2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
With the popularity of concepts such as MPC and privacy computing, many government agencies and financial companies have begun to consider participating in multi-party computing scenarios to expand the application value of data.
Taking the following scenario as an example, a bank may want to obtain data from the Water Conservancy Bureau and the Taxation Bureau to comprehensively calculate the credit rating of each company.
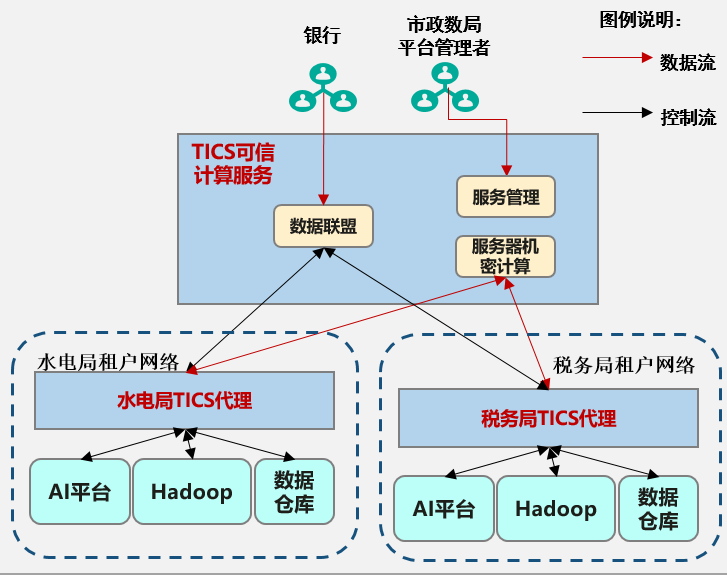
Through strategies such as TEE and MPC, it is possible to prevent the leakage of intermediate data during the calculation process.
However, the calculation results will eventually be returned to the job initiator. For example, when the initiator tries to query [enterprise id, water consumption + electricity consumption], the privacy computing platform can only ensure that the electricity consumption and water consumption are not leaked separately, but cannot ensure that the sum of water consumption and electricity consumption is not leaked. After all, this sum is presented as the calculation result.
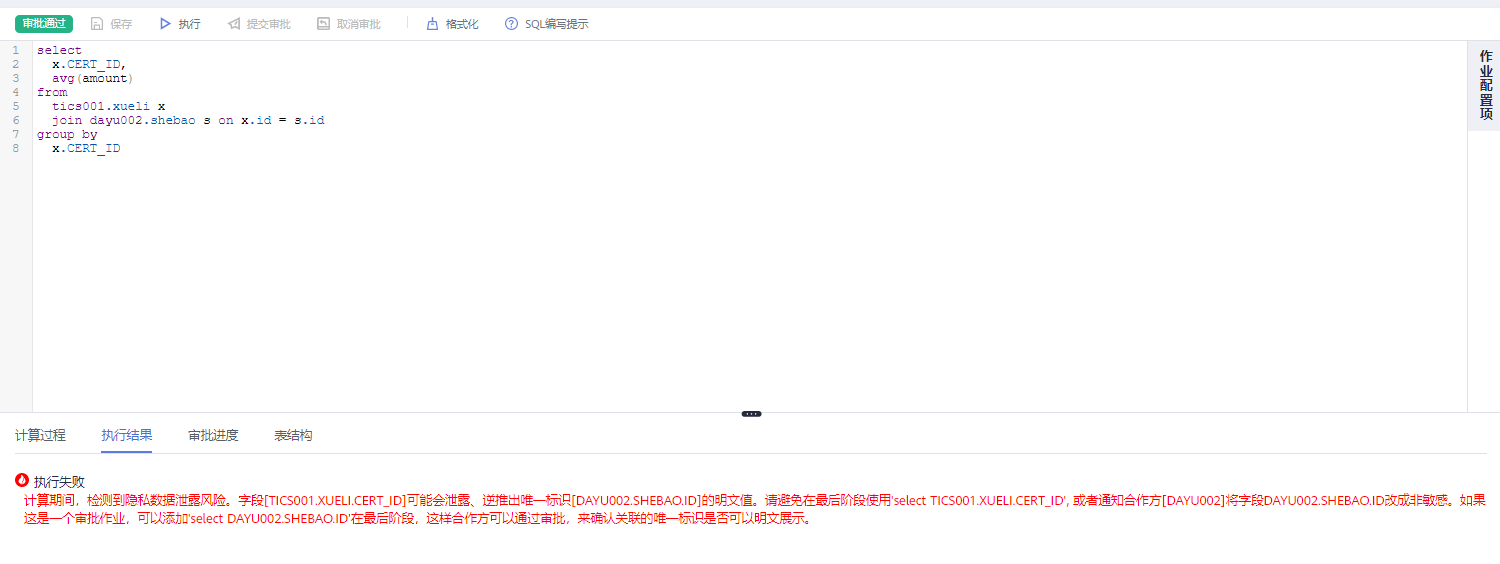
Therefore, the question of "whether the calculation results will leak sensitive data" cannot be solved by strategies such as TEE and MPC.
