2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
The entry point of the shuffle system. ShuffleManager is created in sparkEnv in driver and executor. Register shuffle in driver and read and write data in executor.
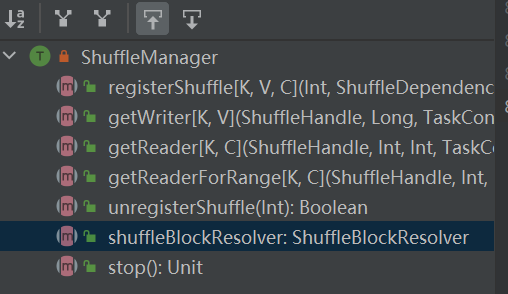
registerShuffle: register shuffle, return shuffleHandle
unregisterShuffle: remove shuffle
shuffleBlockResolver: Get shuffleBlockResolver to handle the relationship between shuffle and block
getWriter: Get the writer corresponding to the partition and call it in the executor's map task
getReader, getReaderForRange: Get the reader of a range of partitions, called in the executor's reduce task
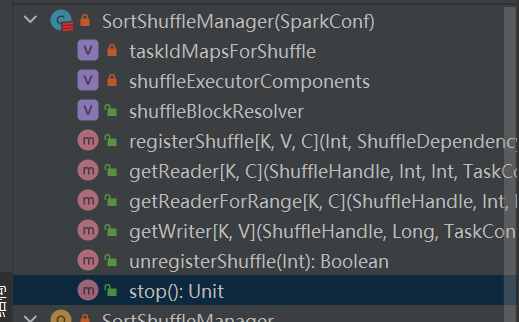
Is the only implementation of shuffleManager.
In a sort-based shuffle, incoming messages are sorted by partition and output to a single file.
The reducer will read a section of the region data from this file.
When the output file is too large to fit in memory, it will spill to disk to generate sorted intermediate result files, which will be merged into a final output file.
There are two ways to sort-based shuffle:
Advantages of serialized sort
In serialized sort mode, the shuffle writer serializes the incoming messages, stores them in a data structure and sorts them.
