2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina







High Innovation | CEEMDAN-VMD-GRU-Attention dual decomposition + gated recurrent unit + attention mechanism multivariate time series prediction
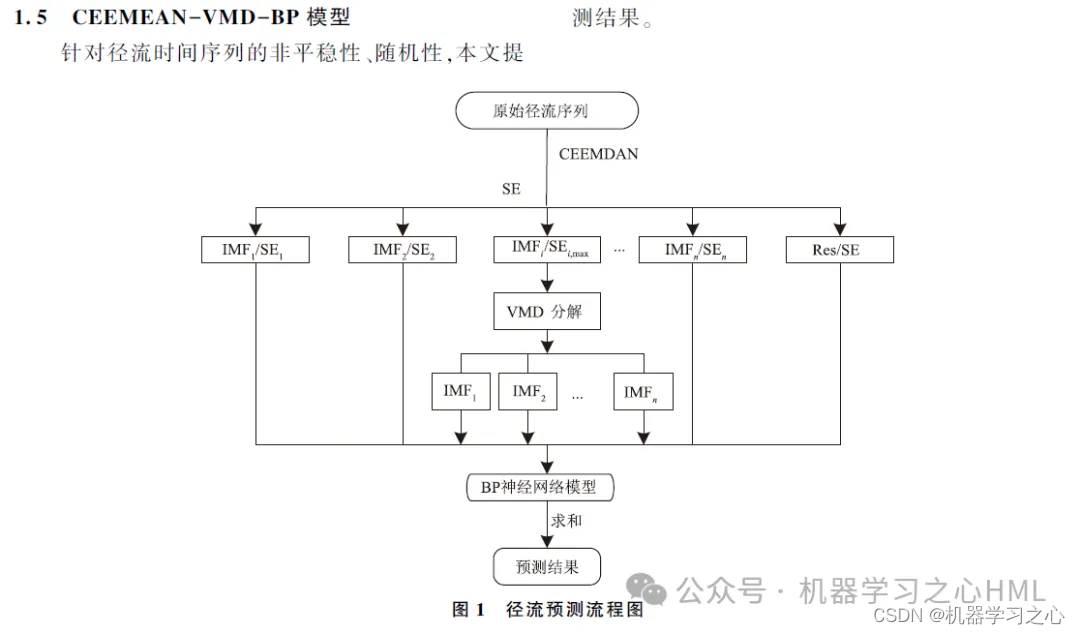
This paper proposes a secondary decomposition method based on CEEMDAN. The sequence decomposed by CEEMDAN is reconstructed through sample entropy. After the complex sequence is decomposed by VMD, each component is predicted by the GRU-Attention model respectively, and finally the prediction results are integrated.
1. Matlab implements CEEMDAN-VMD-GRU-Attention dual decomposition + gated recurrent unit + attention mechanism multivariateTime Series Forecasting(Complete source code and data)
2. CEEMDAN decomposition, calculate sample entropy, perform kmeans clustering based on sample entropy, call VMD to decompose high-frequency components for the second time, and use the high-frequency components and front components decomposed by VMD as convolutional gated recurrent unitsAttention Mechanism ModelThe target outputs are predicted separately and then added together.
3.Multi-variable single output, considering the impact of historical characteristics! Evaluation indicators include R2, MAE, RMSE, MAPE, etc.
4. Novel algorithm. The CEEMDAN-VMD-GRU-Attention model processes data with higher accuracy and can track data trends and changes. The VMD model processes nonlinear, non-stationary, and complex data better than the EMD series, so the reconstructed data is decomposed through the VMD model to improve the accuracy of the model.
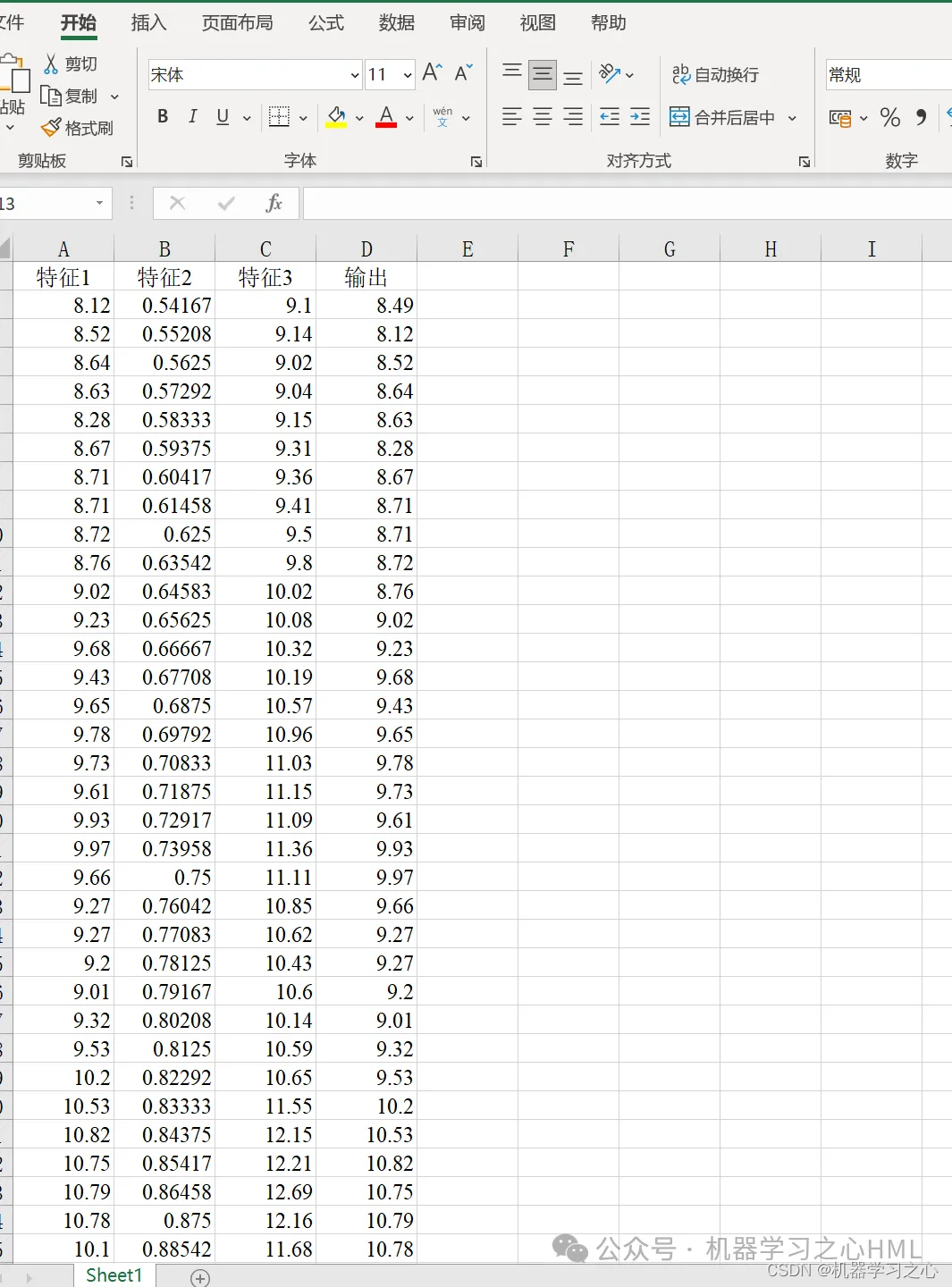
5. It can be used by directly replacing Excel data, with clear annotations, suitable for novices, and directly running the main file to produce drawings with one click.
6. Code features: parametric programming, parameters can be easily changed, clear code programming ideas, and detailed comments.



%% 清空环境变量
warning off % 关闭报警信息
close all % 关闭开启的图窗
clear % 清空变量
clc % 清空命令行
%% 划分训练集和测试集
