le mie informazioni di contatto
Posta[email protected]
2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
Sommario
2. Definire il valore pi greco
3. Definire la funzione di calcolo della direzione
4. Estrai le informazioni richieste dal file txt
5. Calcolare l'angolo di cambio di direzione del target tra foto adiacenti
6. Calcola la distanza in movimento e la velocità del bersaglio tra foto adiacenti
3. Visualizzazione completa del codice
4. Visualizzazione dei risultati
- //字符串分割
- vector<string> split(const string &s, char delimiter) {
- vector<string> tokens;
- string token;
- istringstream tokenStream(s);
- while (getline(tokenStream, token, delimiter)) {
- tokens.push_back(token);
- }
- return tokens;
- }
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846 // piPer ottenere la direzione di movimento del bersaglio nella direzione del piano, questo articolo adotta il metodo della direzione a 360°, comune in campo militare. Cioè, il vero nord è la direzione di 0° e la direzione in senso orario è 0-360°. Ad esempio, la vera direzione est: nel nostro sistema di direzione, è la direzione 90°.
alcuni,
doppio lon1_rad = lon1 * M_PI / 180.0;
doppio lat1_rad = lat1 * M_PI / 180.0;
doppio lon2_rad = lon2 * M_PI / 180.0;
doppio lat2_rad = lat2 * M_PI / 180.0;
È in radianti.
- //方向函数
- double calculateDirectionAngle(double lon1, double lat1, double lon2, double lat2) {
- // Convert degrees to radians
- double lon1_rad = lon1 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lat1_rad = lat1 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lon2_rad = lon2 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lat2_rad = lat2 * M_PI / 180.0;
-
- // Calculate delta longitude and convert to radians
- double delta_lon_rad = (lon2 - lon1) * M_PI / 180.0;
-
- // Calculate y and x components
- double y = sin(delta_lon_rad) * cos(lat2_rad);
- double x = cos(lat1_rad) * sin(lat2_rad) - sin(lat1_rad) * cos(lat2_rad) * cos(delta_lon_rad);
-
- // Calculate direction angle in radians
- double direction_rad = atan2(y, x);
-
- // Convert direction angle to degrees
- double direction_deg = direction_rad * 180.0 / M_PI;
-
