2024-07-12
한어Русский языкEnglishFrançaisIndonesianSanskrit日本語DeutschPortuguêsΕλληνικάespañolItalianoSuomalainenLatina
In addition to the BeautifulSoup library mentioned above, there are two other methods for parsing data: regular expressions and Xpath.
Regular expression (RE for short) is a tool used to describe and match string patterns.
It is widely used in text processing, data validation, text search and replacement, etc. Regular expressions use a special syntax that can perform complex pattern matching on strings.
Regular expression test:Online Regular Expression Tester
Metacharacter: A special symbol with a fixed meaning. Each metacharacter matches only one string by default and cannot match a newline character.
| Metacharacters | describe | Example |
|---|---|---|
. | Matches any character except newline | a.b Can matcha1b、acb |
w | Matches a letter, number, or underscore | w+ matchhello、world_123 |
s | Matches any whitespace character | s+ Matches spaces, tabs, etc. |
d | Matching Numbers | d+ match123、456 |
n | Matches a newline character | hellonworld Matches newline characters |
t | Matches a tab character | hellotworld Matches a tab character |
^ | Matches the beginning of a string | ^Hello matchHello String starting with |
$ | Matches the end of a string | World$ matchWorld End of string |
W | Matches non-letters, non-numbers, and non-underscore characters | W+ match!@#、$%^ |
D | Matches non-numeric characters | D+ matchabc、XYZ |
S | Matches non-whitespace characters | S+ matchhello、world123 |
| `a | b` | Matching Characters a or characterb |
(...) | Capturing the expression in parentheses, indicating a group | (abc) captureabc |
[...] | Matches any character in the square brackets | [abc] matcha、b orc |
[^...] | Matches any character not in the square brackets | [^abc] Match excepta、b、c Any character except |
Quantifier: controls the number of times the preceding metacharacter appears
| quantifier | describe |
|---|---|
* | Repeats zero or more times |
+ | Repeat one or more times |
? | Repeats zero or one time |
{n} | Repeat n times |
{n,} | Repeat n times or more |
{n,m} | Repeat n to m times |
Lazy matching.*?: Match as few characters as possible. Add ? Implement lazy matching.
Greedy Matching.*: Match as many characters as possible. The default repetition metacharacters are greedy.
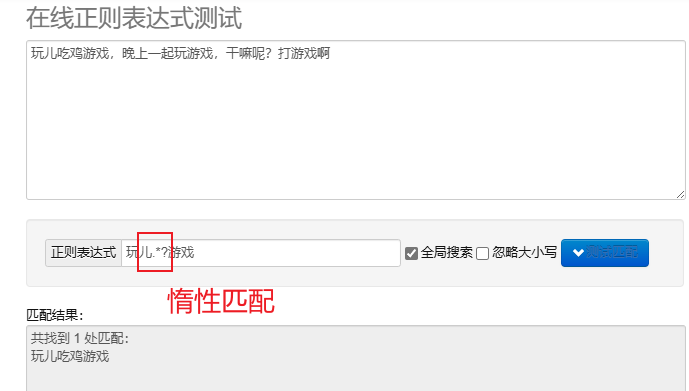
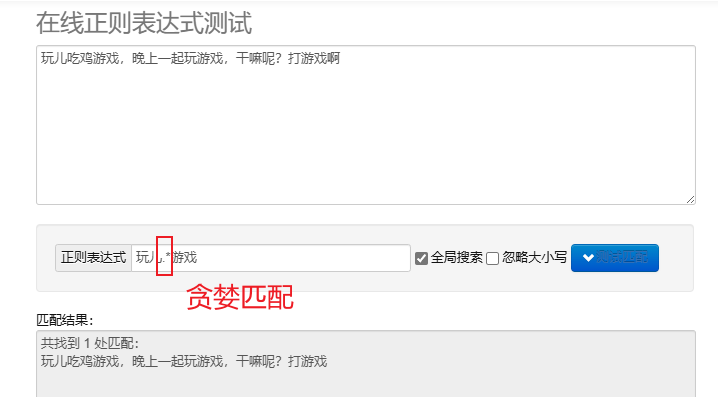
To process regular expressions in Python, you can use re This module provides a set of functions for searching, matching and manipulating strings.