Select the corresponding handle according to different scenarios. The priority is BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle>SerializedShuffleHandle>BaseShuffleHandle
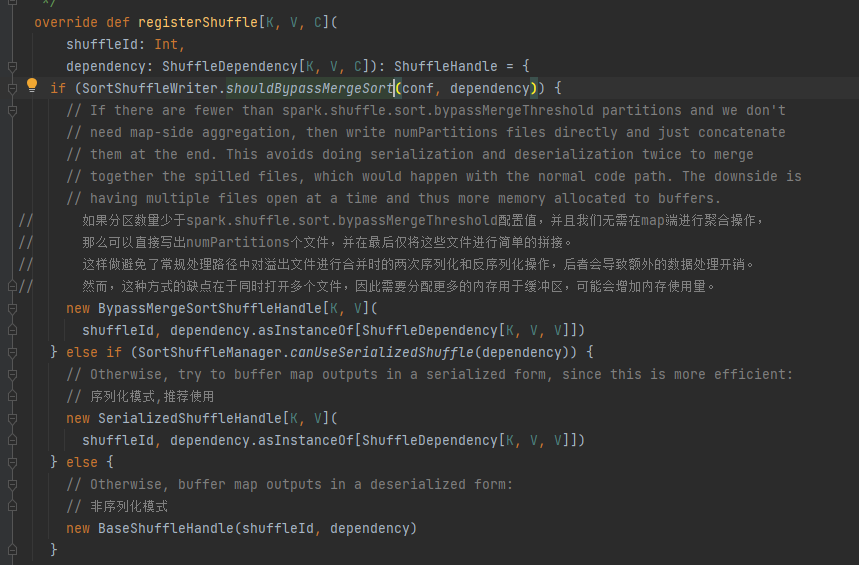
Bypass condition: no mapside, the number of partitions is less than or equal to _SHUFFLE_SORT_BYPASS_MERGE_THRESHOLD_

Serialization handle conditions: The serialization class supports the migration of serialized objects, does not use the mapSideCombine operation, and the number of partitions of the parent RDD is not greater than (1 << 24)
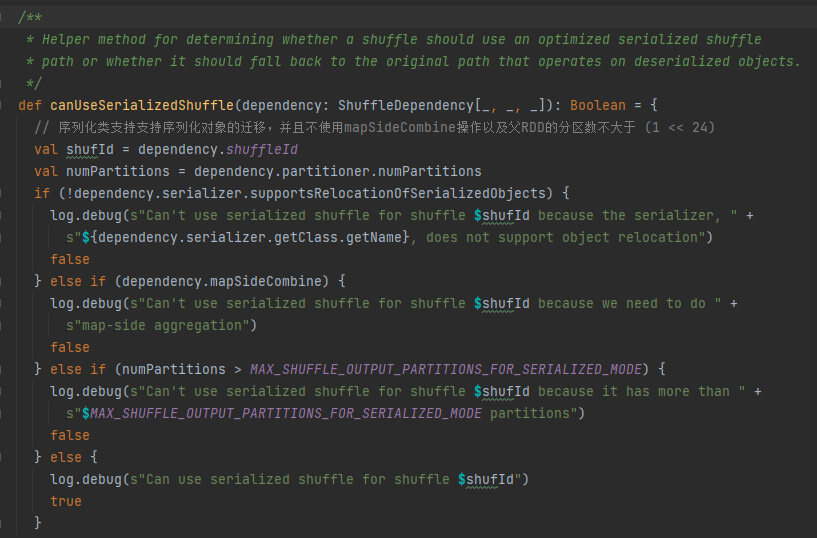
First, cache the shuffle and map information in taskIdMapsForShuffle_
Select the corresponding writer according to the handle corresponding to the shuffle.
BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle->BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter
SerializedShuffleHandle->UnsafeShuffleWriter
BaseShuffleHandle->SortShuffleWriter
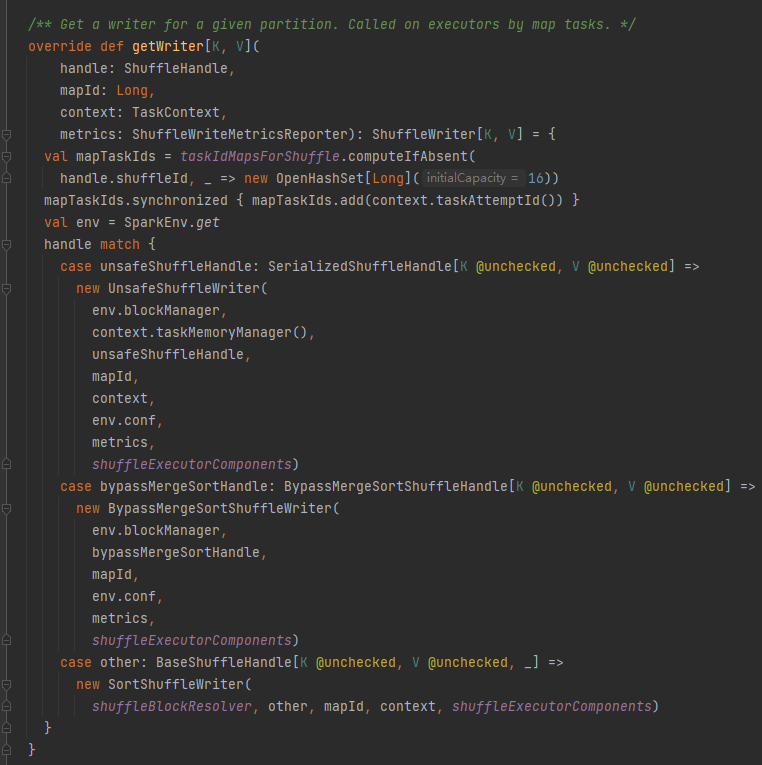
taskIdMapsForShuffle removes the corresponding shuffle and the files generated by the shuffle corresponding map
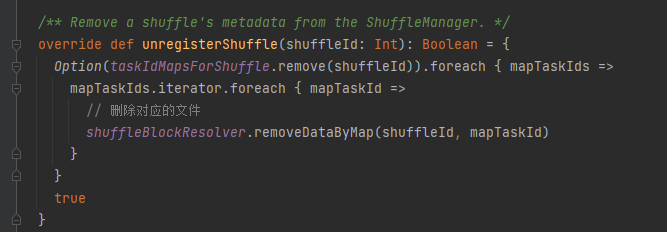
Get all block addresses corresponding to the shuffle file, i.e. blocksByAddress.
