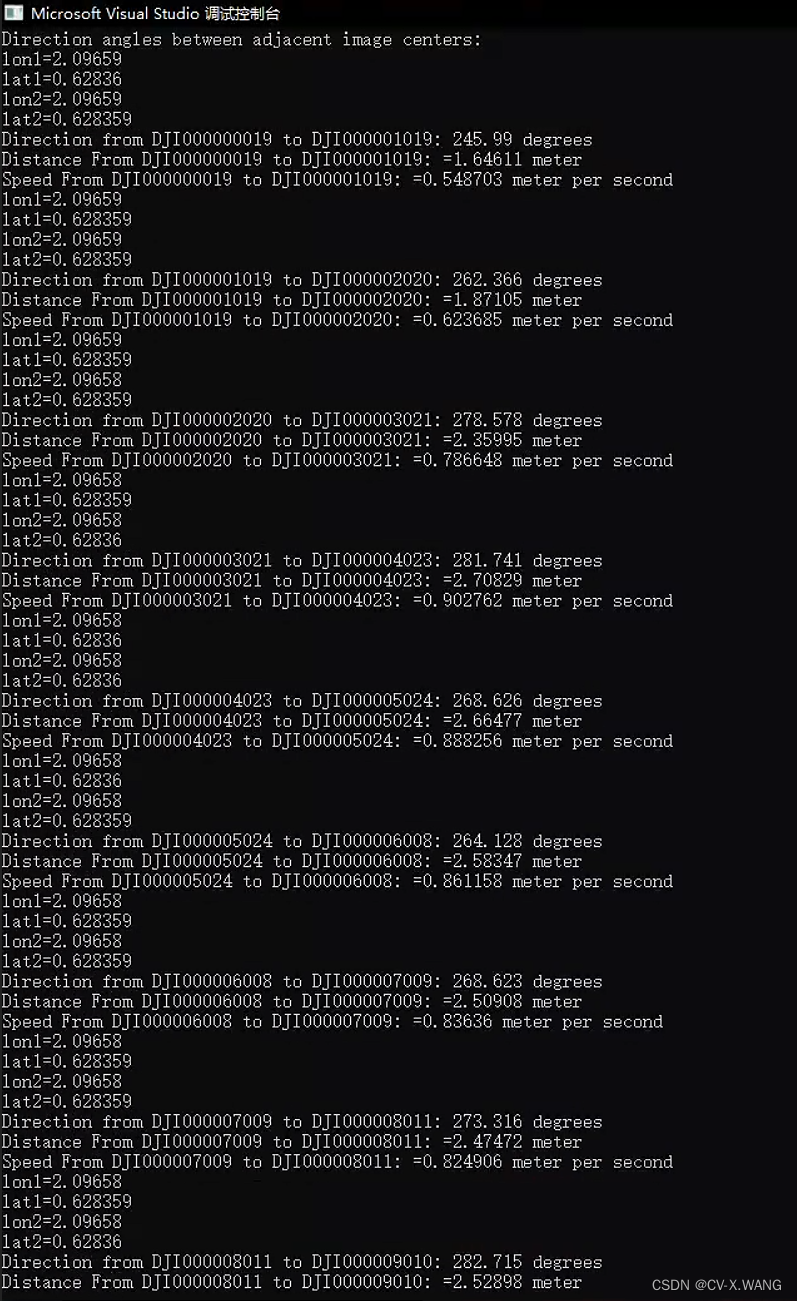
- cout << "Direction angles between adjacent image centers:" << endl;
- for (size_t i = 1; i < extractedData.size(); ++i) {
- //三角函数计算用弧度制
- double lon1 = (stod(extractedData[i - 1][1]))* M_PI/180; // Longitude
- double lat1 = (stod(extractedData[i - 1][2]))* M_PI / 180; // Latitude
- double lon2 = (stod(extractedData[i][1]))* M_PI / 180; // Longitude
- double lat2 = (stod(extractedData[i][2]))* M_PI / 180; // Latitude
- //计算方向变化角也要用弧度制
- double direction_angle = calculateDirectionAngle(lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2);
- cout << "lon1=" << lon1 << endl << "lat1=" << lat1 << endl << "lon2=" << lon2 << endl << "lat2=" << lat2 << endl;
- // Output Direction
- cout << "Direction from " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << direction_angle << " degrees" << endl;
Please note: Here we get the distance calculation formula as:

This is just the simplest demonstration. In actual situations, we need to consider a series of conditions such as the coordinate system and the location of the survey area to obtain a more accurate distance.