| function | describe |
|---|---|
re.search(pattern, string, flags=0) | Searches for a string and returns the first matching object; if no match is found, returns None |
re.match(pattern, string, flags=0) | Matches the pattern from the beginning of the string; if the match is successful, returns the match object, otherwise None |
re.fullmatch(pattern, string, flags=0) | If the entire string matches the pattern, a match object is returned; otherwise, None |
re.findall(pattern, string, flags=0) | Returns a list of all non-overlapping matches in a string |
re.finditer(pattern, string, flags=0) | Returns an iterator of all non-overlapping matches in a string |
re.sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0) | Replace all parts of the matching pattern with the replacement string and return the replaced string |
re.split(pattern, string, maxsplit=0, flags=0) | Split the string according to the pattern match and return the split list |
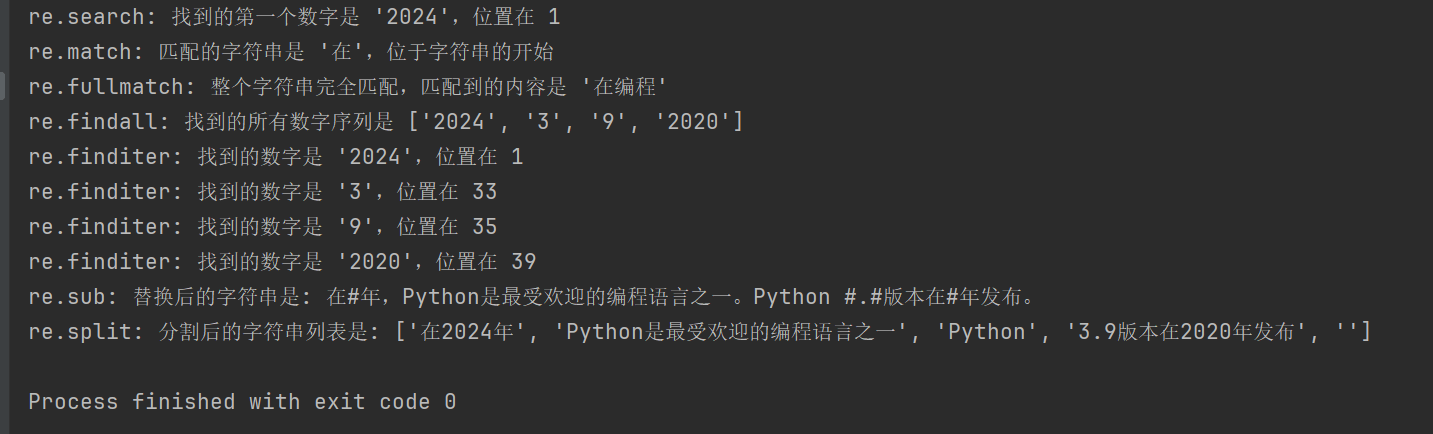
import re
# 示例文本
text = "在2024年,Python是最受欢迎的编程语言之一。Python 3.9版本在2020年发布。"
# 1. re.search() 搜索字符串,返回第一个匹配的对象
# 查找第一个数字序列
search_result = re.search(r'd+', text)
if search_result:
print(f"re.search: 找到的第一个数字是 '{search_result.group()}',位置在 {search_result.start()}")
# 2. re.match() 从字符串起始位置匹配模式
# 匹配字符串开头是否为 '在'
match_result = re.match(r'在', text)
if match_result:
print(f"re.match: 匹配的字符串是 '{match_result.group()}',位于字符串的开始")
# 3. re.fullmatch() 整个字符串完全匹配模式
# 检查整个字符串是否只包含中文字符
fullmatch_result = re.fullmatch(r'[u4e00-u9fff]+', '在编程')
if fullmatch_result:
print(f"re.fullmatch: 整个字符串完全匹配,匹配到的内容是 '{fullmatch_result.group()}'")
# 4. re.findall() 返回字符串中所有非重叠匹配的列表
# 查找所有的数字序列
findall_result = re.findall(r'd+', text)
print(f"re.findall: 找到的所有数字序列是 {findall_result}")
# 5. re.finditer() 返回字符串中所有非重叠匹配的迭代器
# 查找所有的数字序列,并逐一输出
finditer_result = re.finditer(r'd+', text)
for match in finditer_result:
print(f"re.finditer: 找到的数字是 '{match.group()}',位置在 {match.start()}")
# 6. re.sub() 用替换字符串替换匹配模式的所有部分
# 将所有数字替换为 '#'
sub_result = re.sub(r'd+', '#', text)
print(f"re.sub: 替换后的字符串是: {sub_result}")
# 7. re.split() 根据模式匹配分割字符串
# 按照空白字符或标点分割字符串
split_result = re.split(r'[,。 ]+', text)
print(f"re.split: 分割后的字符串列表是: {split_result}")
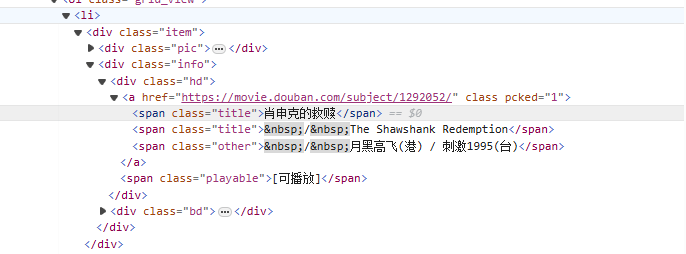
from<li>Tags, and gradually match to the movie name<span class="title">tags, using non-greedy mode (.*?) matches any characters that may exist in the middle until the next explicit token is found, using a named capture group(?P<name>)Extract the movie title part.