Creates a BlockStoreShuffleReader object and returns it.
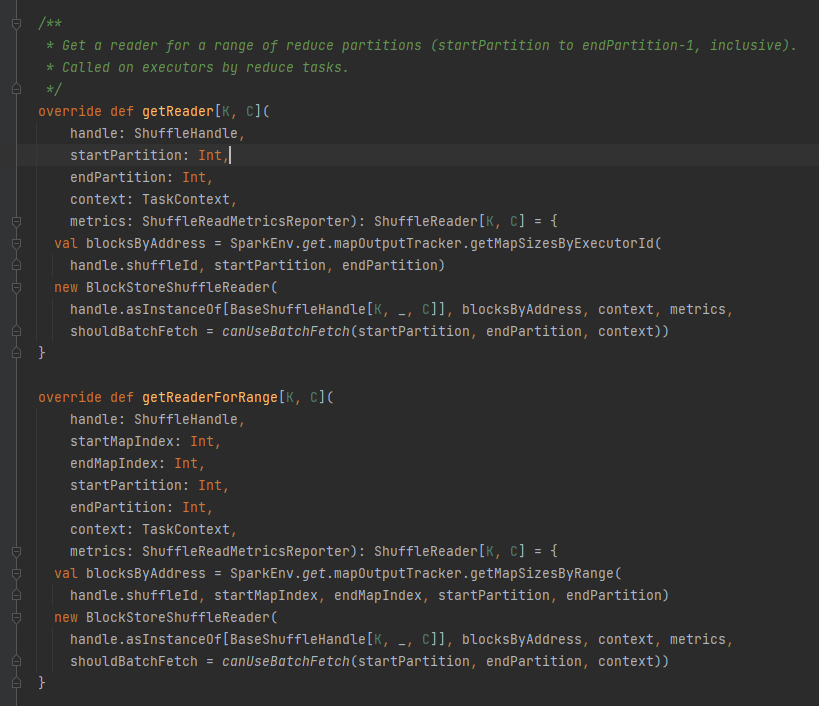
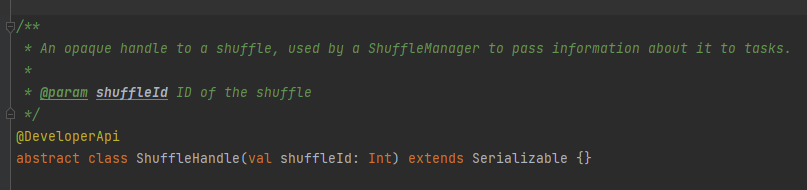
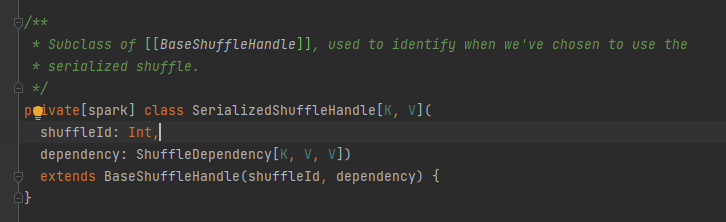
It is mainly used to pass shuffle parameters, and is also a marker to select which writer


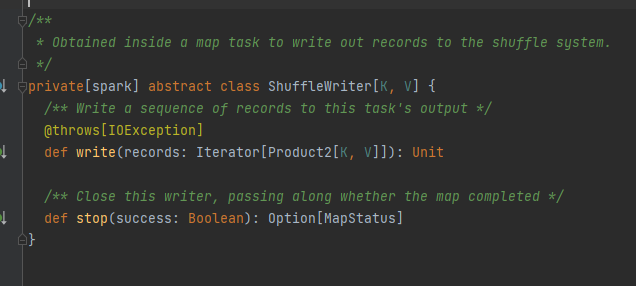
Abstract class, responsible for map task output message. The main method is write, there are three implementation classes
This will be analyzed separately later.