The privacy computing platform forcibly restricts the use of sensitive data by setting complex privacy policies and specifying a few SQL scenarios.
For example, directly rejecting the ID field and exposing sensitive data fields in plain text.
This type of algorithm can protect the aggregation results of sensitive data from being reversed, but it is limited to the aggregation results of sensitive data. If the job initiator has needs beyond the application of the algorithm, it is necessary to rely on other more manual methods to prevent it.
However, due to the complexity of business scenarios, if the rules are too restrictive, it may prevent normal logical operations. If the restrictions are too weak, sensitive data may be maliciously obtained and lost.
Therefore, in multi-party SQL computing, each data provider and job initiator should be able toReaching consensus, confirm that the job's use of data is normal and reasonable.
However, the use of the approval mechanism requires solving the following difficulties:
1. How to parse out the key information required by each participant from a multi-party joint SQL statement so that the participant can confirm the purpose of their own data without exposing the business sensitive information of the initiator.
2. How to prevent the initiator from constructing specific SQL to obtain fields that should not be visible.
Huawei's TICS trusted intelligent computing service already supports the approval function in federated SQL jobs and solves the above problems.
When attempting to initiate a SQL multi-party job, the data provider can review and approve whether the use of such data is allowed.
The specific steps are as follows:
figure 1Submit for approval

At this time, when TICS executes the SQL statement of the analysis job, it will no longer be subject to the syntax restrictions of the privacy rules. At this time, the provider must confirm the purpose of the field before continuing to execute the SQL statement. During the approval process or after approval, if the SQL is modified and saved, it will need to be resubmitted for approval.
After submission, you can view the approver and approval progress at the bottom of the page.
figure 2Approval progress
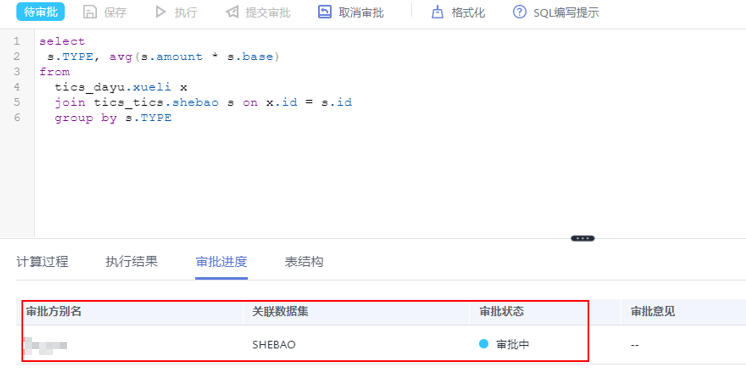
image 3Approval Management
The approval report can be seen on the details page. The report content includes the job initiator, the SQL statement that will be executed on the proxy connector, the description of the function of each field, whether it is visible in the result (that is, displayed in plain text), etc.
Figure 4Details

Figure 5Execute the job