- double lon2_1 = lon2 - lon1;
- double lat2_1 = lat2 - lat1;
- double lon_ = lon2_1 / 2;//1/2的Δlon
- double lat_ = lat2_1 / 2; //1 / 2的Δlat
- double sin2lon_ = sin(lon_)*sin(lon_);//sin²(1/2Δlon)
- double sin2lat_ = sin(lat_)*sin(lat_); //sin²(1 / 2Δlat)
- double cos_lat1 = cos(lat1);
- double cos_lat2 = cos(lat2);
- double sqrtA = sqrt(sin2lat_+ cos_lat1* cos_lat2*sin2lon_);
- //cout << "Direction from " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "sqrtA =" << sqrtA << endl;
- double asinA = asin(sqrtA);
- //长半轴 短半轴 单位是m
- int a_r = 6378137.0;
- int b_r = 6356752;
- double Earth_R = (2 * a_r + b_r) / 3;
- double Distance = 2 * Earth_R*asinA;
- cout << "Distance From " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "=" << Distance <<" meter"<< endl;
- int time = 3;//拍照间隔 s
- double speed = Distance / time;
- cout << "Speed From " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "=" << speed << " meter per second" << endl;
- }
- #include <iostream>
- #include <fstream>
- #include <sstream>
- #include <vector>
- #include <cmath>
-
- using namespace std;
- #define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846 // pi
- // Function to split a string by a delimiter
- vector<string> split(const string &s, char delimiter) {
- vector<string> tokens;
- string token;
- istringstream tokenStream(s);
- while (getline(tokenStream, token, delimiter)) {
- tokens.push_back(token);
- }
- return tokens;
- }
-
- // direction angle in degrees
- //原理是 在平面上以正北方向为0°方向,顺时针为0-360°
- double calculateDirectionAngle(double lon1, double lat1, double lon2, double lat2) {
- // Convert degrees to radians
- double lon1_rad = lon1 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lat1_rad = lat1 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lon2_rad = lon2 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lat2_rad = lat2 * M_PI / 180.0;
-
- // Calculate delta longitude and convert to radians
- double delta_lon_rad = (lon2 - lon1) * M_PI / 180.0;
-
- // Calculate y and x components
- double y = sin(delta_lon_rad) * cos(lat2_rad);
- double x = cos(lat1_rad) * sin(lat2_rad) - sin(lat1_rad) * cos(lat2_rad) * cos(delta_lon_rad);
-
- // Calculate direction angle in radians
- double direction_rad = atan2(y, x);
-
- // Convert direction angle to degrees
- double direction_deg = direction_rad * 180.0 / M_PI;
-
- // Ensure direction angle is within [0, 360) degrees
- if (direction_deg < 0) {
- direction_deg += 360.0;
- }
-
- return direction_deg;
- }
-
- int main() {
- ifstream file("LBH.txt");
- if (!file.is_open()) {
- cerr << "Could not open the file!" << endl;
- return 1;
- }
-
- string line;
- // Skip the header line
- getline(file, line);
-
- vector<vector<string>> extractedData;
-
- // Read each line from the file
- while (getline(file, line)) {
- vector<string> columns = split(line, 't');
- if (columns.size() < 16) {
- cerr << "Invalid line format" << endl;
- continue;
- }
-
- // Extract the required columns: 0, 13, 14, 15
- vector<string> extractedColumns;
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[0]); // Image Name
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[13]); // Longitude
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[14]); // Latitude
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[15]); // Altitude
-
- extractedData.push_back(extractedColumns);
- }
-
- file.close();
-
- // Calculate direction angles between adjacent image centers
- cout << "Direction angles between adjacent image centers:" << endl;
- for (size_t i = 1; i < extractedData.size(); ++i) {
- //三角函数计算用弧度制
- double lon1 = (stod(extractedData[i - 1][1]))* M_PI/180; // Longitude
- double lat1 = (stod(extractedData[i - 1][2]))* M_PI / 180; // Latitude
- double lon2 = (stod(extractedData[i][1]))* M_PI / 180; // Longitude
- double lat2 = (stod(extractedData[i][2]))* M_PI / 180; // Latitude
- //计算方向变化角也要用弧度制
- double direction_angle = calculateDirectionAngle(lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2);
- cout << "lon1=" << lon1 << endl << "lat1=" << lat1 << endl << "lon2=" << lon2 << endl << "lat2=" << lat2 << endl;
- // Output Direction
- cout << "Direction from " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << direction_angle << " degrees" << endl;
-
- double lon2_1 = lon2 - lon1;
- double lat2_1 = lat2 - lat1;
- double lon_ = lon2_1 / 2;//1/2的Δlon
- double lat_ = lat2_1 / 2; //1 / 2的Δlat
- double sin2lon_ = sin(lon_)*sin(lon_);//sin²(1/2Δlon)
- double sin2lat_ = sin(lat_)*sin(lat_); //sin²(1 / 2Δlat)
- double cos_lat1 = cos(lat1);
- double cos_lat2 = cos(lat2);
- double sqrtA = sqrt(sin2lat_+ cos_lat1* cos_lat2*sin2lon_);
- //cout << "Direction from " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "sqrtA =" << sqrtA << endl;
- double asinA = asin(sqrtA);
- //长半轴 短半轴 单位是m
- int a_r = 6378137.0;
- int b_r = 6356752;
- double Earth_R = (2 * a_r + b_r) / 3;
- double Distance = 2 * Earth_R*asinA;
- cout << "Distance From " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "=" << Distance <<" meter"<< endl;
- int time = 3;//拍照间隔 s
- double speed = Distance / time;
- cout << "Speed From " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "=" << speed << " meter per second" << endl;
- }
- //cin.get();
-
- return 0;
- }