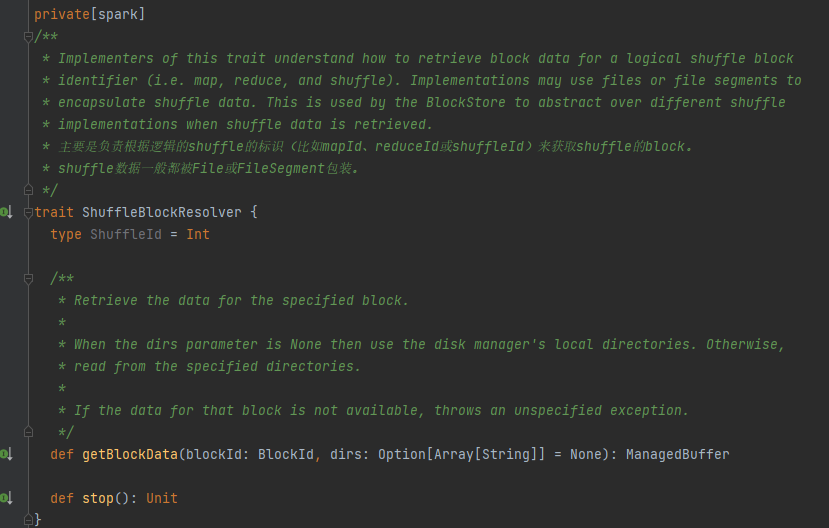
Traits, the implementation class can obtain the corresponding block data according to mapId, reduceId, and shuffleId.
The only implementation class of ShuffleBlockResolver.
Create and maintain a mapping between logical blocks and physical file locations for shuffle block data from the same map task.
The shuffle block data belonging to the same map task will be stored in an integrated data file.
The offsets of these data blocks in the data file are stored separately in an index file.
.data is the suffix of the data file
.index is the index file suffix
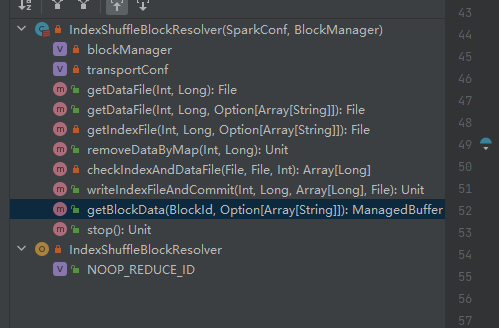