Re expression writing:
<li>.*?<div class="item">.*?<span class="title">(?P<name>.*?)</span>
Crawler code:
import requests
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/125.0.0.0"
}
for start_num in range(0, 250, 25):
response = requests.get(f"https://movie.douban.com/top250?start={start_num}", headers=headers)
# 拿到页面源代码
html = response.text
# 使用re解析数据
obj = re.compile(r'<li>.*?<div class="item">.*?<span class="title">(?P<name>.*?)</span>',re.S)
# 开始匹配
result = obj.finditer(html)
# 打印结果
for it in result:
print(it.group('name'))
XPath is a language for searching in XML documents. It can select nodes or node sets through path expressions. HTML is a subset of XML.
Install the lxml module: pip install lxml
| symbol | explain |
|---|---|
/ | Select from the root node. |
// | Selects nodes in the document from the current node that match the selection, regardless of their position. |
. | Select the current node. |
.. | Selects the parent node of the current node. |
@ | Select Properties. |
| expression | explain |
|---|---|
/bookstore/book | Select all book child nodes under the bookstore node. |
//book | Selects all book nodes in the document, regardless of their location. |
bookstore/book[1] | Select the first book child node under the bookstore node. |
//title[@lang] | Selects all title nodes that have a lang attribute. |
//title[@lang='en'] | Selects all title nodes whose lang attribute is 'en'. |
text(): Select the text of an element.@attr: Select the attribute of the element.contains(): Determine the inclusion relationship.starts-with(): Determine the start part.from lxml import etree
html_content = '''
<html>
<body>
<div class="movie">
<span class="title">肖申克的救赎</span>
<span class="title">The Shawshank Redemption</span>
</div>
<div class="movie">
<span class="title">霸王别姬</span>
<span class="title">Farewell My Concubine</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
'''
# 解析HTML
tree = etree.HTML(html_content)
# 提取电影标题
titles_cn = tree.xpath('//div[@class="movie"]/span[@class="title"][1]/text()')
titles_en = tree.xpath('//div[@class="movie"]/span[@class="title"][2]/text()')
# 打印结果
for cn, en in zip(titles_cn, titles_en):
print(f'中文标题: {cn}, 英文标题: {en}')
//div[@class="movie"]/span[@class="title"][1]/text()
//div[@class="movie"]: Select all classesmovieThe div element.
/span[@class="title"][1]: Select each div with classtitleThe first span element.
/text(): Get the text content of the span element.
//div[@class="movie"]/span[@class="title"][2]/text()
Similar to the above expression, but selects each div with classtitleThe second span element.
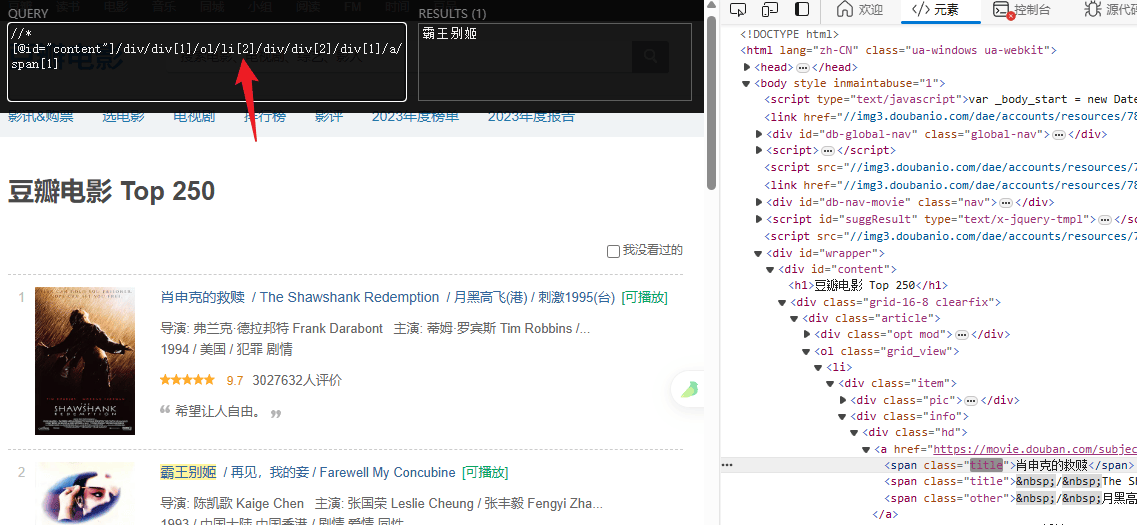
import requests
from lxml import etree
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/125.0.0.0"
}
for start_num in range(0, 250, 25):
response = requests.get(f"https://movie.douban.com/top250?start={start_num}", headers=headers)
# 拿到页面源代码
html = response.text
# 使用lxml解析页面
html = etree.HTML(html)
# 提取电影名字
titles = html.xpath('//*[@id="content"]/div/div[1]/ol/li/div/div[2]/div[1]/a/span[1]/text()')
# 提取评分
ratings = html.xpath('//*[@id="content"]/div/div[1]/ol/li/div/div[2]/div[2]/div/span[2]/text()')
# 打印结果
for title, rating in zip(titles, ratings):
print(f"电影: {title} 评分: {rating}")