- // Ensure direction angle is within [0, 360) degrees
- if (direction_deg < 0) {
- direction_deg += 360.0;
- }
-
- return direction_deg;
- }
-
- ifstream file("LBH.txt");
- if (!file.is_open()) {
- cerr << "Could not open the file!" << endl;
- return 1;
- }
-
- string line;
- // Skip the header line
- getline(file, line);
-
- vector<vector<string>> extractedData;
-
- // Read each line from the file
- while (getline(file, line)) {
- vector<string> columns = split(line, 't');
- if (columns.size() < 16) {
- cerr << "Invalid line format" << endl;
- continue;
- }
-
- // Extract the required columns: 0, 13, 14, 15
- vector<string> extractedColumns;
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[0]); // Image Name
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[13]); // Longitude
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[14]); // Latitude
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[15]); // Altitude
-
- extractedData.push_back(extractedColumns);
- }
-
- file.close();
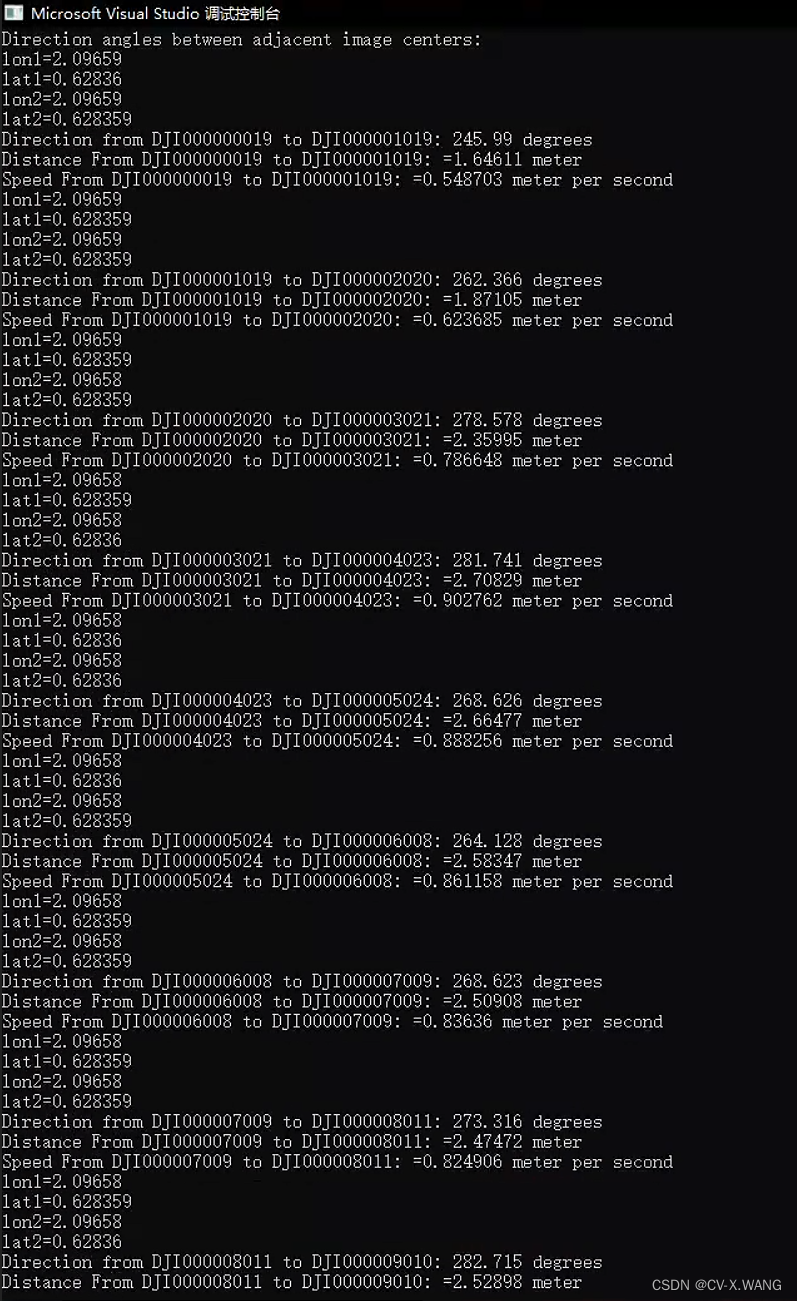
- cout << "Direction angles between adjacent image centers:" << endl;
- for (size_t i = 1; i < extractedData.size(); ++i) {
- //三角函数计算用弧度制
- double lon1 = (stod(extractedData[i - 1][1]))* M_PI/180; // Longitude
- double lat1 = (stod(extractedData[i - 1][2]))* M_PI / 180; // Latitude
- double lon2 = (stod(extractedData[i][1]))* M_PI / 180; // Longitude
- double lat2 = (stod(extractedData[i][2]))* M_PI / 180; // Latitude
- //计算方向变化角也要用弧度制
- double direction_angle = calculateDirectionAngle(lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2);
- cout << "lon1=" << lon1 << endl << "lat1=" << lat1 << endl << "lon2=" << lon2 << endl << "lat2=" << lat2 << endl;
- // Output Direction
- cout << "Direction from " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << direction_angle << " degrees" << endl;
Nota: la formula di calcolo per la distanza che otteniamo qui è:

Questa è solo la dimostrazione più semplice. Nelle situazioni reali, dobbiamo considerare una serie di condizioni come il sistema di coordinate, la posizione dell'area di misurazione, ecc., per ottenere una distanza più precisa.