Get the data file.
Generate ShuffleDataBlockId and call blockManager.diskBlockManager.getFile method to get file
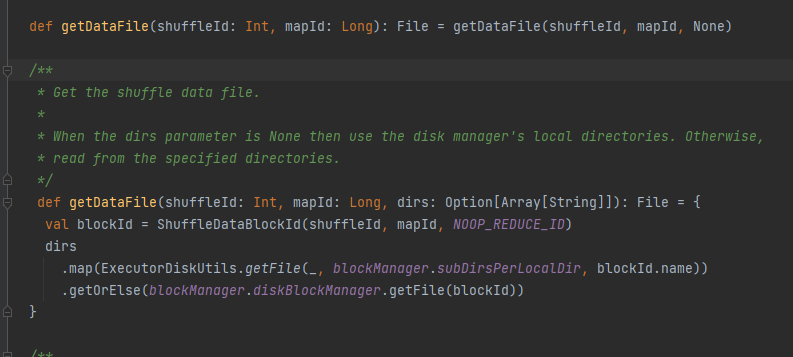
Similar to getDataFile
Generate ShuffleIndexBlockId and call blockManager.diskBlockManager.getFile method to get file

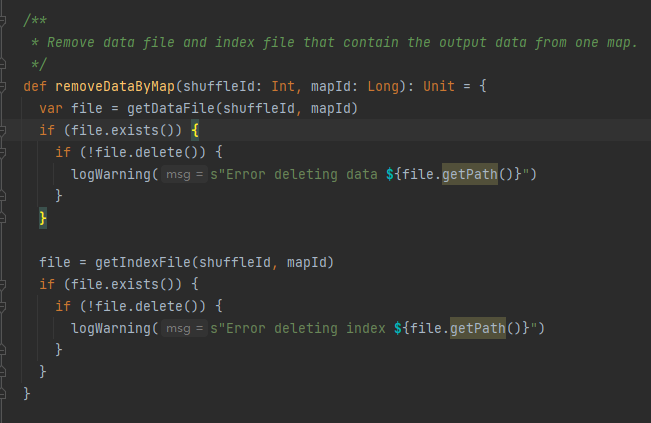
Get the data file and index file according to shuffleId and mapId, and then delete them
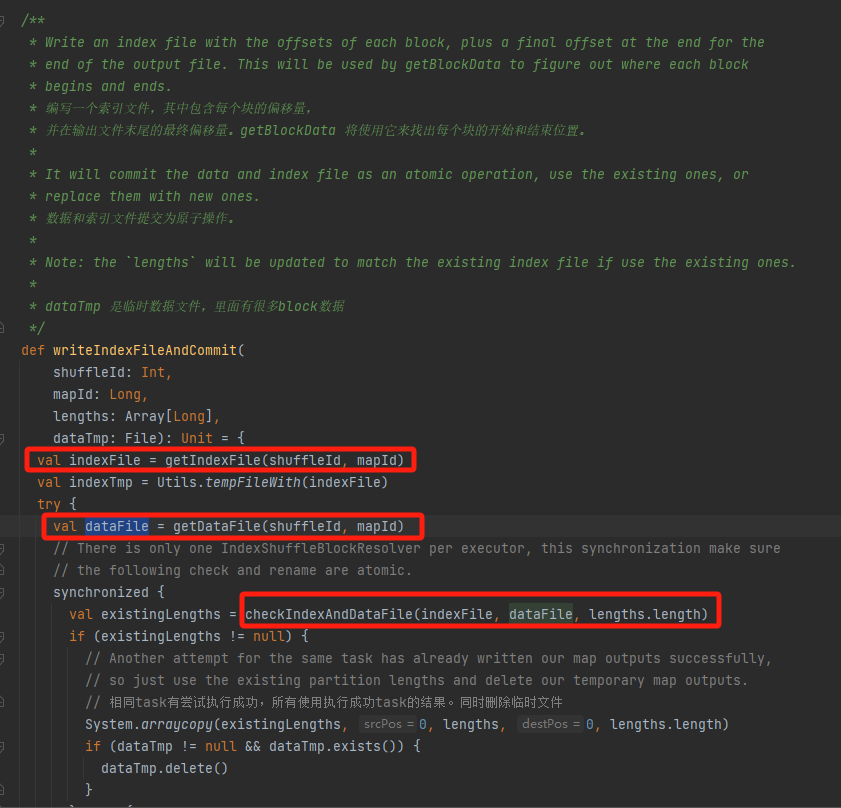
Get the corresponding data file and index file according to mapId and shuffleId.
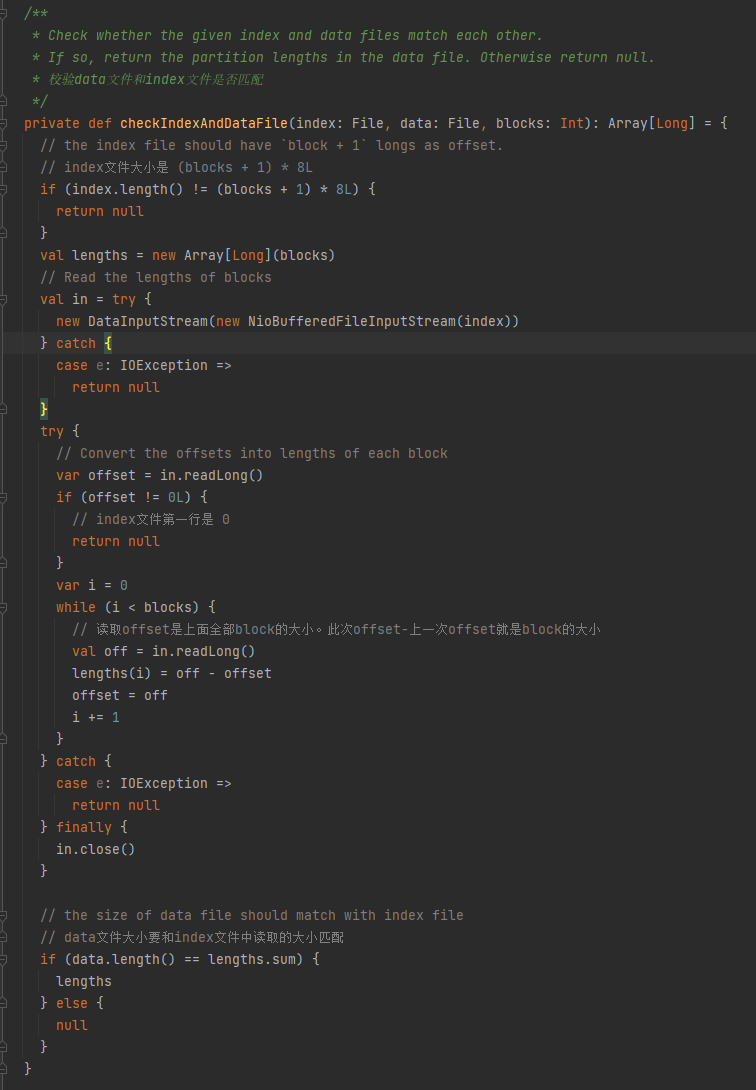
Check whether the data file and index file exist and match each other, and return directly.