P_train = res(1: num_train_s, 1: f_)';
T_train = res(1: num_train_s, f_ + 1: end)';
M = size(P_train, 2);
P_test = res(num_train_s + 1: end, 1: f_)';
T_test = res(num_train_s + 1: end, f_ + 1: end)';
N = size(P_test, 2);
%% 数据归一化
[P_train, ps_input] = mapminmax(P_train, 0, 1);
P_test = mapminmax('apply', P_test, ps_input);
[t_train, ps_output] = mapminmax(T_train, 0, 1);
t_test = mapminmax('apply', T_test, ps_output);
%% 数据平铺
P_train = double(reshape(P_train, f_, 1, 1, M));
P_test = double(reshape(P_test , f_, 1, 1, N));
t_train = t_train';
t_test = t_test' ;
%% 数据格式转换
for i = 1 : M
p_train{i, 1} = P_train(:, :, 1, i);
end
for i = 1 : N
p_test{i, 1} = P_test( :, :, 1, i);
end
%% 参数设置
options = trainingOptions('adam', ... % Adam 梯度下降算法
'MaxEpochs', 100, ... % 最大训练次数
'InitialLearnRate', 0.01, ... % 初始学习率为0.01
'LearnRateSchedule', 'piecewise', ... % 学习率下降
'LearnRateDropFactor', 0.1, ... % 学习率下降因子 0.1
'LearnRateDropPeriod', 70, ... % 经过训练后 学习率为 0.01*0.1
'Shuffle', 'every-epoch', ... % 每次训练打乱数据集
'Verbose', 1);
figure
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(T_train,'k--','LineWidth',1.5);
hold on
plot(T_sim_a','r-','LineWidth',1.5)
legend('真实值','预测值')
title('CEEMDAN-VMD-CNN-GRU-Attention训练集预测效果对比')
xlabel('样本点')
ylabel('数值')
subplot(2,1,2)
bar(T_sim_a'-T_train)
title('CEEMDAN-VMD-GRU-Attention训练误差图')
xlabel('样本点')
ylabel('数值')
disp('…………测试集误差指标…………')
[mae2,rmse2,mape2,error2]=calc_error(T_test,T_sim_b');
fprintf('n')
figure
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(T_test,'k--','LineWidth',1.5);
hold on
plot(T_sim_b','b-','LineWidth',1.5)
legend('真实值','预测值')
title('CEEMDAN-VMD-GRU-Attention测试集预测效果对比')
xlabel('样本点')
ylabel('数值')
subplot(2,1,2)
bar(T_sim_b'-T_test)
title('CEEMDAN-VMD-GRU-Attention测试误差图')
xlabel('样本点')
ylabel('数值')
[1] https://hmlhml.blog.csdn.net/article/details/135536086?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
[2] https://hmlhml.blog.csdn.net/article/details/137166860?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
[3] https://hmlhml.blog.csdn.net/article/details/132372151