- double lon2_1 = lon2 - lon1;
- double lat2_1 = lat2 - lat1;
- double lon_ = lon2_1 / 2;//1/2的Δlon
- double lat_ = lat2_1 / 2; //1 / 2的Δlat
- double sin2lon_ = sin(lon_)*sin(lon_);//sin²(1/2Δlon)
- double sin2lat_ = sin(lat_)*sin(lat_); //sin²(1 / 2Δlat)
- double cos_lat1 = cos(lat1);
- double cos_lat2 = cos(lat2);
- double sqrtA = sqrt(sin2lat_+ cos_lat1* cos_lat2*sin2lon_);
- //cout << "Direction from " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "sqrtA =" << sqrtA << endl;
- double asinA = asin(sqrtA);
- //长半轴 短半轴 单位是m
- int a_r = 6378137.0;
- int b_r = 6356752;
- double Earth_R = (2 * a_r + b_r) / 3;
- double Distance = 2 * Earth_R*asinA;
- cout << "Distance From " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "=" << Distance <<" meter"<< endl;
- int time = 3;//拍照间隔 s
- double speed = Distance / time;
- cout << "Speed From " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "=" << speed << " meter per second" << endl;
- }
- #include <iostream>
- #include <fstream>
- #include <sstream>
- #include <vector>
- #include <cmath>
-
- using namespace std;
- #define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846 // pi
- // Function to split a string by a delimiter
- vector<string> split(const string &s, char delimiter) {
- vector<string> tokens;
- string token;
- istringstream tokenStream(s);
- while (getline(tokenStream, token, delimiter)) {
- tokens.push_back(token);
- }
- return tokens;
- }
-
- // direction angle in degrees
- //原理是 在平面上以正北方向为0°方向,顺时针为0-360°
- double calculateDirectionAngle(double lon1, double lat1, double lon2, double lat2) {
- // Convert degrees to radians
- double lon1_rad = lon1 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lat1_rad = lat1 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lon2_rad = lon2 * M_PI / 180.0;
- double lat2_rad = lat2 * M_PI / 180.0;
-
- // Calculate delta longitude and convert to radians
- double delta_lon_rad = (lon2 - lon1) * M_PI / 180.0;
-
- // Calculate y and x components
- double y = sin(delta_lon_rad) * cos(lat2_rad);
- double x = cos(lat1_rad) * sin(lat2_rad) - sin(lat1_rad) * cos(lat2_rad) * cos(delta_lon_rad);
-
- // Calculate direction angle in radians
- double direction_rad = atan2(y, x);
-
- // Convert direction angle to degrees
- double direction_deg = direction_rad * 180.0 / M_PI;
-
- // Ensure direction angle is within [0, 360) degrees
- if (direction_deg < 0) {
- direction_deg += 360.0;
- }
-
- return direction_deg;
- }
-
- int main() {
- ifstream file("LBH.txt");
- if (!file.is_open()) {
- cerr << "Could not open the file!" << endl;
- return 1;
- }
-
- string line;
- // Skip the header line
- getline(file, line);
-
- vector<vector<string>> extractedData;
-
- // Read each line from the file
- while (getline(file, line)) {
- vector<string> columns = split(line, 't');
- if (columns.size() < 16) {
- cerr << "Invalid line format" << endl;
- continue;
- }
-
- // Extract the required columns: 0, 13, 14, 15
- vector<string> extractedColumns;
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[0]); // Image Name
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[13]); // Longitude
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[14]); // Latitude
- extractedColumns.push_back(columns[15]); // Altitude
-
- extractedData.push_back(extractedColumns);
- }
-
- file.close();
-
- // Calculate direction angles between adjacent image centers
- cout << "Direction angles between adjacent image centers:" << endl;
- for (size_t i = 1; i < extractedData.size(); ++i) {
- //三角函数计算用弧度制
- double lon1 = (stod(extractedData[i - 1][1]))* M_PI/180; // Longitude
- double lat1 = (stod(extractedData[i - 1][2]))* M_PI / 180; // Latitude
- double lon2 = (stod(extractedData[i][1]))* M_PI / 180; // Longitude
- double lat2 = (stod(extractedData[i][2]))* M_PI / 180; // Latitude
- //计算方向变化角也要用弧度制
- double direction_angle = calculateDirectionAngle(lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2);
- cout << "lon1=" << lon1 << endl << "lat1=" << lat1 << endl << "lon2=" << lon2 << endl << "lat2=" << lat2 << endl;
- // Output Direction
- cout << "Direction from " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << direction_angle << " degrees" << endl;
-
- double lon2_1 = lon2 - lon1;
- double lat2_1 = lat2 - lat1;
- double lon_ = lon2_1 / 2;//1/2的Δlon
- double lat_ = lat2_1 / 2; //1 / 2的Δlat
- double sin2lon_ = sin(lon_)*sin(lon_);//sin²(1/2Δlon)
- double sin2lat_ = sin(lat_)*sin(lat_); //sin²(1 / 2Δlat)
- double cos_lat1 = cos(lat1);
- double cos_lat2 = cos(lat2);
- double sqrtA = sqrt(sin2lat_+ cos_lat1* cos_lat2*sin2lon_);
- //cout << "Direction from " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "sqrtA =" << sqrtA << endl;
- double asinA = asin(sqrtA);
- //长半轴 短半轴 单位是m
- int a_r = 6378137.0;
- int b_r = 6356752;
- double Earth_R = (2 * a_r + b_r) / 3;
- double Distance = 2 * Earth_R*asinA;
- cout << "Distance From " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "=" << Distance <<" meter"<< endl;
- int time = 3;//拍照间隔 s
- double speed = Distance / time;
- cout << "Speed From " << extractedData[i - 1][0] << " to " << extractedData[i][0] << ": " << "=" << speed << " meter per second" << endl;
- }
- //cin.get();
-
- return 0;
- }