If the match does not exist, a new index temporary file is generated, and then the new index file and data file are renamed and returned.

Assume that the shuffle has three partitions, and the corresponding data sizes are 1000, 1500, and 2500 respectively.
Index file, the first line is 0, followed by the cumulative values of partition data, the second line is 1000, the third line is 1000+1500=2500, and the third line is 2500+2500=5000.
Data files are stored in order of partition size.

Check whether the data file and index file match. If they do not match, return null. If they match, return an array of the partition size.
1. The index file size is (blocks + 1) * 8L
2. The first line of the index file is 0
3. Get the size of the partition and write it into lengths. The summary value of lengths is equal to the size of the data file.
If the above three conditions are met, lengths is returned, otherwise null is returned
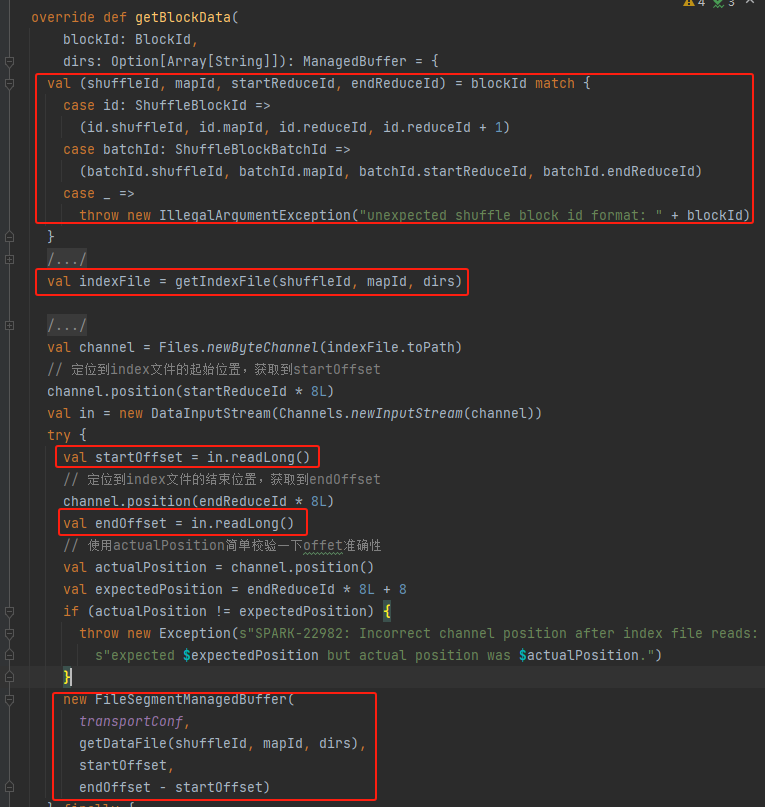
Get shuffleId, mapId, startReduceId, endReduceId
Get the index file
Read the corresponding startOffset and endOffset
Generate FileSegmentManagedBuffer using data file, startOffset, endOffset and return